

钦州湾与马尼拉湾岸线时空变化与围填海分析
|
张文良(2000—),男,山东昌乐人,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为海岸带资源环境遥感,(E-mail)dixinzwl@163.com; |
收稿日期: 2024-07-02
修回日期: 2024-09-04
网络出版日期: 2025-03-14
基金资助
自然资源部专项业务费项目(CB202202015)
自然资源部第四海洋研究所基本科研业务费资助项目(202109)
Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Shoreline Changes and Reclamation in the Qinzhou Bay and the Manila Bay
Received date: 2024-07-02
Revised date: 2024-09-04
Online published: 2025-03-14
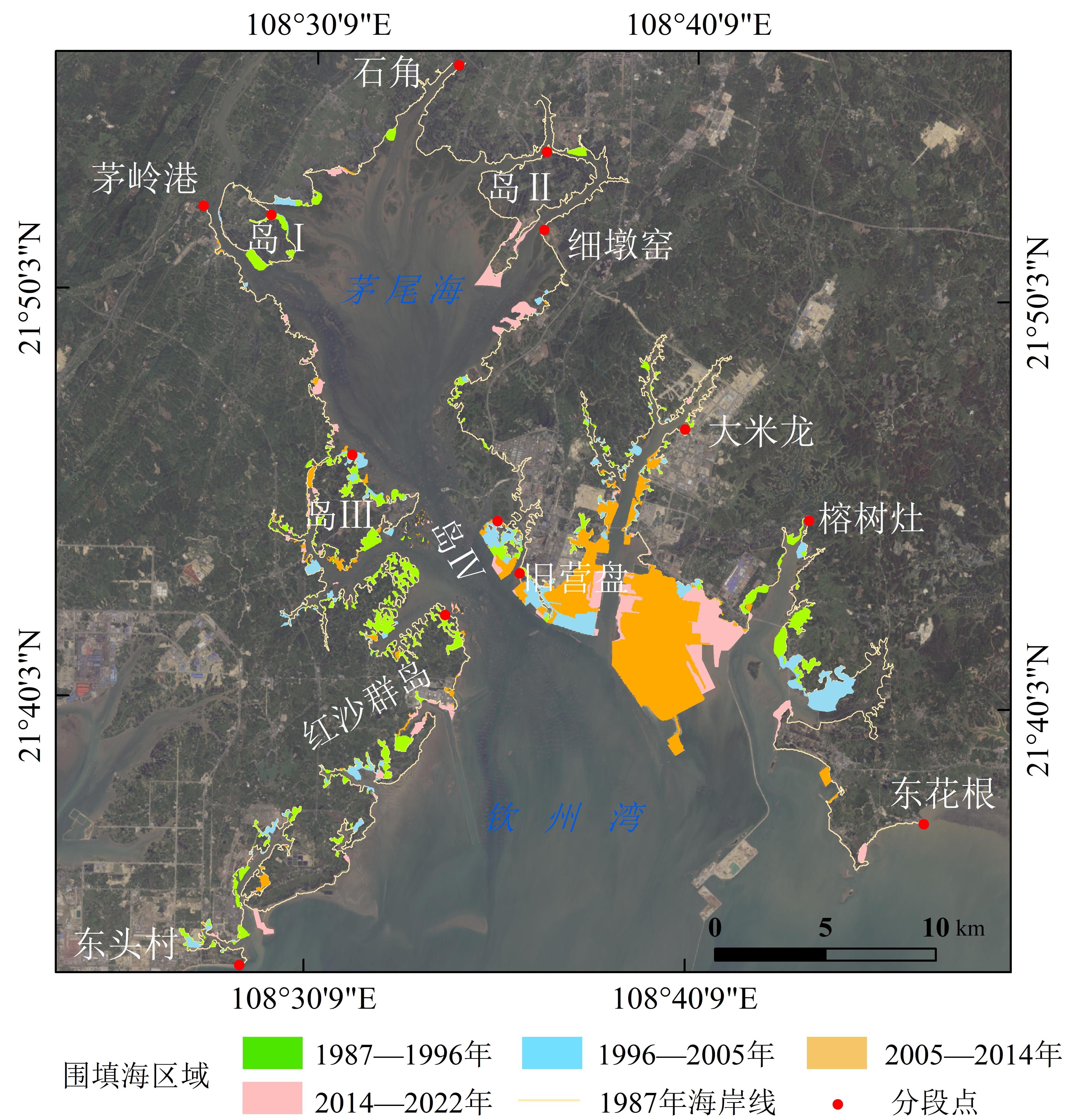
近40年来,中国钦州湾和菲律宾马尼拉湾海岸线发生了显著变化,了解其变化规律对区域海岸带管理和规划具有重要意义。文章基于Google Earth Engine (GEE)平台,利用改进的归一化水体指数(Modified Normalized Difference Water Index, MNDWI)和大津(Otsu)算法,结合数字岸线分析系统(Digital Shoreline Analysis System, DSAS),对两地近40年的海岸线时空变化特征及其驱动因素进行分析。结果表明,1987—2022年,钦州湾海岸线长度增加了44.78 km,总体呈现向海推进趋势,平均变化速率达6.81 m/a,自然岸线占比不断下降而人工岸线比例上升。相比之下,马尼拉湾海岸线变化相对较小,总长度减少1.05 km,平均变化速率为2.36 m/a,自然岸线占比持续下降。钦州湾围填海强度指数和年均空间扩展速率均大于马尼拉湾。两地海岸线演变的特征均是受到围填海活动的显著影响,而港口码头建设和围海养殖是围填海的主要驱动因素。
张文良 , 郭俊丽 , 刘卓成 , 时连强 , 龚照辉 , 张达恒 . 钦州湾与马尼拉湾岸线时空变化与围填海分析[J]. 热带地理, 2025 , 45(3) : 489 -503 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20240441
Over the past 40 years, significant changes have occurred along the coastlines of Qinzhou Bay in China and Manila Bay in the Philippines. Understanding the patterns of these changes is important for the management and planning of coastal zones. This study is based on the Google Earth Engine platform, using the modified normalized difference water index, combined with the Otsu algorithm and the Digital Shoreline Analysis System, to extract the coastlines of Qinzhou Bay in China and Manila Bay in the Philippines over the past 40 years, and then analyze the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of the two coastlines and the situation of reclamation. The results show that in the past 40 years, the coastline of Qinzhou Bay has generally advanced towards the sea, with a coastline length increase of 44.78 km, an average End Point Rate(EPR)of 6.81 m/a, and average Linear Regression Rate(LRR)of 6.16 m/a. Natural coastline length continued to decrease, whereas the proportion of artificial coastlines continued to increase. The Index of Coastline Utilization degree (ICUD) values show an upward trend, whereas the Index of Coastline Type Diversity (ICTD) values show a continuously decreasing trend. The Manila Bay coastline first increased and then decreased, with an overall decrease of 1.05 km—a relatively small change. The coastline also shows a trend of advancing towards the sea with an average EPR of 2.36 m/a and average LRR of 2.32 m/a. The proportion of natural coastlines continued to decline, whereas that of artificial coastlines gradually increased. The ICUD values showed a steadily increasing trend, whereas the ICTD values showed a downward trend. The cumulative area of reclamation in Qinzhou Bay has reached 6,674.27 hm2, with an average annual expansion rate of 196.30 hm2/a. Reclamation activities were significantly active and large-scale. However, the cumulative reclamation area of Manila Bay is only 1,718.59 hm2, with an average annual expansion rate of 50.55 hm2/a, indicating relatively limited reclamation activities. The reclamation intensity index and annual spatial expansion rate of Qinzhou Bay were higher than those of Manila Bay. Overall, compared to Manila Bay, the Qinzhou Bay coastline exhibited more significant characteristics in terms of change amplitude, change speed, and reclamation intensity. Reclamation activities have a significant impact on coastline changes, and port and dock construction and aquaculture are the main driving factors for reclamation.

Key words: remote sensing; coastline; reclamation; Qinzhou Bay; Manila Bay
表1 用于海岸线提取的Landsat影像Table 1 Landsat images for shoreline extraction |
| 区域 | 卫星/传感器 | 成像时间 | 分辨率/m | 潮高/cm | 云量/% | 卫星/传感器 | 成像时间 | 分辨率/m | 潮高/cm | 云量/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 钦州湾 | Landsat5/TM | 1987-10-26 | 30 | 365 | 0.03 | Landsat5/TM | 1987-09-08 | 30 | 296 | 6 |
| 1996-10-02 | 386 | 5 | 1996-01-04 | 221 | 9 | |||||
| 2005-10-11 | 422 | 0.02 | 2006-10-30 | 205 | 0.03 | |||||
| Landsat8/OLI | 2014-01-05 | 402 | 1.22 | Landsat8/OLI | 2014-01-21 | 452 | 1.44 | |||
| Landsat9/OLI-2 | 2022-01-19 | 332 | 17.15 | Landsat9/OLI-2 | 2022-12-21 | 321 | 16.73 | |||
| 马尼拉湾 | Landsat5/TM | 1988-03-03 | 30 | 152 | 14 | Landsat5/TM | 1989-04-07 | 30 | 144 | 15 |
| 1997-04-29 | 114 | 13 | 1997-06-16 | 159 | 16 | |||||
| 2004-07-05 | 202 | 10 | 2004-04-16 | 112 | 17 | |||||
| Landsat8/OLI | 2014-02-07 | 267 | 4.28 | Landsat8/OLI | 2015-10-24 | 116 | 8.59 | |||
| Landsat8/OLI | 2022-01-12 | 130 | 14.78 | Landsat8/OLI | 2022-05-12 | 94 | 15.37 |
表2 研究区岸线提取精度验证Table 2 Verification of shoreline extraction accuracy in the research area |
| 区域 | 距离/m | 点数/个 | 占比/% | 累计占比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 钦州湾 | ≤15 | 1032 | 51.32 | 51.32 |
| >15~30 | 472 | 23.47 | 74.79 | |
| >30~45 | 304 | 15.12 | 89.91 | |
| >45~60 | 134 | 6.66 | 96.57 | |
| >60 | 69 | 3.43 | 100 | |
| 马尼拉湾 | ≤15 | 965 | 64.33 | 64.33 |
| >15~30 | 221 | 14.73 | 79.06 | |
| >30~45 | 104 | 13.07 | 92.13 | |
| >45~60 | 134 | 4.20 | 96.33 | |
| >60 | 76 | 3.67 | 100 |
表3 不同类型岸线人力作用强度指数Table 3 Strength index of manpower of different types of shoreline |
| 一级岸线类型 | 二级岸线类型 | 人力作用强度指数 |
|---|---|---|
| 自然岸线 | 基岩岸线 | 1 |
| 砂质岸线 | 1 | |
| 生物岸线 | 1 | |
| 淤泥质岸线 | 1 | |
| 人工岸线 | 围垦养殖岸线 | 2 |
| 工程建设岸线 | 3 |
表4 围填海强度等级Table 4 Intensity class of reclamation |
| R值/(hm2·km-1) | 强度级别 | 指标意义 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 ≤ R <10 | 1级 | 围填海开发程度较低,开发潜力大 |
| 10 ≤ R < 20 | 2级 | 围填海压力较小,具有较大发开潜力 |
| 20 ≤R < 50 | 3级 | 围填海到达一定程度,继续开发受一定限制 |
| 50 ≤ R < 100 | 4级 | 围填海压力大,不宜继续围填海 |
| R ≥ 100 | 5级 | 围填海压力巨大,确有需要可拆除原有围填海项目 |
图9 1988—2022年马尼拉湾海岸线EPR分布Fig.9 Distribution of EPR along the coastline of the Manila Bay during 1988-2022 |
1 http://earthengine.googl-e.com
2 https://www.noaa.gov
张文良:野外调查、数据处理、图件制作、论文撰写与修改;
郭俊丽:研究思路、论文修改、方法指导;
刘卓成:野外调查、论文修改;
时连强:研究思路、方法指导、论文修改、基金支持;
龚照辉、张达恒:野外调查、数据处理。
|
Almeida L P, Oliveira I E D, Lyra R, Dazzi R L S, and Klein A H D F. 2021. Coastal Analyst System from Space Imagery Engine (CASSIE): Shoreline Management Module. Environmental Modelling and Software, (6): 105033.
|
|
毕京鹏.2019.海岸线时空变迁遥感监测与分析——以泰国和马六甲海峡为例.青岛:山东科技大学.
Bi Jingpeng. 2019. Remote Sensing Monitoring and Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Changes of Coastlines: A Case Study of Thailand and Malacca Strait. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology.
|
|
Chu L X, Francis O, Martin S, Dirk T, Daniel H, Thomas B, and Iulian T. 2020. Monitoring Long-Term Shoreline Dynamics and Human Activities in the Hangzhou Bay, China, Combining Daytime and Nighttime EO Data. Earth Big Data, 4(3): 1-23.
|
|
Crowell M, Leatherman S P, and Buckley M K. 1991. Historical Shoreline Change: Error Analysis and Mapping Accuracy. Journal of Coastal Research, 7(3): 839-852.
|
|
Ekercin S. 2007. Coastline Change Assessment at the Aegean Sea Coasts in Turkey Using Multitemporal Landsat Imagery. Journal of Coastal Research, 23(3): 691-698.
|
|
Fairchild I J, Baker A, Borsato A, Frisia S, Hinton R W, Mcdermott F, and Tooth A F. 2001. Annual to Sub-Annual Resolution of Multiple Trace-Element Trends in Speleothems. Journal of the Geological Society, 158(5): 831-841.
|
|
冯炳斌,王日明,黎树式,黄鹄,胡宝清.2022.钦州湾人工海滩剖面变化过程.热带海洋学报,41(4):51-60.
Feng Bingbin, Wang Riming, Li Shushi, Huang Hu, and Hu Baoqing. 2022. Changes of the Artificial Beach Profile in the Qinzhou Bay. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 41(4): 51-60.
|
|
葛振鹏,戴志军,谢华亮,魏稳,林益帆,高近娟.2014. 北部湾海湾岸线时空变化特征研究.上海国土资源,35(2):49-53.
Ge Zhenpeng, Dai Zhijun, Xie Hualiang, Wei Wen, Lin Yifan, and Gao Jinjuan. 2014. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of the Shoreline along the Beibu Gulf. Shanghai Land & Resources, 35(2): 49-53.
|
|
龚照辉,时连强,张达恒,张华国.2022.中越典型港湾海岸线与围填海的遥感比较——以防城湾和海防港为例.海洋学研究,40(3):62-72.
Gong Zhaohui, Shi Lianqiang, Zhang Daheng, and Zhang Huaguo. 2022. Comparative Study on Remote Sensing of Coastlines and Reclamation of Typical Bays in China and Vietnam: Taking Fangcheng Bay and Haiphong Port as Examples. Journal of Marine Sciences, 40(3): 62-72.
|
|
贾明明,刘殿伟,王宗明,汤旭光,董张玉.2013.面向对象方法和多源遥感数据的杭州湾海岸线提取分析.地球信息科学学报,15(2):262-269.
Jia Mingming, Liu Dianwei, Wang Zongming, Tang Xuguang, and Dong Zhangyu. 2013. Coastline Extraction and Analysis of Hangzhou Bay Using Object-Oriented Method and Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Journal of Geo Information Science, 15(2): 262-269.
|
|
黎树式,黄鹄.2018.近50年钦江水沙变化研究.广西科学,25(4):409-417.
Li Shushi and Huang Hu. 2018. Variations of Runoff and Sediment in Qinjing River in the Past 50 Years. Guangxi Sciences, 25(4): 409-417.
|
|
李梦,曹庆先,胡宝清,姜宁.2022.近60年广西钦州湾岸线变迁与开发利用空间格局评价.海洋技术学报,41(6):76-86.
Li Meng, Cao Qingxian, Hu Baoqing, and Jiang Ning. 2022. Spatial Pattern Change of the Coastline Development and Utilization of Qinzhou Bay in Recent 60 Years. Journal of Ocean Technology, 41(6): 76-86.
|
|
李鹏,普思寻,李振洪,王厚杰.2020.2000年以来胶州湾海岸线光学与SAR多源遥感变化监测研究.武汉大学学报(信息科学版),45(9):1485-1492.
Li Peng, Pu Sixun, Li Zhenhong, and Wang Houjie. 2020. Coastline Change Monitoring of Jiaozhou Bay from Multi-Source SAR and Optical Remote Sensing Images Since 2000. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 45(9): 1485-1492.
|
|
马梓程,陈思,张倩,贾凤鸣,何博彧.2022.基于DSAS模型协同GEE长时序影像的巽他海峡东海岸岸线变迁时空分析及预测.资源环境与工程,36(6):836-842.
Ma Zicheng, Chen Si, Zhang Qian, Jia Fengming, and He Boyu. 2022. Spatiotemporal Analysis and Prediction of Coastline Changes in the East Coast of the Sunda Strait Based on DSAS Model and GEE Long Time Series Images. Resources Environment&Engineering, 36(6): 836-842.
|
|
Otsu Nobuyuki. 1979. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern, 9: 62-66.
|
|
钱健,陈立红,丰卫华,向芸芸,王志富.2018.椒江口海域围填海强度及环境影响分析.海洋开发与管理,35(9):62-66.
Qian Jian, Chen Lihong, Feng Weihua, Xiang Yunyun, and Wang Zhifu. 2018. Analysis of Reclamation Intensity and Environmental Impact in Jiaojiang Estuary. Ocean Development and Management, 35(9): 62-66.
|
|
任治敏,易慧,阮明浩.2018.深圳市岸线资源遥感调查.城市勘测,(1):45-51.
Ren Zhimin, Yi Hui, and Ruan Minghao. 2018. The Study of Coastline in Shenzhen City Based on Remote Sensing. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, (1): 45-51.
|
|
Sheng G F, Yang W, Deng X P, He C, Cao Y F, and Sun H. 2012. Coastline Detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Images by Integrating Watershed Transformation and Controllable Gradient Vector Flow (GVF) Snake Model. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 37(3): 375-383.
|
|
申家双,翟京生,郭海涛.2009.海岸线提取技术研究.海洋测绘,29(6):74-77.
Shen Jiashuang, Zhai Jingsheng, and Guo Haitao. 2009. Study on Coastline Extraction Technology. Marine Surveying and Mapping, 29(6): 74-77.
|
|
宋艳华,焦利民,刘稼丰,许刚.2021.城市扩张程度的影响因素分析——以武汉市为例.武汉大学学报(信息科学版),46(3):417-426.
Song Yanhua, Jiao Limin, Liu Jiafeng, and Xu Gang. 2021. Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Degree of Urban Expansion: Taking Wuhan City as an Example. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 46(3): 417-426.
|
|
孙晓林,吴孟泉,田佳慧,陆嘉琪,于涵.2019.近30年威海市海岸线时空变化及其驱动力.应用海洋学学报,38(2):206-213.
Sun Xiaolin, Wu Mengquan, Tian Jiahui, Lu Jiaqi, and Yu Han. 2019. Driving Forces and Spatio-Temporal Variation of Weihai Coastline in Recent 30 Years. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 38(2): 206-213.
|
|
王厚军,袁广军,刘亮,林宁.2021.海岸线分类及划定方法研究.海洋环境科学,40(3):430-434.
Wang Houjun, Yuan Guangjun, Liu Liang, and Lin Ning. 2021. Effective Methodologies for Coastline Classification and Delimitation. Marine Environmental Science, 40(3): 430-434.
|
|
卫诗韵,付东洋,刘大召,徐华兵,李高聪,程阳艳.2023.改革开放40年深圳海岸线变化的遥感监测.热带地理,43(5):986-1004.
Wei Shiyun, Fu Dongyang, Liu Dazhao, Xu Huabing, Li Gaocong, and Cheng Yangyan. 2023. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Shenzhen Coastline Changes over the Past 40 Years. Tropical Geography, 43(5): 986-1004.
|
|
毋亭.2016.近70年中国大陆岸线变化的时空特征分析.烟台:中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所.
Wu Ting. 2016. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Mainland Coastline Changes in China in Nearly 70 years. Yantai: Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
|
|
谢春艳,李峙,张建兵.2021.防城港-钦州的海岸线遥感监测与时空分析.测绘地理信息,46(2):25-29.
Xie Chunyan, Li Zhi, and Zhang Jianbing. 2021. Remote Sensing Monitoring and Spatial-Temporal Analysis of Coastal Lines between Fangchenggang City and Qinzhou City. Journal of Geomatics, 46(2): 25-29.
|
|
徐涵秋.2005.利用改进的归一化差异水体指数(MNDWI)提取水体信息的研究.遥感学报,(5):589-595.
Xu Hanqiu. 2005. A Study on Information Extraction of Water Body with the Modified Normalized Difference Water Index(MNDWI). Journal of Remote Sensing, (5): 589-595.
|
|
尹楠楠,汤军,杨元维,高贤军,宋树华.2023.1989―2021年粤港澳大湾区海岸线变迁及土地利用变化.海洋地质前沿,39(5):1-11.
Yin Nannan, Tang Jun, Yang Yuanwei, Gao Xianjun, and Song Shuhua. 2023. Variations of Shoreline and Land Use in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area from 1989 to 2021. Marine Geology Frontiers, 39(5): 1-11.
|
|
张静,景海涛,樊盛华.2020.基于海岸线数据库的遥感图像海陆分割.电子测量技术,43(23):115-120.
Zhang Jing, Jing Haitao, and Fan Shenghua. 2020. Sea-Land Segmentation for Remote Sensing Imagery Based on Coastline. Database. Electronic Measurement Technology, 43(23): 115-120.
|
|
赵连杰,吴孟泉,郑龙啸,栾绍鹏,赵贤峰.2022.胶东半岛北部海岸线时空变迁及驱动分析.自然资源遥感,34(4):87-96.
Zhao Lianjie, Wu Mengquan, Zheng Longxiao, Luan Shaopeng, and Zhao Xianfeng. 2022. Temporal-Spatial Changes and Driving Analysis of the Northern Shorelines of Jiaodong Peninsula. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 34(4): 87-96.
|
|
赵士祺,徐艳东,陈建强,魏潇,王玉祯.2023.基于GEE的1985—2020年胶州湾形态变化及驱动因素分析.海洋湖沼通报,45(6):12-18.
Zhao Shiqi, Xu Yandong, Chen Jianqiang, Wei Xiao, and Wang Yuzhen. 2023. Morphological Change of Jiaozhou Bay from 1985 to 2020 Its Driving Factors as Were Revealed with GEE. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 45(6): 12-18.
|
|
中华人民共和国国务院.2018.国务院关于加强滨海湿地保护严格管控围填海的通知. (2018-07-14)[2023-10-25]. https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2018/content_5313946.htm.
The State Council of the People's Republic of China. 2018. Notice of the State Council on Strengthening the Protection of Coastal Wetlands and Strictly Regulating Sea Reclamation. (2018-07-14)[2023-10-25]. https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2018/content_5313946.htm.
|
|
朱国强.2015.近30年南海周边国家海岸线时空变化研究.兰州:兰州交通大学.
Zhu Guoqiang. 2015. Research on Spatial-Temporal Changes of Coastline in Countries around the South China Sea in Recent Three Decades. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiaotong University.
|
|
朱琳,黄玉玲,杨刚,孙伟伟,陈超.2023.基于GEE的杭州湾海岸线遥感提取与时空演变分析.自然资源遥感,35(2):50-60.
Zhu Lin, Huang Yuling, Yang Gang, Sun Weiwei, and Chen Chao. 2023. Information Extraction and Spatio-Temporal Evolution Analysis of the Coastline in Hangzhou Bay Based on Google Earth Engine and Remote Sensing Technology. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 35(2): 50-60.
|
|
Zhu Q T, Li P, Li Z H, Pu S X, Wu X, Bi N S, and Wang H J. 2021. Spatiotemporal Changes of Coastline over the Yellow River Delta in the Previous 40 Years with Optical and SAR Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 13: 1940
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |