

区域建构:佛山融入粤港澳大湾区建设的政策和策略响应
|
陈品宇(1991—),男,广西玉林人,博士研究生,主要研究方向为城市与区域发展、旅游与文化地理,(E-mail)1530024804@qq.com。 |
收稿日期: 2019-08-05
要求修回日期: 2019-09-29
网络出版日期: 2019-11-08
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(41771156)
中央高校基本科研业务费项目华东师范大学共享交叉基金(人文社会科学)项目(2019ECNU-GXJC002)
2019年度广东佛山社科规划项目——青年项目
版权
Region Building: The Policy and Strategy Response of Foshan Integrating into the Construction of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
Received date: 2019-08-05
Request revised date: 2019-09-29
Online published: 2019-11-08
Copyright
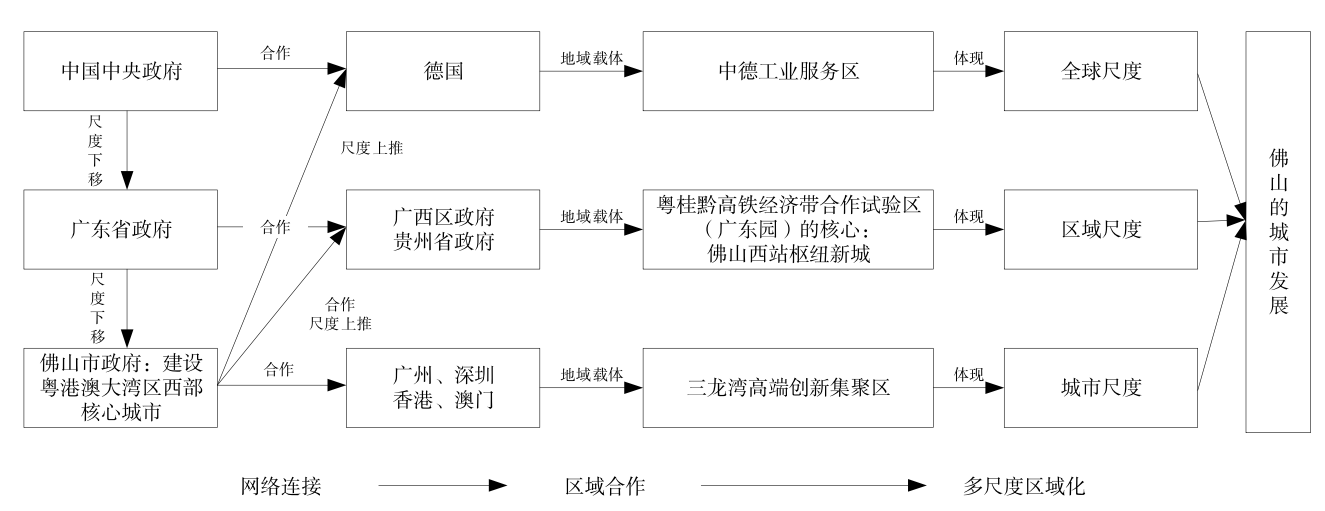
区域的社会建构议题较少得到国内学者的关注。既有关于粤港澳大湾区的研究,也鲜有涉及具体城市政府的行动和策略。为此,文章采取政策话语分析方法探索佛山融入粤港澳大湾区建设的政策和策略响应,作为弥补上述问题的文献空白。研究发现,佛山把区域身份建构为粤港澳大湾区西部核心城市,从战略统一上确定了佛山融入粤港澳大湾区的策略和行动方向。佛山与不同城市和区域之间建立关系网络,形成不同尺度作用下的区域合作地域载体。表现为3个方面:1)在城市尺度上,佛山与广州、深圳、香港和澳门等城市建立合作联系,建设三龙湾高端创新集聚区为地域载体,将松散的资源重新盘整,进一步提高统筹地区发展和聚集资源要素的能力,培育新的地方增长极以保持竞争优势。2)在区域尺度上,佛山与广西和贵州建立合作联系,建设佛山西站枢纽新城为地域载体,连接西南地区,把粤桂黔高铁经济合作带作为其经济腹地。3)在全球尺度上,佛山与德国建立合作联系,建设中德工业服务区为地域载体,创造地方—全球尺度的连接渠道,嵌入全球的市场经济。佛山案例展示了区域作为不同尺度上多个行动者的节点汇合,如何把区域资产与国家和跨国经济联系起来,从而生产与再生产新国家空间。文章回应了新区域地理学从社会建构主义视角审视区域发展问题,也回应了中国城市网络研究的最新呼吁。在实践中为其他城市如何融入粤港澳大湾区建设乃至区域发展问题提供了借鉴。
陈品宇 , 李鲁奇 . 区域建构:佛山融入粤港澳大湾区建设的政策和策略响应[J]. 热带地理, 2019 , 39(5) : 625 -634 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003181
The social construction of region has received little attention from Chinese scholars; there are few studies regarding the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area from the perspective of city government’s actions and strategies. Instead, most of the literature focuses on its political impacts, economic patterns, and urban spatial structures. This paper adopts the discourse analysis method to explore the policy and response strategy of Foshan integrating into the construction of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area, with the intention to fill in the gap mentioned above. This approach allows for an analysis of how local governments are embedded into the larger network during the process of regional construction to expand urban development space and achieve more economic development. Additionally, it will enrich the literature with information about the construction of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from the perspective of urban government. This study found that Foshan has constructed its regional identity as the core city of the western part of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area, and this helps determine the strategy and direction for how Foshan might integrate into the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area through strategic unification. In particular, Foshan is neither a provincial capital city nor a Special Economic Zone, making it difficult for Foshan to have the same political status and administrative power as Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Hong Kong, and Macao. There is also a certain disparity in the allocation of resources. In this context, Foshan has established a network of relations with different cities and regions, forming different regionalization at different scales, including the urban, regional, and global scales. These strategies are reflected in three aspects. At the urban scale, Foshan connects to cities, including Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Hong Kong, and Macao, and it has built the Sanlong Bay high-end innovation cluster (Sanlongwan) as a regional platform, which aims to reconsolidate resources. This improves Foshan’s ability to coordinate regional development and fosters new local growth poles to maintain a competitive advantage. At the regional scale, Foshan aims to connect to the Guangxi and Guizhou provinces, building the Foshan West Railway Station Hub at New Town (Foshan Xizhan Shuniu Xincheng) as a regional platform, making the Guangdong-Guangxi-Guizhou High-speed Railway Economic Cooperation Zone(Yue-Gui-Qian Gaotie Jingji Hezuoqu) and even the Southwest China as its economic hinterland. At the global scale, Foshan is connected to Germany, building the Sino-German industrial service area (Zhongde Gongye Fuwuqu) as a regional platform, which has created local-global connectivity channels, embedding itself into the global market economy. The Foshan case demonstrates how the region, as a confluence of multiple factors at different scales, generates important insights into how new state spaces of development are produced and reproduced to dovetail regional assets with national and transnational economic ties. This study responds to the New Regional Geography from the perspective of social constructivism to examine regional development issues. Additionally, it responds to the latest appeals for China’s urban network research, and in practice, it clarifies how other cities can more easily integrate into the construction of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area, and these results may even be useful for regional development.


| 1 |
|
| 2 |
安宁, 冯秋怡, 朱竑 . 2019. 基于报业话语的广州非裔社区的空间想象分析. 地理学报, 74(8):1650-1662.
[
|
| 3 |
安宁, 马凌, 朱竑 . 2018. 政治地理视野下的粤港澳大湾区发展思考. 地理科学进展, 37(12):1633-1643.
[
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
陈品宇, 李鲁奇, 孔翔 . 2019. 尺度重组理论视角下的粤港澳大湾区建设研究. 人文地理, 34(1):54-62.
[
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
佛山日报. 2019 a. 为建设国际一流湾区和世界级城市群作出佛山贡献. 佛山日报,2019-03-13(A01).
[ Foshan Daily. 2019 a. Foshan: Making a Contribution to Building a World-class Bay Area and City Cluster. Foshan Daily, 2019-03-13 (A01). ]
|
| 11 |
佛山日报. 2019 b. 高起点高质量全力推进大湾区建设. 佛山日报, 2019-03-20(F01).
[Foshan Daily. 2019 b. Building the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area with High Starting Point and Quality. Foshan Daily, 2019-03-20 (F01). ]
|
| 12 |
佛山日报. 2019c. 聚焦重点领域关键环节重点项目. 佛山日报, 2019-04-03(F01).
[Foshan Daily. 2019c. Focusing on Key Projects in Key Area. Foshan Daily, 2019-04-03 (F01). ]
|
| 13 |
|
| 14 |
|
| 15 |
|
| 16 |
李亚, 尹旭, 何鉴孜 . 2015. 政策话语分析:如何成为一种方法论. 公共行政评论,( 5):55-73.
[
|
| 17 |
梁育填, 查子萱, 许堞, 李郇 . 2018. 国内外高速铁路的区域效应研究进展——兼谈粤桂黔高铁经济带区域合作的思考. 广西大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 40(5):93-97.
[
|
| 18 |
刘云刚, 叶清露 . 2013. 区域发展中的路径创造和尺度政治——对广东惠州发展历程的解读. 地理科学, 33(9):1029-1036.
[
|
| 19 |
罗小龙, 沈建法 . 2007. 长江三角洲城市合作模式及其理论框架分析. 地理学报, 62(2):115-126.
[
|
| 20 |
罗小龙, 沈建法 . 2008. 基于共同利益关系的长江三角洲城市合作——以长江三角洲城市经济协调会为例. 经济地理, 28(4):17-21.
[
|
| 21 |
|
| 22 |
|
| 23 |
马海涛, 黄晓东, 李迎成 . 2018. 粤港澳大湾区城市群知识多中心的演化过程与机理. 地理学报, 73(12):2297-2314.
[
|
| 24 |
马向明, 陈洋 . 2017. 粤港澳大湾区:新阶段与新挑战. 热带地理, 37(6):762-774.
[
|
| 25 |
马学广, 李鲁奇 . 2016. 国外人文地理学尺度政治理论研究进展. 人文地理, 31(2):6-12.
[
|
| 26 |
马学广, 李鲁奇 . 2017. 城际合作空间的生产与重构:基于领域、网络与尺度的视角. 地理科学进展, 36(12):1510-1520.
[
|
| 27 |
|
| 28 |
|
| 29 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 31 |
潘峰华, 方成, 李仙德 . 2019. 中国城市网络研究评述与展望. 地理科学, 39(7):1093-1101.
[
|
| 32 |
彭芳梅 . 2017. 粤港澳大湾区及周边城市经济空间联系与空间结构——基于改进引力模型与社会网络分析的实证分析. 经济地理, 37(12):57-64.
[
|
| 33 |
|
| 34 |
|
| 35 |
|
| 36 |
|
| 37 |
|
| 38 |
|
| 39 |
张虹鸥, 王洋, 叶玉瑶, 金利霞, 黄耿志 . 2018. 粤港澳区域联动发展的关键科学问题与重点议题. 地理科学进展, 37(12):1587-1596.
[
|
| 40 |
赵晓斌, 强卫, 黄伟豪, 线实 . 2018. 粤港澳大湾区发展的理论框架与发展战略探究. 地理科学进展, 37(12):1597-1608.
[
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |