

基于多源数据融合的农村建筑智能识别与三维建模方法研究
|
陈彪(1987—),男,湖南邵阳人,高级工程师,学士,主要从事计算机三维技术等方面的研究工作,(E-mail)chenb@ augurit.com; |
收稿日期: 2022-09-09
修回日期: 2023-01-15
网络出版日期: 2023-02-28
基金资助
城市信息模型(CIM)平台关键技术研发及广州示范应用(202103050001)
Intelligent Recognition and 3D Modeling of Rural Buildings Based on Multi-Source Data Fusion
Received date: 2022-09-09
Revised date: 2023-01-15
Online published: 2023-02-28
中国幅员辽阔且农村房屋数量庞大、分布广泛,乡村地区低成本、广覆盖的信息采集和建模一直是乡村信息化亟待解决的问题。文章提出了一种简易的农村三维建筑建模方式,即基于多源数据融合的农村建筑智能识别与三维建模方法,并以广东省云浮市新兴县河村为研究对象,建立精细化三维建筑模型。该方法分为粗模生成和深化建模2个阶段。首先,在粗模生成阶段,基于高分辨率遥感影像和Mask R_CNN技术识别建筑物,确定房屋位置并拉伸生成基础白模;在深化阶段,外业采集员根据实际情况,基于农村建筑模型库将基础白模替换为更精细的、参数化的白模;然后,通过简单的手机拍摄及纹理处理,实现建筑立面纹理的补充;最后,通过坐标匹配、影像地形融合、三维轻量化等技术形成真实的、可存储和可交换的三维建筑模型,可支撑乡村调查、乡村规划、乡村建设、共同缔造等应用。该方法简单易用,降低了常规建模在数据采集、处理等技术方面的高要求,为农村地区提供一种低成本、高效率的“大众化”建筑三维重建方法。
陈彪 , 彭欣月 , 周素红 , 陈家亮 , 孔宪娟 , 卞明月 , 林高远 . 基于多源数据融合的农村建筑智能识别与三维建模方法研究[J]. 热带地理, 2023 , 43(2) : 190 -201 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003633
China's rural areas are vast, and housing construction is the primary organization of farmers' living spaces and an essential focus of the national implementation of rural revitalization. However, there is a lack of rural housing census data and methods that quickly and accurately establish a rural three-dimensional (3D)-building model. The existing 3D-building modeling techniques, including manual modeling and oblique photography modeling, are encountering the problem of high cost and do not meet the construction requirements of low cost and comprehensive coverage. With the development of satellite remote sensing technology in China, building recognition based on high-resolution remote sensing images has become a convenient and rapid technical tool. At the same time, with the widespread use of smartphones and their potent computing power, people can easily and quickly access the Internet and receive a three-dimensional display. Compared with two-dimensional products, three-dimensional products can show rural buildings, terrain, and landscape more clearly, enhance the refined management of rural areas, and improve enthusiasm to participate in rural construction. Therefore, this study proposes a simple rural 3D building modeling method based on multi-source data fusion, namely intelligent identification and 3D modeling for rural buildings. This method consists of two stages: rough model generation and deepening. In the rough model generation stage, the building is identified based on high-resolution remote sensing images and Mask R_CNN technology, the location of the building is determined, and the basic white model is obtained by stretching. In the deepening stage, field collectors replace the basic white model with a more refined and parameterized model based on the rural building model library, according to the actual situation. Subsequently, they supplement the building facade texture through smartphone photography and texture processing. Finally, a physical, storable, and exchangeable 3D-building model is obtained through coordinate matching, image terrain fusion, 3D-lightweight technology, and other technologies. This study adopts the modeling strategy of gradual deepening to reduce the modeling cost. The associated high-resolution remote sensing image recognition technology and mobile phone-based 3D modeling and display technologies are relatively advanced. Based on the characteristics of architectural styles in rural areas, a set of rural building-model libraries based on CSG technology was constructed. Model replacement, model size adjustment, texture mapping, and other operations were quickly used to build a refined 3D model. Finally, the 3D models were lightly processed and fused with the image topography and other data, which meets the demand for smooth browsing from various aspects. The 3D model of Hecun Village in Xinxing County was experimentally reconstructed, illustrating that the method can support applications such as rural surveys, rural planning, rural construction, and co-production. The modeling results show that the method is simple, easy to use, and reduces the high requirements of conventional modeling in terms of data acquisition and processing. It can provide a low-cost, highly efficient, and prevalent 3D-reconstruction method for rural regions, which is suitable for widespread promotion.
图3 Mask R_CNN算法的核心网络结构 Fig.3 The core network structure of the Mask R_CNN algorithm |
图4 建筑掩膜面积正态分布验证 [a. 原始遥感建筑影像;b. 建筑掩膜图像;c. 掩膜像素面积计算;d. 原始影像与掩膜像素面积叠加图;e. 掩膜面积直方图及正态曲线;f. 根据正态分布阈值控制删除的建筑(红色线框)]Fig.4 Verification of normal distribution of building mask area[a. Original remote sensing building image; b. building mask image; c. calculation of mask pixel area; d. overlay of original image and mask pixel area; e. mask area histogram and normal curve; f. controlled deletion of buildings according to normal distribution threshold (red frame)] |
表1 基本屋顶模型生成算法Table 1 Basic Roof Model Generation Algorithm |
| 屋顶样式 | 屋顶效果 | CSG运算过程 |
|---|---|---|
| 平屋顶 (PingRoof) | 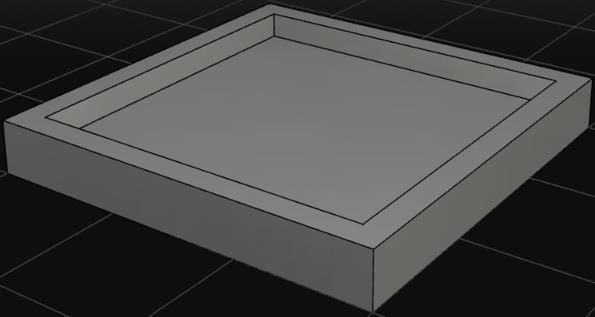 | ①定义屋面板宽、长、高 ,构造一个立方体C1; ②定义墙厚t 1、屋面板厚t 2,以C1的底面中心为原点,垂直底边的两方向分别为x、y轴建立坐标系,构造新的立方体C2,且C2的宽、长、高分别为 ; ③利用布尔运算,对2个立方体进行差运算,则PingRoof=C1¬C2。 |
| 人字型屋顶 (RidgeRoof) | 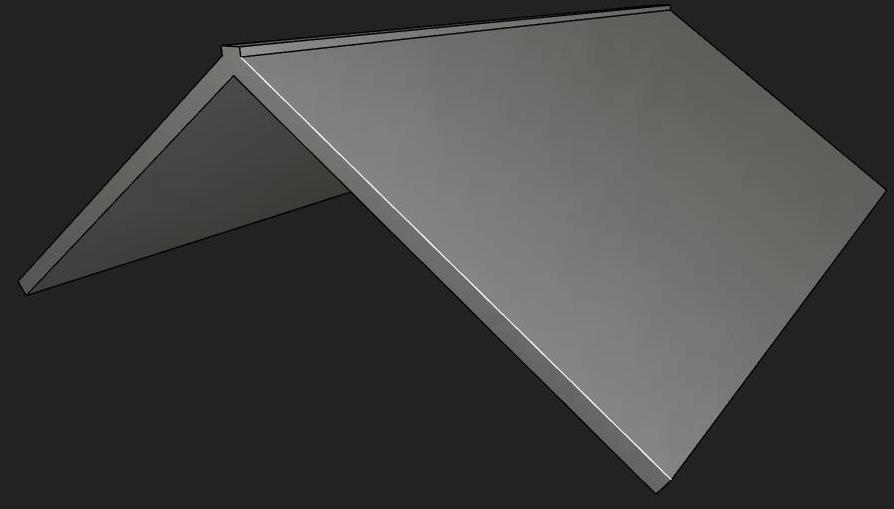 | ①定义屋顶高度、屋面坡度 ,坡面长l; ②建立一侧坡面由立方体 构建,其中 , ,t为坡面厚度,将其沿着y轴旋转角度θ,并移动一定距离z=g,最终构造得到图形T1; ③另外一侧坡面可通过x轴镜像方式,构造得到图形T2; ④建立屋顶横梁,其由立方体 构建,并移动距离z=g到屋顶位置,最终构造得到图形T3; ⑤将左右屋顶坡面和屋顶横梁合并得到人字形屋顶,RidgeRoof=T1 U T2 U T3。 |

1 * ,表示检测结果掩膜与直值掩膜之间的重叠程度,其中Area of Overlap为检测掩膜与直值掩膜的交集,Area of Union为检测掩膜与真值掩膜的并集,通常情况下,当 时即认为检测成功。
陈 彪:参与论文统筹、论文指导和写作及校稿,论文实验分析;
彭欣月:参与论文的写作、实验分析和实地调研;
周素红:参与指导;
陈家亮:参与实验和实地调研;
孔宪娟:参与指导和校稿;
卞明月、林高远:参与实验。
|
Bittner K, Adam F, Cui Shiyong, Kӧrner M, and Reinartz P. 2018. Building Footprint Extraction from VHR Remote Sensing Images Combined with Normalized DSMs Using Fused Fully Convolutional Networks. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 11 (8): 2615-2629.
|
|
曹治国,陈华. 2006. IKONOS卫星图像的快速三维场景重建. 计算机与数字工程,(11):9-11,15.
Cao Zhiguo, and Chen Hua. 2006. Quick 3D Reconstruction of the IKONOS-Satellite Stereo Images. Computer & Digital Engineering, (11): 9-11, 15.
|
|
程慧. 2013. 基于图像的数字城市自动化重建技术研究. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工程大学.
Cheng Hui. 2013. Research on Technology of Digital City Automatic Reconstruction Based on Image. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University.
|
|
陈良超,詹勇,王俊勇. 2018. 一种倾斜摄影实景三维模型单体化方法. 测绘通报,(6):68-72,108.
Chen Liangchao, Zhan Yong, and Wang Junyong. 2018. A Method of Achieving Single Body for Real 3D Model Generated by Oblique Photography. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (6): 68-72, 108.
|
|
古杰,周素红,闫小培,郑重. 2013. 中国农村居民生活水平的时空变化过程及其影响因素. 经济地理,33(10):124-131.
Gu Jie, Zhou Suhong, Yan Xiaopei, and Zheng Zhong. 2013. Spatial-Temporal Variations of Rural Residents' Living Standard and Its Influence Factors in China. Economic Geography, 33(10): 124-131.
|
|
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, and Girshick R. 2017. Mask R_CNN. Venice: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 1-12.
|
|
胡舒,王树根,王越,李欣. 2020. 基于Mask R_CNN的高分遥感影像建筑物目标检测研究. 测绘地理信息,46(1):1-7.
Hu Shu, Wang Shugen, Wang Yue, and Li Xin. 2020. Building Object Detection in High-Resolution Remote Sensing Image Based on Mask R-CNN. Journal of Geomatics, 46(1): 1-7.
|
|
李大军,何维龙,郭丙轩,李茂森,陈敏强. 2019. 基于Mask-RCNN的建筑物目标检测算法. 测绘科学,44(10):172-180.
Li Dajun, He Weilong, Guo Bingxuan, Li Maosen, and Chen Minqiang. 2019. Building Target Detection Algorithm Based on Mask R-CNN. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 44(10): 172-180.
|
|
Lin Chungan, and Nevatia R. 1998. Building Detection and Description from a Single Intensity Image. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 72(2): 101-121.
|
|
李德仁,刘立坤,邵振峰. 2015. 集成倾斜航空摄影测量和地面移动测量技术的城市环境监测. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),40(4):427-435,443.
Li Deren, Liu Likun, and Shao Zhenfeng. 2015. An Integration of Oblique Photogrammetry and Mobile Mapping System for Urban Geographical Conditions Monitoring. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 40(4): 427-435, 443.
|
|
连蓉,丁忆,罗鼎,魏文杰,李朋龙,林熙. 2017. 倾斜摄影与近景摄影相结合的山地城市实景三维精细化重建与单体化研究. 测绘通报,(11):128-132.
Lian Rong, Ding Yi, Luo Ding, Wei Wenjie, Li Penglong, and Lin Xi. 2017. Research on 3D Fine Reconstruction and Model Singling of Mountainous City Combined with Oblique Photography and Close Range Photography. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (11): 128-132.
|
|
陆清屿,李秋洁,童岳凯,王明霞,袁鹏成. 2021. 基于Mask R_CNN的行道树实例分割方法. 林业工程学报,6(5):154-160.
Lu Qingyu, Li Qiujie, Tong Yuekai, Wang Mingxia, and Yuan Pengcheng. 2021. Building Object Detection in High-Resolution Remote Sensing Image Based on Mask R-CNN. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 6(5): 154-160.
|
|
龙北平,刘锟铭,李政. 2021. 乡村区域建筑物自动三维建模方法研究. 地理空间信息,19(7):96-100.
Long Beiping, Liu Kunming, and Li Zheng. 2021. Research on Automatic 3D Modeling Method for Buildings in Rural Areas. Geospatial Information, 19(7): 96-100.
|
|
Ostu N. 2007. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man & Cybernetics, 9(1): 62-66.
|
|
隋刚,刘国栋,张锦. 2003. CSG方法在建筑物三维建模中的应用研究. 太原理工大学学报,34(6):691-693,718.
Sui Gang, Liu Guodong, and Zhang Jin. 2003. Study on Applying CSG Method to 3D Model of Buildings. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 34(6): 691-693, 718.
|
|
单杰,李志鑫,张文元. 2019. 大规模三维城市建模进展. 测绘学报,48(12):1523-1541.
Shan Jie, Li Zhixin, and Zhang Wenyuan. 2019. Recent Progress in Large-Scale 3D City Modeling. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 48(12): 1523-1541.
|
|
孙保燕,杨正阳,陈款,涂峻伦. 2019. 融合航摄影像与地面照片三维重建技术在考古中的应用. 科学技术与工程,19(17):262-266.
Sun Baoyan, Yang Zhengyang, Chen Kuan, and Tu Junlun. 2019. Application of Three-Dimensional Reconstruction Technology Combining Aerial Photography and Ground Photography in Archaeology. Science Technology and Engineering, 19(17): 262-266.
|
|
宋森森,贾振红,杨杰,Nikola K. 2019. 结合Ostu阈值法的最小生成树图像分割算法. 计算机工程与应用,55(9):178-183.
Song Sensen, Jia Zhenhong, Yang Jie, and Nikola K. 2019. Image Segmentation Algorithm of Minimum Spanning Tree Combined with Ostu Threshold Method. Computer Engineering and Applications, 55(9): 178-183.
|
|
王琦,葛文庚. 2012. 3D建筑重建的纹理提取与映射方法的实现. 四川大学学报(工程科学版),44(S1):198-202.
Wang Qi, and Ge Wengeng. 2012. 3D Building Reconstruction Texture Extraction and Mapping Implementation. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 44(S1): 198-202.
|
|
文雄飞,张穗,张煜,李喆. 2016. 无人机倾斜摄影辅助遥感技术在水土保持动态监测中的应用潜力分析. 长江科学院院报,33(11):93-98.
Wen Xiongfei, Zhang Sui, Zhang Yu, and Li Zhe. 2016. Potential of Remote Sensing Technology Assisted by UAV Oblique Photography Applied to Dynamic Monitoring of Soil and Water Conservation. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 33(11): 93-98.
|
|
王利忠,张宏海,仲波,牛铁. 2019. 基于深度学习的高分遥感影像乡镇建筑物识别方法. 科研信息化技术与应用,10(1):88-95.
Wang Lizhong, Zhang Honghai, Zhong Bo, and Niu Tie. 2019. Township Buildings Identification Using Deep Learning on High-Resolution Satellite Imagery. E-Science Technology & Application, 10(1): 88-95.
|
|
王艳阳,梁宇哲,罗伟玲,谢贻新,刘济坤. 2020. 基于高分遥感影像和POI的国土空间规划现状细化调查. 热带地理,40(4):649-658.
Wang Yanyang, Liang Yuzhe, Luo Weiling, Xie Yixin, and Liu Jikun. 2020. Investigating Land Use Types for the Spatial Planning of National Land Based on High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery and Point of Interest. Tropical Geography, 40 (4): 649-658.
|
|
徐涛,朱紫阳,丁华祥,肖建能,赵耀龙. 2022. 乡村振兴背景下广东省农村宅基地房屋特征. 热带地理,42(1):148-159.
Xu Tao, Zhu Ziyang, Ding Huaxiang, Xiao Jianneng, and Zhao Yaolong. 2022. The Characteristics of Rural Homestead Housing in Guangdong Province Under the Background of Rural Revitalization. Tropical Geography, 42 (1): 148-159.
|
|
谢小魁,陈青海,谢红霞,周清. 2016. 基于遥感和地理信息系统的建筑三维快速建模——以湖南农业大学为例. 绿色科技,(4):182-184.
Xie Xiaokui, Chen Qinghai, Xie Hongxia, and Zhou Qing. 2016. Three-Dimensional Rapid Modeling of Architecture Based on Remote Sensing and GIS: Taking the Hunan Architecture University as an Example. Journal of Green Science and Technology, (4): 182-184.
|
|
Yu Dawen, Ji Shunping, Liu Jin, and Wei Shiqing. 2021. Automatic 3D Building Reconstruction from Multi-View Aerial Images with Deep Learning. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 171: 155-170.
|
|
张春敏,丁亚杰,徐庆. 2018. 基于倾斜摄影技术的城市三维快速建模方法研究. 现代测绘,41(6):33-35.
Zhang Chunmin, Ding Yajie, and Xu Qing. 2018. Research on Urban Three-Dimensional Rapid Modeling Method on Tilt Photography. Modern Surveying and Mapping, 41(6): 33-35.
|
|
张俊辉,艾海滨,王庆栋,韩晓霞. 2020. 高分辨率光学卫星影像全球重点区域三维建模方法——以迪拜市为例. 测绘通报,(7):22-28.
Zhang Junhui, Ai Haibin, Wang Qingdong, and Han Xiaoxia. 2020. 3D Modeling Method of High-Resolution Optical Satellite Imagery for Global Key Regions: Taking Dubai City as an Example. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (7): 22-28.
|
|
张茂正,燕宁娜,赵振炜. 2022. 基于空地影像联合的精细化三维建模应用研究. 工程建设,54(5):1-5.
Zhang Maozheng, Yan Ningna, and Zhao Zhenwei. 2022. Research on Application of Refined 3D Modeling Based on Air-Ground Image. Engineering Construction, 54(5): 1-5.
|
|
周晓敏,孟晓林,张雪萍,弥永宏. 2016. 倾斜摄影测量的城市真三维模型构建方法. 测绘科学,41(9):159-163.
Zhou Xiaomin, Meng Xiaolin, Zhang Xueping, and Mi Yonghong. 2016. A Method of Urban Real 3D Model Building Based on Oblique Photogrammetry. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 41(9): 159-163.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |