

长三角城际房地产投资网络的空间格局与影响因素
|
戴靓(1989—),女,江苏镇江人,博士,副教授,硕士生导师,主要研究方向为城市网络与区域发展,(E-mail)9120181027@nufe.edu.cn; |
收稿日期: 2024-07-19
修回日期: 2024-08-16
网络出版日期: 2024-12-11
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42271212)
江苏省研究生科研创新计划项目(KYCX24_1993)
The Spatial Pattern and Influencing Factors of the Intercity Real Estate Investment Network in the Yangtze River Delta
Received date: 2024-07-19
Revised date: 2024-08-16
Online published: 2024-12-11
基于房地产企业之间真实的股权投资数据,构建2018—2022年的长三角城际房地产投资网络。从节点层级、流量层级、组团格局、整体拓扑方面,分析长三角房地产跨城投资的空间结构特征,并通过指数随机图模型探讨城市属性、城际关系和内生结构因素对跨城投资的影响。研究发现:1)上海、杭州、南京在长三角的跨城投资额位居前三名,引资规模最大的相继是杭州、苏州和南京,城市的中心地位呈现一定的非对称性。合肥的中介性突出,是安徽城市融入区域房地产市场的枢纽;2)长三角城际房地产投资组团与行政区划高度耦合,形成江苏、浙江、安徽3个省域组团和上海对近邻城市苏州、南通、盐城的辐射组团。城际投资流集中而引资流分散,区域房地产资本流动兼具核心边缘分层和小世界特征;3)城市化和全球化对投资和引资具有双向驱动,地方化对城市引资的影响突出;城际关系中组织邻近对跨城投资的促进作用最强;内生结构依赖也是跨城投资不可忽视的驱动力,主要表现为互惠效应、投资模式中的择优依附和传递闭合效应。
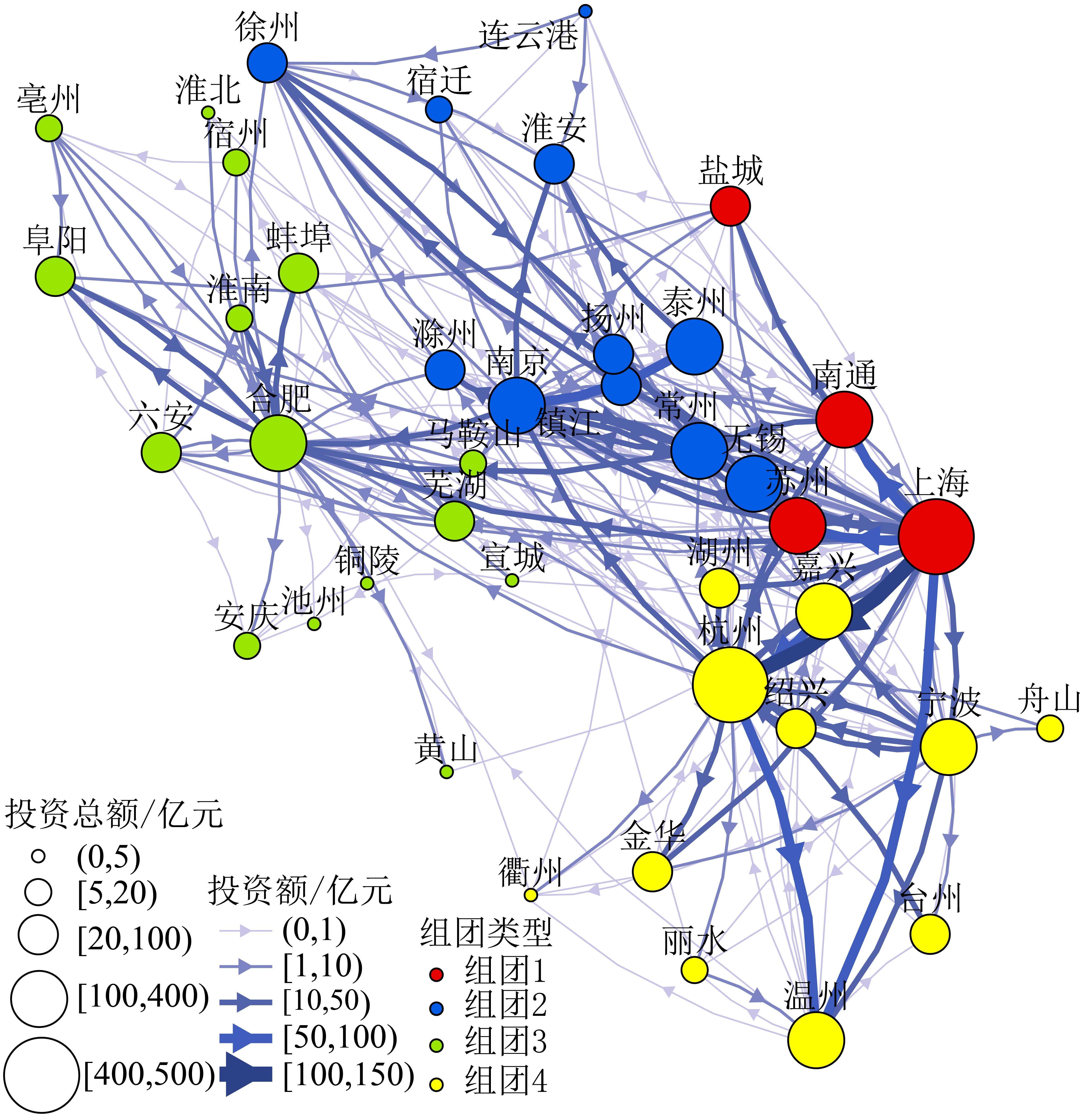
戴靓 , 吕一凡 , 郑慧彬 , 李鲁奇 . 长三角城际房地产投资网络的空间格局与影响因素[J]. 热带地理, 2024 , 44(12) : 2154 -2167 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20240477
Intercity investments of real estate enterprises can spur flows of regional capital, information, talent, and technology, thus serving as a crucial means for optimizing resource allocation, narrowing regional disparities, and guiding the coordinated development of the real estate market. The existing literature has mostly focused on using stock indicators and attribute data to explore the differences in the regional real estate market and the influencing factors. This study attempts to propose new findings of regional real estate markets from the perspectives of 'space of flows' and urban networks. Based on the equity investment data of real estate enterprises, this study constructed an intercity real estate investment network in the Yangtze River Delta for the period 2018–2022 and investigated the spatial and structural characteristics of intercity real estate investments in the region from the dimensions of node hierarchy, flow hierarchy, community pattern, and overall topology. Next, this study explored how urban attribute, intercity dyadic, and endogenous structural factors influence the intercity investment network using exponential random graph models. The results show the following: (1) Shanghai, Hangzhou, and Nanjing rank in the top three in terms of total intercity investment outflows in the Yangtze River Delta, while Hangzhou, Suzhou, and Nanjing have attracted the largest intercity investment inflows, suggesting that the central position of cities presents a certain asymmetry. Hefei plays a prominent intermediary role and is a hub for other cities in the Anhui Province to integrate into the regional real estate market. 2) The communities of the intercity real estate investment network in the Yangtze River Delta are highly coupled with administrative divisions, forming three provincial communities in Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Anhui and an inter-provincial radiating community between Shanghai and its neighboring cities of Suzhou, Nantong, and Yancheng. Intercity investment outflows are concentrated, investment inflows are dispersed, and regional real estate capital flows have both core-periphery structures and small-world characteristics. 3) Urbanization and globalization can promote bidirectional intercity investments, that is, investment inflows and outflows, while the degree of localization drives intercity investment inflows. The positive impact of organizational proximity on intercity investments is the most pronounced among the dyadic relationship factors. Endogenous forces are also crucial to intercity real estate investments and are mainly manifested in reciprocity, preferential attachment, and hierarchical transitivity in intercity investment modes.

表1 节点层级排名前10的城市 (亿元)Table 1 Top ten cities in the rankings of node hierarchy |
| 排序 | 城市 | 中心性 | 城市 | 投资额 | 城市 | 引资额 | 城市 | 中介性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 上海 | 588 | 上海 | 506 | 杭州 | 193 | 合肥 | 393 |
| 2 | 杭州 | 539 | 杭州 | 347 | 苏州 | 181 | 上海 | 279 |
| 3 | 南京 | 325 | 南京 | 164 | 南京 | 162 | 杭州 | 153 |
| 4 | 苏州 | 261 | 宁波 | 112 | 温州 | 157 | 南京 | 108 |
| 5 | 合肥 | 187 | 合肥 | 95 | 南通 | 122 | 宁波 | 75 |
| 6 | 宁波 | 166 | 泰州 | 94 | 合肥 | 92 | 苏州 | 49 |
| 7 | 温州 | 158 | 常州 | 80 | 无锡 | 89 | 常州 | 48 |
| 8 | 南通 | 143 | 苏州 | 80 | 上海 | 82 | 淮安 | 41 |
| 9 | 常州 | 132 | 嘉兴 | 55 | 嘉兴 | 70 | 亳州 | 40 |
| 10 | 嘉兴 | 124 | 镇江 | 32 | 宁波 | 53 | 徐州 | 38 |
表2 指数随机图的统计量设定Table 2 Statistics and explanation in exponential random graph models |
| 类型 | 统计量 | 示意图 | 变量解释 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基础效应 | 边 | edges |  | 投资流动的基准倾向,类似于常数项 |
| 城市 属性 因素 | 发送者效应 | nodeocov(Uemp) |  | 地方化、城市化、全球化程度高会促进城市投资的支配力 |
| nodeocov(Hemp) | ||||
| nodeocov(FDI) | ||||
| 接收者效应 | nodeicov(Uemp) |  | 地方化、城市化、全球化程度高会促进城市投资的吸引力 | |
| nodeicov(Hemp) | ||||
| nodeicov(FDI) | ||||
| 城际关系 因素 | 协网络 | edgecov(dis) |  | 地理邻近会促进城际投资 |
| 同配性 | nodematch(pro) | 组织邻近会促进城际投资 | ||
| nodematch(adm) | 制度邻近会促进城际投资 | |||
| 网络 结构 因素 | 互惠性 | mutual |  | 单向资本投入获得回馈互惠的倾向 |
| 扩张性 | gwodegree |  | 城际投资关系呈星形分布的倾向 | |
| 聚敛性 | gwidegree | 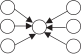 | 城际引资关系呈星形分布的倾向 | |
| 传递闭合性 | ttriple |  | 3个城市间形成等级传递式资本流动关系倾向 | |
| 循环闭合性 | ctriple | 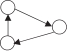 | 3个城市间形成扁平循环式资本流动关系倾向 | |
表3 指数随机图模型的拟合结果Table 3 Estimation results of exponential random graph models |
| 类型 | 统计量 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基础效应 | edges | -23.796***(-2.504) | -23.920***(-2.715) | -17.986***(-2.928) | -17.008***(-3.104) |
| 城市属性因素 | nodeocov(Uemp) | 1.362***(-0.216) | 1.354***(-0.215) | 1.026***(-0.202) | 0.674**(-0.234) |
| nodeocov(Hemp) | 0.138(-0.197) | 0.020(-0.204) | 0.020(-0.196) | 0.190(-0.229) | |
| nodeocov(FDI) | 0.459**(-0.160) | 0.530***(-0.155) | 0.528***(-0.153) | 0.440**(-0.151) | |
| nodeicov(Uemp) | 0.875***(-0.241) | 0.864***(-0.251) | 0.665*(-0.266) | 0.519*(-0.231) | |
| nodeicov(Hemp) | 1.354***(-0.215) | 1.362***(-0.216) | 1.026***(-0.202) | 0.674**(-0.234) | |
| nodeicov(FDI) | 0.277**(-0.147) | 0.276**(-0.151) | 0.275**(-0.169) | 0.155**(-0.137) | |
| 城际关系因素 | edgecov(dis) | -0.726***(-0.178) | -0.744***(-0.177) | -0.881***(-0.177) | -0.901***(-0.188) |
| nodematch(pro) | 2.239***(-0.257) | 2.213***(-0.247) | 2.112***(-0.246) | 2.019***(-0.250) | |
| nodematch(adm) | -0.384*(-0.238) | -0.386*(-0.248) | -0.680**(-0.260) | -0.775**(-0.295) | |
| 结构依赖因素 | mutual | 1.413***(0.293) | 1.392***(0.288) | 1.377***(0.289) | |
| gwodegree | 1.872***(0.494) | 2.482***(0.496) | |||
| gwidegree | -1.480*(1.320) | -0.028*(-0.013) | |||
| ttriple | 0.164***(-0.032) | ||||
| ctriple | -0.173*(-0.085) | ||||
| AIC | 815.595 | 817.669 | 802.880 | 797.045 | |
| BIC | 869.619 | 877.096 | 873.112 | 878.082 | |
| Log Likelihood | -397.797 | -397.834 | -388.440 | -383.523 | |
|

1 资料来源:https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2019/content_5462503.htm
2 https://www.qcc.com/web/search/advance
3 资料来源:https://www.nanjing.gov.cn/bmdt/202208/t20220825_3682041.html
戴 靓:负责思路设计、论文撰写、修改与校对;
吕一凡:负责数据处理、网络模拟;
郑慧彬:负责数据收集、网络分析和可视化;
李鲁奇:负责论文撰写、修改与校对。
|
安徽省统计局,国家统计局安徽调查总队. 2023. 2023安徽统计年鉴. 北京:中国统计出版社.
Anhui Provincial Bureau of Statistics, Survey Office of the National Bureau of Statistics in Anhui. 2023. Anhui Statistical Yearbook 2023. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
|
|
Blondel V D, Guillaume J L, Lambiotte R, and Lefebvre E. 2008. Fast Unfolding of Community in Large Networks. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, 10: P10008.
|
|
Broekel T and Bednarz M. 2018. Disentangling Link Formation and Dissolution in Spatial Networks: An Application of a Two-Mode STERGM to a Project-Based R&D Network in the German Biotechnology Industry. Networks and Spatial Economics, 18: 677-704.
|
|
Castells M. 1996. The Rise of the Network Society. Oxford: Blackwell, 453-459.
|
|
陈明华,刘华军,孙亚男,何礼伟. 2016. 城市房价联动的网络结构特征及其影响因素:基于中国69个大中城市月度数据的经验考察. 南方经济,(1):71-88.
Chen Minghua, Liu Huajun, Sun Ya'nan, and He Liwei. 2016. Empirical Study on the Characteristics of Network Structure and Its Influence Factors of Urban Housing Price Linkage: Based on Monthly Data of 69 Large and Medium Cities in China. South China Journal of Economics, (1): 71-88.
|
|
戴靓,丁子军,马海涛,曹湛,王瑞霖. 2024. 粤港澳大湾区技术转移的空间关联与内生动力. 地理学报,79(6):1503-1520.
Dai Liang, Ding Zijun, Ma Haitao, Cao Zhan, and Wang Ruilin. 2024. Spatial Linkages and Endogenous Mechanisms of Technology Transfer in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Acta Geographica Sinica, 79(6): 1503-1520.
|
|
Dai L, Derudder B, Cao Z, and Ji Y. 2023. Examining the Evolving Structures of Intercity Knowledge Networks: The Case of Scientific Collaboration in China. International Journal of Urban Sciences, 27(3): 371-389.
|
|
冯冬梅. 2015.中国房地产业对经济的影响及趋势分析. 北京:对外经济贸易大学.
Feng Dongmei. 2015. Analysis of the Impact of China's Real Estate Industry and Trend. Beijing: University of International Business and Economics.
|
|
高鹏,何丹,宁越敏,韩明珑. 2021. 长三角地区城市投资联系水平的时空动态及影响因素. 地理研究,40(10):2760-2779.
Gao Peng, He Dan, Ning Yuemin, and Han Minglong. 2021. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Factors of Urban Investment Linkage Level in the Yangtze River Delta. Geographical Research, 40(10): 2760-2779.
|
|
高鹏,宁越敏,何丹,张凡. 2023. 企业异地投资视角下长三角城市经济增长的网络外部性研究. 地理科学,43(7):1216-1226.
Gao Peng, Ning Yuemin, He Dan, and Zhang Fan. 2023. Network Externalities of Urban Economic Growth in the Yangtze River Delta from the Perspective of Enterprises' Non-Local Investment. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 43(7): 1216-1226.
|
|
古恒宇,黎宇翔,劳昕,卢琳,张亮. 2024. 疫情期间中国春运人口流动网络特征及其影响因素. 经济地理,44(5):53-63.
Gu Hengyu, Li Yuxiang, Lao Xin, Lu Lin, and Zhang Liang. 2024. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Population Flow Network during China's Spring Festival under COVID-19 Pandemic. Economic Geography, 44(5): 53-63.
|
|
桂钦昌,杜德斌,刘承良,侯纯光. 2022. 基于随机行动者模型的全球科学合作网络演化研究. 地理研究,41(10):2631-2647.
Gui Qingchang, Du Debin, Liu Chengliang, and Hou Chunguang. 2022. The Evolution of the Global Scientific Collaboration Network: A Stochastic Actor-Oriented Model Approach. Geographical Research, 41(10): 2631-2647.
|
|
胡国建,陈传明,陈丽娟,王强,金星星. 2018. 企业跨区域投资格局及其影响因素:以福建上市企业为例. 经济地理,38(9):138-146.
Hu Guojian, Chen Chuanming, Chen Lijuan, Wang Qiang, and Jin Xingxing. 2018. Enterprise's Cross-Region Investment Pattern and Its Determinants: A Case Study of Fujian Listed Firms. Economic Geography, 38(9): 138-146.
|
|
胡国建,陆玉麒. 2020. 基于企业视角的城市网络研究进展、思考和展望. 地理科学进展,39(9):1587-1596.
Hu Guojian and Lu Yuqi. 2020. Progress, Thoughts, and Prospect of Urban Network Research Based on Enterprise Perspective. Progress in Geography, 39(9): 1587-1596.
|
|
胡志强,苗长虹,华明芳,刘丽. 2018. 中国外商投资区位选择的时空格局与影响因素. 人文地理,33(5):88-96.
Hu Zhiqiang, Miao Changhong, Hua Mingfang, and Liu Li. 2018. Spatio Temporal Patterns and Location Factors of FDI in China. Human Geography, 33(5): 88-96.
|
|
黄忠华,李书萱,杜雪君. 2022. 长三角一体化发展下城市地价时空格局及影响机制研究. 中国土地科学,36(2):53-62.
Huang Zhonghua, Li Shuxuan, and Du Xuejun. 2022. Spatial-Temporal Pattern and Influence Mechanism of Urban Land Prices under the Integrated Development of the Yangtze River Delta. China Land Science, 36(2): 53-62.
|
|
Hunter D R. 2007. Curved Exponential Family Models for Social Networks. Social Networks, 29(2): 216-230.
|
|
纪宇凡,戴靓,丁子军,周腾. 2022. 中国城市房地产企业网络的结构特征. 资源开发与市场,38(2):156-162.
Ji Yufan, Dai Liang, Ding Zijun, and Zhou Teng. 2022. Structural Characteristics of the Intercity Network of Real Estate Enterprises in China. Resource Development and Market, 38(2): 156-162.
|
|
江苏省统计局,国家统计局江苏调查总队. 2023. 江苏统计年鉴2023. 北京:中国统计出版社.
Jiangsu Provincial Bureau of Statistics, Survey Office of the National Bureau of Statistics in Jiangsu. 2023. Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook 2023. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
|
|
冷硕峰,席广亮,甄峰. 2023. 长三角数字经济网络演化特征及影响因素. 热带地理,43(4):620-635.
Leng Shuofeng, Xi Guangliang, and Zhen Fen. 2023. Evolutionary Characteristics and Influencing Factors of the Digital Economic Network in the Yangtze River Delta. Tropical Geography, 43(4): 620-635.
|
|
冷硕峰,席广亮,甄峰,刘翰阳. 2024. 基于企业股权关联的长三角数字经济网络演变和空间扩展模式研究. 人文地理,39(3):81-91,182.
Leng Shuofeng, Xi Guangliang, Zhen Fen, and Liu Hanyang. 2024. The Evolution and the Spatial Expansion Pattern of the Digital Economy Network in the Yangtze River Delta Region Based on Interfirm Investment Relationship. Human Geography, 39(3): 81-91, 182.
|
|
李聪,卢明华,张金哲,余加丽. 2022. 京津冀城市群产业投资网络演变及影响因素研究. 人文地理,37(5):162-170.
Li Cong, Lu Minghua, Zhang Jinzhe, and Yu Jiali. 2022. Evolution and Influencing Factors of Industrial Investment Network in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Human Geography, 37(5): 162-170.
|
|
李仙德. 2014. 基于上市公司网络的长三角城市网络空间结构研究. 地理科学进展,33(12):1587-1600.
Li Xiande. 2014. Spatial Structure of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Network Based on the Pattern of Listed Companies Network. Progress in Geography, 33(12): 1587-1600.
|
|
李哲睿,甄峰,傅行行. 2019. 基于企业股权关联的城市网络研究:以长三角地区为例. 地理科学,39(11):1763-1770.
Li Zherui, Zhen Feng, and Fu Xingxing. 2019. Mapping Urban Network Through Inter-Firm Investment Relationship: A Case Study of Yangtze River Delta. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 39(11): 1763-1770.
|
|
李周平,傅春,李远刚,刘小钰. 2024. 基于企业投资路径的城市网络结构演化研究:以长三角地区为例. 热带地理,44(7):1236-1248.
Li Zhouping, Fu Chun, Li Yuangang, and Liu Xiaoyu. 2024. Structure Evolution of Urban Network through Enterprise Investment Routes: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Delta. Tropical Geography, 44 (7): 1236-1248.
|
|
刘程军,陈亦婷,陈秋驹,陈国亮,周建平. 2023. 企业投资视角下金融科技的空间联系网络演化与影响因素. 经济地理,43(2):136-146.
Liu Chengjun, Chen Yiting, Chen Qiuju, Chen Guoliang, and Zhou Jianping. 2023. Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Spatial Connection Network of Financial Technology from the Perspective of Enterprise Investment. Economic Geography, 43(2): 136-146.
|
|
Liu X J and Derudder B. 2013. Analyzing Urban Networks through the Lens of Corporate Networks: A Critical Review. Cities, 31: 430-437.
|
|
卢明华,周悦颜,刘汉初,许欣. 2020. 北京企业对河北直接投资的时空动态特征及影响因素. 地理科学进展,39(3):389-401.
Lu Minghua, Zhou Yueyan, Liu Hanchu, and Xu Xin. 2020. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Influencing Factors of Direct Investment in Hebei Province by Beijing's Enterprises. Progress in Geography, 39(3): 389-401.
|
|
罗超亮,符正平,刘冰,王曦. 2022. 战略性新兴产业国际贸易网络的演化及动力机制研究.国际贸易问题,(3):121-139.
Luo Chaoliang, Fu Zhengping, Liu Bing, and Wang Xi. 2022. Research on the Evolution of Strategic Emerging Industries' International Trade Network and Its Dynamic Mechanism. Journal of International Trade, (3): 121-139.
|
|
马海涛. 2020. 知识流动空间的城市关系建构与创新网络模拟. 地理学报,75(4):708-721.
Ma Haitao. 2020. The Theoretical Construction and Network Simulation of Intercity Innovative Relationships in Knowledge Flow Space. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(4): 708-721.
|
|
马学广,张钊,蒋策. 2023. 基于先进制造业投资的中国城市网络空间联系与结构研究. 人文地理,38(3):108-117,154.
Ma Xueguang, Zhang Zhao, and Jiang Ce. 2023. Research on Spatial Connection and Structure of Chinese Urban Network Based on Advanced Manufacturing Investment. Human Geography, 38(3): 108-117, 154.
|
|
Pan F H, Bi W K, Lenzer J, and Zhao X B. 2017. Mapping Urban Networks Through Inter-Firm Service Relationships: The Case of China. Urban Studies, 54(16): 3639-3654.]
|
|
潘竟虎,杨亮洁. 2017. 中国地级及以上城市房价收入比的时空分异. 干旱区地理,40(6):1274-1281.
Pan Jinghu and Yang Liangjie. 2017. Spatial-Temporal Differentiation of Housing Price-to-Income Ratio at Prefecture Level Cities in China. Arid Land Geography, 40(6): 1274-1281.
|
|
秦娅风,郭建科,董梦如,郭姝. 2021. 基于企业投资行为的中国沿海城市产业网络空间联系特征. 地域研究与开发,40(6):19-24.
Qin Yafeng, Guo Jianke, Dong Mengru, and Guo Shu. 2021. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Industrial Network in Coastal Cities of China Based on Enterprise Investment Behavior. Areal Research and Development, 40(6): 19-24.
|
|
Robins G, Morris M, Pattison P, Kalish Y, and Lusher D. 2007. An Introduction to Exponential Random Graph (p*) Models for Social Networks. Social Network, 29(2): 173-191.
|
|
上海市统计局,国家统计局上海调查总队. 2023. 2023上海统计年鉴. 北京:中国统计出版社.
Shanghai Municipal Bureau of Statistics, Survey Office of the National Bureau of Statistics in Shanghai. 2023. Shanghai Statistical Yearbook 2023. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
|
|
盛科荣,张红霞,赵超越. 2019. 中国城市网络关联格局的影响因素分析:基于电子信息企业网络的视角. 地理研究,38(5):32-46.
Sheng Kerong, Zhang Hongxia, and Zhao Chaoyue. 2019. Determinants of the Urban Spatial Network in China: An Analysis through the Lens of Corporate Networks within Electronic Information Industry. Geographical Research, 38(5): 32-46.
|
|
Shi S, Wall R, and Pain K. 2018. Exploring the Significance of Domestic Investment for Foreign Direct Investment in China: A City-network Approach. Urban Studies, 56(12): 2447-2464.
|
|
宋伟轩,陈艳如,孙洁,何淼. 2020. 长三角一体化区域城市房价空间分异的模式与效应. 地理学报,75(10):2109-2125.
Song Weixuan, Chen Yanru, Sun Jie, and He Miao. 2020. Spatial Differentiation of Urban Housing Prices in Integrated Region of Yangtze River Delta. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(10): 2109-2125.
|
|
唐晓彬,崔茂生. 2020. “一带一路”货物贸易网络结构动态变化及其影响机制. 财经研究,46(7):138-153.
Tang Xiaobin and Cui Maosheng. 2020. Research on the Dynamic Change of Goods Trade Network Structure and Its Impact Mechanism of Countries along the Belt and Road. Journal of Finance and Economics, 46(7): 138-153.
|
|
唐子来,赵渺希. 2010. 经济全球化视角下长三角区域的城市体系演化: 关联网络和价值区段的分析方法. 城市规划学刊,(1):29-34.
Tang Zilai and Zhao Miaoxi. 2010. Economic Globalization and Transformation of Urban System in the Yangtze River Delta Region: Interlocking Network and Value-Added Hierarchy. Urban Planning Forum, (1): 29-34.
|
|
汪传江. 2019. 中国城市间投资网络的结构特征与演化分析: 基于企业并购视角. 工业技术经济,38(2):87-96.
Wang Chuanjiang. 2019. Analysis of Structural Characteristics and Evolution of China's Cross-City Investment Network: Based on the Perspective of Mergers and Acquisitions. Journal of Industrial Technological Economics, 38(2): 87-96.
|
|
汪菲,罗皓,王长建,叶玉瑶,张虹鸥,林晓洁,陈静. 2023. 金融联系视角下粤港澳大湾区城市网络空间结构及其影响因素. 热带地理,43(4):581-595.
Wang Fei, Luo Hao, Wang Changjian, Ye Yuyao, Zhang Hong'ou, Lin Xiaojie, and Chen Jing. 2023. Spatial Structure and Influencing Factors of Urban Network in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from the Financial Relationships Perspective. Tropical Geography, 43(4): 581-595.
|
|
王姣娥,车恩瑜,肖凡. 2024.中国航空货运时空格局演变与影响因素研究. 热带地理,44(5):771-782.
Wang Jiao'e, Che Enyu, and Xiao Fan. 2024. Spatiotemporal Pattern and Influencing Factors of Air Cargo Transport in China. Tropical Geography, 44(5): 771-782.
|
|
王磊,李安琪,杨文毅,张伊娜. 2019. 城际房地产消费流的空间格局与驱动因素研究:以长江中游城市群为例. 湖北社会科学,(12):46-55.
Wang Lei, Li Anqi, Yang Wenyi, and Zhang Yina. 2019. Research on the Spatial Pattern and Driving Factors of Intercity Real Estate Consumption Flows: A Case Study of the Mid-Yangtze Urban Agglomeration. Hubei Social Sciences, (12): 46-55.
|
|
吴炫,杨家文. 2019. 流动量与关注度视角下的城市网络结构: 以广州、深圳为例. 地理科学进展,38(12):1843-1853.
Wu Xuan and Yang Jiawen. 2019. City Network by Mobility and Attention Indices: A Comparison of Guangzhou and Shenzhen. Progress in Geography, 38(12): 1843-1853.
|
|
徐宁,李仙德. 2020. 上海上市公司对外投资网络演变及其影响因素研究. 地理科学进展,39(4):553-566.
Xu Ning and Li Xiande. 2020. Evolution of Shanghai Listed Companies' Outward Investment Network and Its Determinants. Progress in Geography, 39(4): 553-566.
|
|
尹上岗,马志飞,吴小影,李在军. 2020. 中国城市住宅售租比时空分异格局及影响机制. 长江流域资源与环境,29(3):547-556.
Yin Shanggang, Ma Zhifei, Wu Xiaoying, and Li Zaijun. 2020. Spatial-Temporal Differentiation and Influence Mechanism of the Urban Housing Price-to-Rent Ratio in China. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 29(3): 547-556.
|
|
于瀚辰,周麟,沈体雁. 2019. 制造业企业区位选择集聚经济指向的空间效应. 地理研究,38(2):273-284.
Yu Hanchen, Zhou Lin, and Shen Tiyan. 2019. Location Selection and Spatial Effects of Agglomeration Economy in Manufacturing Enterprises. Geographical Research, 38(2): 273-284.
|
|
Zhang W, Chong Z, Li X, and Nie G. 2020. Spatial Patterns and Determinant Factors of Population Flow Networks in China: Analysis on Tencent Location Big Data. Cities, 99: 102640.
|
|
张泽,唐子来. 2018. 证券资本流动视角下的城市关联网络特征:以上海为例. 同济大学学报:社会科学版,29(3):54-61.
Zhang Ze and Tang Zilai. 2018. Urban Interlocking Network Features from the Perspective of Securities Capital Flows: The Case Study of Shanghai. Tongji University Journal Social Science Section, 29(3): 54-61.
|
|
Zhang Z and Wang Z. 2022. Cyberspace-Based Urban Networks: Visualising and Exploring China's Intercity Interaction from a New Perspective. Environment and Planning A: Economy and Space, 54(3): 454-460.
|
|
浙江省统计局,国家统计局浙江调查总队. 2023. 2023浙江统计年鉴. 北京:中国统计出版社.
Zhejiang Provincial Bureau of Statistics, Survey Office of the National Bureau of Statistics in Zhejiang. 2023. Zhejiang Statistical Yearbook 2023. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
|
|
周建平,刘程军,徐维祥,李露,周梦瑶,侯和宏. 2021. 电子商务背景下快递企业物流网络结构及自组织效应:以中通快递为例. 经济地理,41(2):103-112.
Zhou Jianping, Liu Chengjun, Xu Weixiang, Li Lu, Zhou Mengyao, and Hou Hehong. 2021. Logistics Network Structure of Express Delivery Companies and Their Self-Organization Effect Under the Background of E-Commerce: Taking ZTO Express as an Example. Economic Geography, 41(2): 103-112.
|
|
周小平,秦振扬,赵松,柴铎. 2019. 中国住宅地价房价比的空间格局、演变特征及影响因素:基于35个大中城市的空间计量分析. 中国土地科学,33(1):40-48.
Zhou Xiaoping, Qin Zhenyang, Zhao Song, and Chai Duo. 2019. The Spatial Pattern, Evolution Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Land Share in Housing Price in China: A Spatial Econometric Analysis of 35 Large and Medium-Size Cities. China Land Science, 33(1): 40-48.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |