

广东西樵山40—50 ka B P地质遗迹与古人类活动新发现
收稿日期: 2024-08-13
修回日期: 2024-09-24
网络出版日期: 2024-10-10
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42472035);中国科学院广州地球化学研究所同位素地球化学国家重点实验室项目(SKLaBIGZC-21-01)
New Insights into Geoheritage and Modern Human Activity in Xiqiaoshan, Guangdong Province, Over the Past 40‒50 ka
Received date: 2024-08-13
Revised date: 2024-09-24
Online published: 2024-10-10
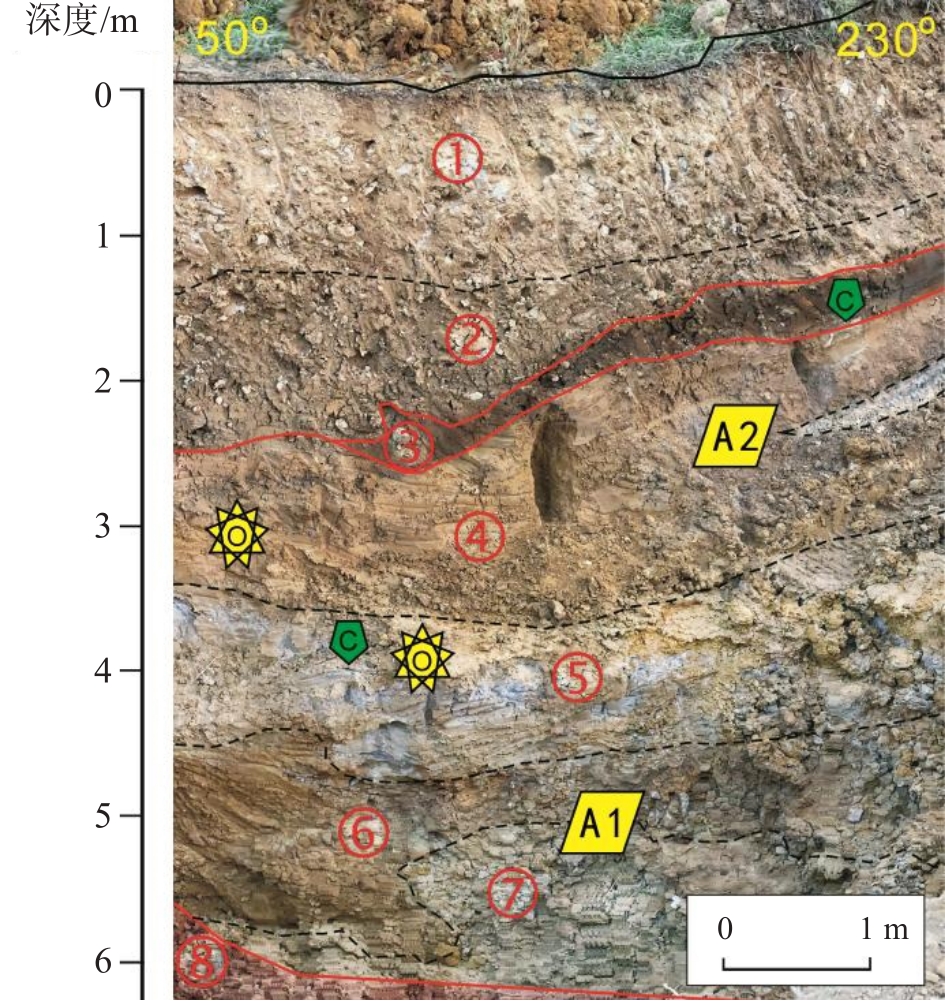
1958—1999年,在广东省佛山市南海区西樵镇一带发现了众多记录了史前人类活动的石器地点,石器中包括双肩石器和细石器。迄今为止,“西樵山遗址”被认定是4—7 ka B P的大型新石器时期采石场和加工场。2011—2022年,笔者经多次地质遗迹和地质环境调查,在西樵山东南麓富贤村北面发现了良好的第四纪地层剖面。地质探槽剖面测量和地质年代学研究表明:富贤地点存在2套原始沉积地层:上部为第四纪全新世沼泽相地层,AMS14C校正年龄为5052—5409 a B P;下部为第四纪晚更新世冲积-洪积相地层,AMS14C校正年龄为38420—40502 a B P,OSL(光释光)年龄为41.977—43.796 ka B P;在晚更新世地层中发现2层含旧石器层,下部A1层主要石器类型有较大型刮削器、尖刃器、舌型刃器及小型石片工具,如各类刮削器、锯齿刃器、凹缺器、石刀、使用石片、石核等,包括带铤斧型小石刀;上部A2层明显出现更多石刀类型且常常附带修背和修铤工作,其中一件用于生产细小长石片的原始楔形石核引人关注。据平均沉积速率计算,下部A1石器层年龄为46.511—47.325 ka B P,上部A2石器层年龄为41.977—42.167 ka B P;距今大于5 ka的全新世沉积物中的石制品数量虽少,但器物类型仍具有明显继承性与发展性特点。本文的发现更新并延伸了西樵山国家地质公园和“西樵山文化”的内涵,首次突破了珠江三角洲地区有确切年代的晚更新世旧石器遗存的纪录,追踪到大约40—50 ka现代人在华南沿海的足迹,揭示了同期石器工业的面貌及其文化内涵的发展特征和演变。研究表明,在MIS3间冰段相对湿热时期以及MIS2相对干冷阶段,富贤地点的古人类面临环境变化的挑战而开启了新的生计模式,这对于揭示现代人对全球和区域环境变化的响应与适应的科学问题具有重要意义。
朱照宇 , 黄慰文 , 关燕萍 , 潘炳炎 , 侯亚梅 , 李保生 , 张俊岭 , 曾提 , 欧阳婷萍 , 李明坤 , 贺辰戋 , 丁盛昌 , 闫龑 , 彭莎莎 , 胡巧 , 吕惠萍 . 广东西樵山40—50 ka B P地质遗迹与古人类活动新发现[J]. 热带地理, 2024 , 44(10) : 1737 -1747 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20240531
Between 1958 and 1999, notable lithic localities recorded prehistoric activities in Xiqiao Town of Nanhai District, Foshan City, Guangdong Province, from which double-shouldered and microlith-stone artefacts were uncovered. Currently, the "Xiqiaoshan site" is recognized as a substantial Neolithic quarry and processing location, dating back to 4‒7 ka B P. Subsequently, from 2011 to 2022, we conducted multiple geological environmental surveys and analyses on Xiqiaoshan Mountain. A well-preserved Quaternary stratigraphic profile was discovered north of Fuxian village in the southeast foothills of Xiqiaoshan Mountain. The sedimentological, geochemical, and geochronological results indicate the presence of two primary sedimentary strata in the Fuxian locality. The upper unit comprises the Holocene swamp facies, with a calibrated AMS14C dating range from 5052‒5409 a B P; whereas, the lower unit comprises the late Pleistocene alluvial-diluvial strata, with a calibrated AMS14C dating range from 38420‒40502 a B P, and an optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating range of 41.977‒43.796 ka B P. Late Pleistocene strata yielded two sand-gravel layers containing Paleolithic artefacts, which are marked as layers A1 and A2. The predominant artefacts in lower layer A1 include larger scrapers, pointed tools, tongue-shaped edged tools, and small flake tools, such as various scrapers, denticulates, notches, knives, utilized flakes, and cores, including tanged axe-shaped knives. In the upper layer A2, backed or tanged knives appear more frequently. The other small flake tools from this layer (A2) were not significantly different from those in lower layer A1. One bifacially prepared core for producing small elongated flakes is of particular interest for this artefact. Based on the average deposition rate, the computational age of the A1 layer was 46.511‒47.325 ka B P, whereas that of the A2 layer was 41.977‒42.167 ka B P. Although the number of artefacts within the Holocene sediments (>5 ka B P) overlying the late Pleistocene strata is limited, the characteristics of inheritance and development are still evident in the types of artefacts. The discovery presented in this study has completely updated and extended the connotation of Xiqiaoshan National Geopark and "Xiqiaoshan culture,"breaking through the late Pleistocene Paleolithic remains records with exact dating in the Pearl River Delta region for the first time. Therefore, a ground-breaking discovery can accurately trace the footsteps of modern humans in the coastal areas of South China from 40‒50 ka. It also reveals the rich features of lithic industry and the developmental characteristics and evolution of its cultural connotations during this period. The present study shows that during the relatively warm and humid conditions of marine isotope stages 3 (MIS3) interglacial period and the subsequent cold and arid stage of MIS2, human population in the Fuxian locality encountered environmental challenges and adopted new subsistence strategy, which is of great significance for understanding modern human responses and adaptations to global and regional environmental and climate change.

| 邓聪. 1997. 环珠江三角洲大湾文化地貌试析. 热带地理,17(2):179-183. | |
| Deng Cong. 1997. Notes on Geomorphology of the Tai Wan Culture in the Circum-Pearl River Delta. Tropical Geography, 17(2): 179-183. | |
| 广东省博物馆. 1959. 广东南海西樵山出土的石器. 考古学报,(4):1-15. | |
| The Kwangtung Provincial Museum. 1959. Stone Implements Unearthed at His Ch'iao Shan, Nan Hai county, Kwangtung. Acta Archaeologica Sinica, (4): 1-15. | |
| 广东省文物考古研究所,南海市博物馆. 1999. 广东南海市西樵山佛子庙遗址的发掘. 考古,(7):28-37. | |
| Guangdong Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology, and Nanhai Museum. 1999. A Excavation at Fozimiao site in Xiqiaoshan, Nanhai city, Guangdong Province. .Archaeology, (7): 28-37. | |
| Ge J, Zhang X, Wang S, Li L, He W, Jin Y, Zhang P, Xu B, Deng C, Olsen J W, Guo Z, and Gao X. 2024. New Dating Indicates Intermittent Human Occupation of the Nwya Devu Paleolithic Site on the High-Altitude Central Tibetan Plateau during the Past 45,000 Years. Science China Earth Sciences, 67(2): 531-551. | |
| 贺辰戋,朱照宇,张俊岭,欧阳婷萍,曾提,闫龑,胡巧,丁盛昌,李明坤,彭莎莎,吕惠萍,黄慰文,潘炳炎. 2024a. 广东省佛山市南海区西樵山遗址地质地貌基本特征//王宏,吴振宇,卢筱洪. 西樵山石器. 广州:岭南美术出版社,105-129. | |
| He Chenjian, Zhu Zhaoyu, Zhang Junling, Ouyang Tingping, Zeng Ti, Yan Yan, Hu Qiao, Ding Shengchang, Li Mingkun, Peng Shasha, Lv Huiping, Huang Weiwen, Pan Bingyan. 2024a. The Geological and Geomorphic Feature of the Xiqiaoshan Site in Nanhai District, Foshan City, Guangdong Province. In: Wang Hong, Wu Zhenyu, and Lu Xiaohong. The Artefacts in Xiqiaoshan Site. Guangzhou: Lingnan Art Publishing House, 105-129. | |
| 贺辰戋,张桂华,梁定辉,李明坤,张俊岭,李结涛,关燕萍,彭莎莎,丁盛昌,曾提,王云鹏,欧阳婷萍,朱照宇. 2024b. 珠江三角洲花斑粘土磁学特征及其沉积环境实例研究. 第四纪研究,44(5):1349-1361. | |
| He Chenjian, Zhang Guihua, Liang Dinghui, Li Mingkun, Zhang Junling, Li Jietao, Guan Yanping, Peng Shasha, Ding Shengchang, Zeng Ti, Wang Yunpeng, Ouyang Tingping, and Zhu Zhaoyu. 2024b. A Case Study of Magnetic Properties and Sedimentary Environment of the Spotted Clay in the Pearl River Delta. Quaternary Sciences, 44(5): 1349-1361. | |
| 黄慰文,李春初,王鸿寿,黄玉昆. 1979. 广东南海县西樵山遗址的复查. 考古,(4):289-299,316. | |
| Huang Weiwen, Li Chunchu, Wang Hongshou, and Huang Yukun. 1979. Reexamination of the Xiqiaoshan Site at Nanhai County, Guangdong. Archaeology, (4): 289-299, 316. | |
| 黄慰文. 1993. 关于西樵山石器制作场的几个问题. 文物,(4):40-44,31. [Huang Weiwen. 1993. On Some Aspects of the Artefact Workshop of Xiqiaoshan. Cultural Relics, (4): 40-44, 31.] | |
| Huang Weiwen, Li Chunchu, Wang Hongshou, and Huang Yukun.1982. Reexamination of a Microlithic Site at Xiqiaoshan, Nanhai County, Guangdong. Current Anthropology, 23(5): 487-492. | |
| 黄镇国,李平日,张仲英,李孔宏,乔彭年. 1982. 珠江三角洲形成发育演变. 广州:科学普及出版社广州分社,1-274. | |
| Huang Zhenguo, Li Pingri, Zhang Zhongying, Li Konghong, and Qiao Pengnian. 1982. Evolution of the Pearl River Delta. Guanzhou: Science Popularization Press Guangzhou Branch, 1-274. | |
| 黄镇国,张伟强,江璐明. 2003. 中国热带MIS3气候特征探讨. 第四纪研究,23(1):77-82. | |
| Huang Zhenguo, Zhang Weiqiang, and Jiang Luming. 2003. Climatic Characteristics in Tropic Areas of China during MIS3. Quaternary Sciences, 23(1): 77-82. | |
| 贾兰坡. 1960. 广东地区古人类学及考古学研究的未来希望. 学术研究,(3):37-42. | |
| Jia Lanpo. 1960. Hope for the Future on the Research of Paleoanthropology and Archeology in Guangdong Area. Academic Research, (3): 37-42. | |
| 黎烈均,梁致荣,刘彝筠. 1992. 一批考古、地质样品的14C年龄数据报道. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),31(1):137-139. | |
| Li Liejun, Liang Zhirong, and Liu Yijun. 1992. Radiocarbon Dating for a Large Number of Geological and Archaeological Samples. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 31(1): 137-139. | |
| 黎芷嫣,谭一洺,黄耿志. 2024. 珠三角城市群流动人口居留意愿的特征分异及影响因素. 热带地理,44(8):1513-1526. | |
| Li Zhiyan, Tan Yiming, and Huang Gengzhi. 2024. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Floating Population's Settlement Intention in the Pearl River Delta. Tropical Geography, 44 (8): 1513-1526. | |
| 李松生. 1991. 西樵山考古研究的发展. 中山大学学报(社会科学版),(4):74-79. | |
| Li Songsheng, 1991. The Research Progress on Archaeology in Xiqiaoshan. Journal of Sun Yat-sen University (Social Sciences Edition), (4): 74-79. | |
| 罗春科,周永章,杨小强,陈炳辉,付伟,钟莉莉. 2004. 西樵山地质公园旅游景观形成、分类及其综合评价. 热带地理,24(4):387-390. | |
| Luo Chunke? Zhou Yongzhang? Yang Xiaoqiang? Chen Binghui? Fu Wei? and Zhong Lili. 2004. Formation? Classification and Synthetical Evaluation of the Geological Tourism Landscapes at the Xiqiao Hill? Guangdong. Tropical Geography, 24(4): 387-390. | |
| 王宏,吴振宇,卢筱洪. 2024. 西樵山石器. 广州:岭南美术出版社,1-329. | |
| Wang Hong, Wu Zhenyu, and Lu Xiaohong. 2024. The Artefacts in Xiqiaoshan Site. Guangzhou: Lingnan Art Publishing House, 1-329. | |
| Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L, An Z S, Wu J Y, Shen C C, and Dorale J A. 2001. A High-Resolution Absolute-Dated Late Pleistocene Monsoon Record from Hulu Cave, China. Science, 294(5550): 2345-2348. | |
| 吴伟鸿,王宏,谭惠忠,张镇洪. 2006. 香港深涌黄地峒遗址试掘简报. 人类学学报,25(1):56-67. | |
| Wu Weihong, Wang Hong, Tan Huizhong, and Zhang Zhenhong. 2006. Preliminary Report on Trial Excavation at Wong Tei Tung Archaeological Site, Sham Chung, Hong Kong SAR. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 25(1): 56-67. | |
| Xiong Haixian, Zong Yongqiang, Huang Guangqing, and Fu Shuqing. 2020. Human Drivers Accelerated the Advance of Pearl River Deltaic Shoreline in the Past 7500 Years. Quaternary Science Reviews, 246 (106545): 1-13. | |
| 杨式挺. 1985. 试论西樵山文化. 考古学报,(1):9-32. | |
| Yang Shiting. 1985. Liminary Study on the Siqiaoshan Culture. Acta Archaeologica Sinica, (1): 9-32. | |
| 杨石霞,浣发祥,王宏,吴振宇,卢筱洪,李京亚. 2022. 广东西樵山细石叶石核的开发策略. 人类学学报,41(5):804-815. | |
| Yang Shixia, Huan Faxiang, Wang Hong, Wu Zhenyu, Lu Xiaohong, and Li Jingya. 2022. Reduction Strategy of the Microblade Cores from the Xiqiaoshan Site in Guangdong. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 41(5): 804-815. | |
| Yang S X, Zhang J F, Yue J P, Wood R, Guo Y J, Wang H, Luo W G, Zhang Y, Raguin E, Zhao K L, Zhang Y X, Huan F X, Hou Y M, Huang W W, Wang Y R, Shi J M, Yuan B Y, Olle A, Queffelec A, Zhou L P, Deng C L, d'Errico F, and Petraglia M. 2024. Initial Upper Palaeolithic material culture by 45,000 years ago at Shiyu in northern China. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 8(3): 1-12. DOI: 10.1038/s41559-023-02294-4. | |
| 易顺民,刘卫平,卢薇. 2010. 广东西樵山泥石流特征及防治对策,热带地理,30(6):656-662. | |
| Yi Shunmin, Liu Weiping, and Lu Wei. 2010. Debris Flow in Xiqiao Hill and Its Control. Tropical Geography, 30(6): 656-662. | |
| 张杰龙.2013. 西樵山遗址与西樵山文化文集. 广州:广东旅游出版社,1-331. | |
| Zhang Jielong. 2013. The Anthology on Xiaoqiaoshan Site and Xiqiaoshan Culture. Guangzhou: Guangdong Tourism Press, 1-331. | |
| 张镇洪. 1993. 1986—1987年西樵山发掘简报. 文物,(9):32-39. | |
| Zhang Zhenhong. 1993. Brief Report on the Excavation in Xiqiaoshan during 1986-1987. Cultural Relics, (9): 32-39. | |
| 曾骐. 1981. 西樵山东麓的细石器. 考古与文物,(4):1-13. | |
| Zeng Qi. 1981. The Microlith in the East Piedmont of Xiqiaoshan. Archaeology and Cultural Relics, (4): 1-13. | |
| 曾骐,李松生. 1988. 1986—1987年西樵山考古的新收获. 中山大学学报,(3):74-77,73. | |
| Zeng Qi and Li Songsheng. 1988. New Results of Archeology in the Xiqiaoshan Site during 1986-1987. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, (3): 74-77, 73. | |
| 郑卓,汤永杰,郑艳伟,黄康有,韩子云,宗永强,李平日,谭惠中.2016. 西江—北江及珠江三角洲汇流区全新世泥炭腐木层时空分布与环境变化.热带地理,36(3):313-325. | |
| Zheng Zhuo, Tang Yongjie, Zheng Yanwei, Huang Kangyou, Han Ziyun, Zong Yongqiang, Li Pingri, and Tan Huizhong. 2016. Environmental Changes Inferred from Spatial-Temporal Distribution of Holocene Buried Peat Layers in Lower Reaches of the Xijiang and Beijiang and the River Confluence of Pearl River Delta. Tropical Geography, 36(3): 313-325. | |
| 中山大学调查组. 1959. 广东南海县西樵山石器的初步调查. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),(1):44-56. | |
| Zhongshan University Survey Group. 1959. The Preliminary Study of the Stone Artifacts from Xiqiaoshan, Nanhai County, Guangdong. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, (1): 44-56. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |