

间断式潜堤对岛礁次重力波水动力特性影响研究
喻仞石:数据处理与论文撰写;
屈 科:提出论文选题与研究方法;
聂文军:物理试验与数据采集。
|
喻仞石(1998—),男,湖南长沙人,硕士研究生,研究方向为波浪水动力、海岸工程,(E-mail)2741475975@qq.com; |
收稿日期: 2025-02-23
修回日期: 2025-03-19
网络出版日期: 2025-06-30
基金资助
国家重点研发计划课题(2022YFC3103601)
Influence of Intermittent Submerged Breakwater on the Hydrodynamic Impacts of Infragravity Waves on Fringing Reef
Received date: 2025-02-23
Revised date: 2025-03-19
Online published: 2025-06-30
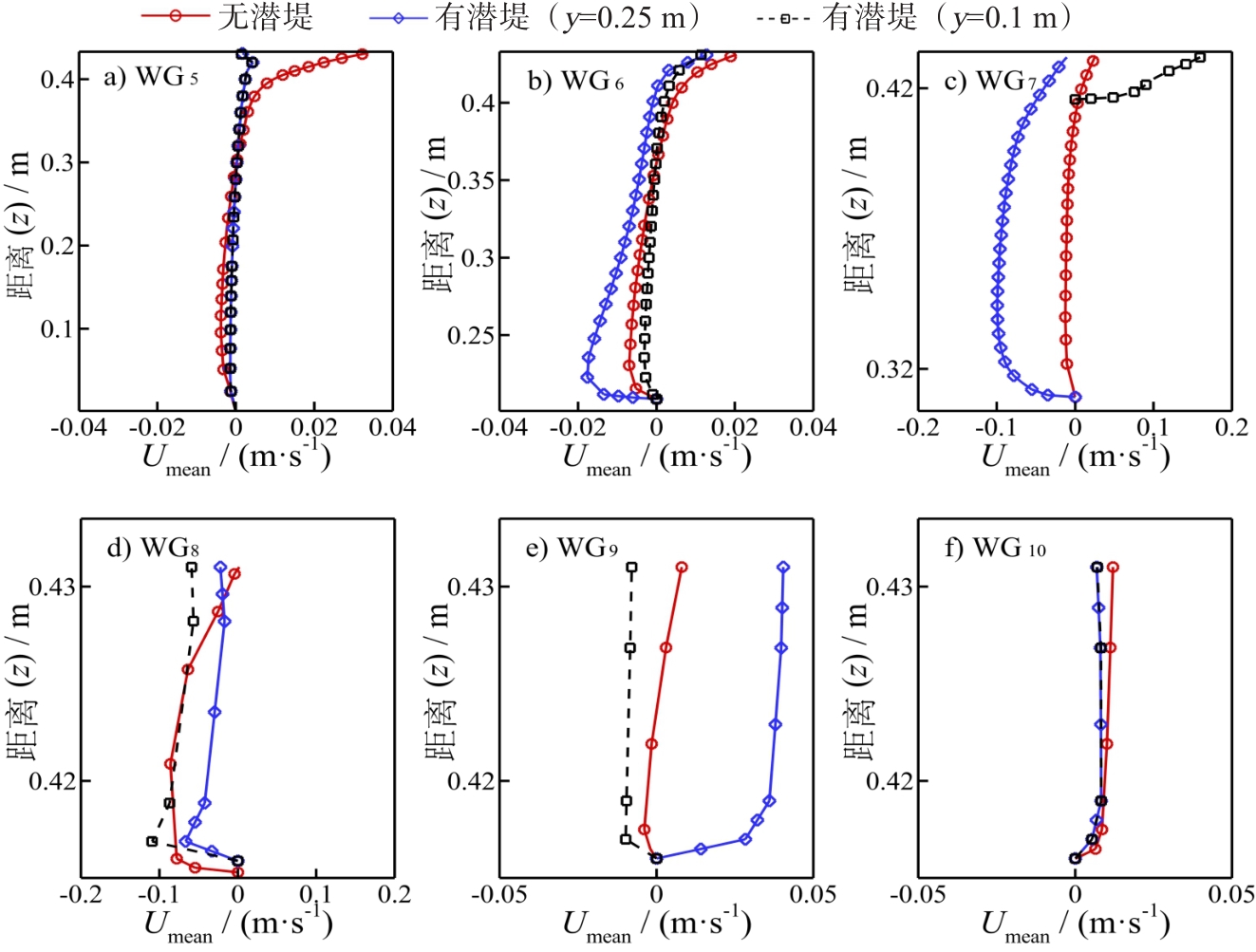
珊瑚岛礁地貌作为海岸的天然屏障,能耗散大部分入射波浪能量,从而保护岸滩免受侵蚀。然而,近年来因人类活动,产生了不可逆的破坏,导致岛屿失去了天然屏障的保护。在此背景下,岛礁修复工程成为保障岛屿安全的重要途径。为揭示潜堤在岛礁地形上的水动力特性,针对有无潜堤2种情况,对一系列非规则波进行物理试验和数值模拟。结果表明:间断潜堤的存在能降低礁坪上的低频能量、次重力波波高、礁坪增水以及波浪爬高。当有效波高和堤顶水深取最小试验值时,间断潜堤对波浪爬高和礁坪增水的削减效果最为显著;同时,堤顶水深的增大会使使短波在爬高中的贡献增加。潜堤的间断宽度增大可进一步增强其对波浪爬高和礁坪增水的削减效果,并削弱次重力波在礁坪上的共振放大效应,而谱峰周期的增大则会增强此效应。最后,通过数值模拟发现,间断潜堤的存在使间断处产生急促的离岸流,并削弱礁坪上的向岸流速。
喻仞石 , 屈科 , 聂文军 . 间断式潜堤对岛礁次重力波水动力特性影响研究[J]. 热带地理, 2025 , 45(6) : 1034 -1044 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20250105
Coral reef systems are vital natural barriers that dissipate wave energy and protect coastlines. However, anthropogenic damage has severely compromised this protective function, necessitating restoration efforts such as submerged breakwaters. To understand the influence of discontinuous submerged breakwaters on wave hydrodynamics over reef flats, this study employed physical model experiments and numerical simulations. A series of irregular waves were tested under scenarios with and without a breakwater, systematically varying the key parameters: significant wave height, water depth over the breakwater crown, spectral peak period, and gap width. The results demonstrate that discontinuous submerged breakwaters reduce the hydrodynamic loads on reef flats by generating wave reflection and refraction, as well as by enhancing the viscous dissipation of rip currents at discontinuities with incident waves. Specifically, breakwaters reduce the infragravity wave energy and wave heights, wave-induced set-up on the reef flat, and maximum wave run-up on the back reef slope. The reduction in wave run-up and reef flat set-up is most significant under minimal significant wave height conditions. Increasing the water depth over the breakwater crown can lead to incomplete wave breaking, thereby causing a relative increase in the contribution of short waves to the total wave run-up. Increasing the gap width enhances the effectiveness of the breakwater in reducing both the run-up and set-up, while simultaneously weakening the resonance amplification of infragravity waves on the reef flat. Conversely, increasing the spectral peak period intensifies infragravity wave resonance. Finally, the complex hydrodynamics along the reef are revealed using the waves2Foam model in OpenFOAM to construct a three-dimensional numerical wave flume. The study found that abrupt rip currents are generated at the discontinuities of submerged breakwaters while simultaneously reducing the onshore flow velocity over the reef flat. In conclusion, discontinuous submerged breakwaters are a viable engineering measure for mitigating coastal hazards in degraded reefs by reducing damage to infragravity waves, wave set-ups, and wave run-ups. These findings provide essential mechanistic insights and quantitative guidance for designing effective reef restoration and protection structures that incorporate submerged breakwaters.

表1 测点位置Table 1 Position of measuring points |
| 测点编号 | 测点位置/m | 测点编号 | 测点位置/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| WG1 | 18.29 | WG8 | 26.06 |
| WG2 | 18.59 | WG9 | 26.765 |
| WG3 | 18.89 | WG10 | 27.845 |
| WG4 | 22 | WG11 | 28.74 |
| WG5 | 23 | WG12 | 29.68 |
| WG6 | 24.535 | WG13 | 30.56 |
| WG7 | 25.28 | WG14 | — |
表2 试验工况设置Table 2 Experimental condition setting table |
| 工况 | 有效波高 (Hs)/m | 堤顶水深 (d)/m | 谱峰周期 (Tp)/s | 间断宽度 (w)/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.06 | 0 | 1.5 | 无潜堤 |
| A2 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1 | 无潜堤 |
| A3 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1.25 | 无潜堤 |
| A4 | 0.04 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 无潜堤 |
| A5 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 无潜堤 |
| A6 | 0.08 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 无潜堤 |
| A7 | 0.1 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 无潜堤 |
| A8 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1.75 | 无潜堤 |
| A9 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 1.5 | 无潜堤 |
| A10 | 0.06 | 0.045 | 1.5 | 无潜堤 |
| B1 | 0.06 | 0 | 1.5 | 0.15 |
| B2 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1 | 0.15 |
| B3 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1.25 | 0.15 |
| B4 | 0.04 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 0.15 |
| B5 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 0.15 |
| B6 | 0.08 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 0.15 |
| B7 | 0.1 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 0.15 |
| B8 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1.75 | 0.15 |
| B9 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 1.5 | 0.15 |
| B10 | 0.06 | 0.045 | 1.5 | 0.15 |
| C1 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 0.05 |
| C2 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| C3 | 0.06 | 0.015 | 1.5 | 0.2 |
表3 有无间断潜堤下礁坪增水与波浪爬高的显著性分析Table 3 Significance analysis of water increase and wave run-up on reef flat with or without intermittent submerged breakwater |
| 分析要素 | 有无间断潜堤 | 均值 | t值 | 显著性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 礁坪增水 | 无 | 0.014 4 | 3.97 | 0.05 |
| 有 | 0.012 9 | |||
| 波浪爬高 | 无 | 0.078 7 | 6.11 | 0.001 |
| 有 | 0.071 6 |
图7 有潜堤地形下不同有效波高(HS )、堤顶水深(d)、间断宽度(w)、谱峰周期(TP )下HIG 与HSS 的沿礁分布Fig.7 Distribution of infragravity wave height(HIG ), short-wave wave height(HSS ) along the reef under different effective wave heights(HS ), reef water depths(d), discontinuous widths(w), and spectral peak periods(TP ) with submerged breakwater topography |
| 次重力波波高(HIG ) | 短波波高(HSS ) | |
| 有 效 波 高(HS ) |  | |
| 堤 顶 水 深 (d) | ||
| 间 断 宽 度 (w) | ||
| 谱 峰 周 期(TP ) | ||
|
Brander R W, Kench P S, and Hart D. 2004. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Wave Characteristics across a Reef Platform, Warraber Island, Torres Strait, Australia. Marine Geology, 207(1/4): 169-184.
|
|
Buckley M L, Lowe R J, Hansen J E, Dongeren A R, and Storlazzi C D. 2018. Mechanisms of Wave‐Driven Water Level Variability on Reef‐Fringed Coastlines. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 123(5): 3811-3831.
|
|
蔡锋. 2015. 中国海滩养护技术手册. 北京:海洋出版社. [Cai Feng. 2015. China Beach Nourishment Manual. Beijing: China Ocean Press. ]
|
|
Cheriton O M, Storlazzi C D, and Rosenberger K J. 2016. Observations of Wave Transformation over a Fringing Coral Reef and the Importance of Low‐Frequency Waves and Offshore Water Levels to Runup, Overwash, and Coastal Flooding. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 121(5): 3121-3140.
|
|
陈杰,蒋昌波,曹永港,郭杰. 2008. 斜坡上潜堤透射系数实验研究. 中国科技论文在线,(7):517-523.
Chen Jie, Jiang Changbo, Cao Yonggang, and Guo Jie. 2008. Experimental Study of Transmission Coefficient of Waves over Submerged Breakwater on a Sloping Bed. China Science and Technology Journal Online, (7): 517-523.
|
|
Cho Y S, Lee J I, and Kim Y T. 2004. Experimental Study of Strong Reflection of Regular Water Waves over Submerged Breakwaters in tandem. Ocean Engineering, 31(10): 1325-1335.
|
|
Chyon M S A, Rahman A, and Rahman M A. 2017. Comparative Study on Hydrodynamic Performance of Porous and Non-Porous Submerged Breakwater. Procedia Engineering, 194: 203-210.
|
|
Dattatri J, Raman H, and Shankar N J. 1978. Performance Characteristics of Submerged Breakwaters. Coastal Engineering.
|
|
Dean R G, Campbell T J. Beach Nourishment. Springer Handbook of Ocean Engineering, 2016: 635-652.
|
|
Ferrario F, Beck M W, Storlazzi C D,Micheli F, Shepard C C, and Airoldi L. 2014. The Effectiveness of Coral Reefs for Coastal Hazard Risk Reduction and Adaptation. Nature Communications, 5(1): 1-9.
|
|
虢磊,屈科,黄竞萱. 2024. 多向聚焦波作用下透水潜堤消波特性数值模拟研究. 海洋通报,43(4):483-496.
Guo Lei, Qu Ke, and Huang Jingxuan. 2024. Numerical Study on Performance of Submerged Permeable Breakwater under Impacts of Multi-Directional Focused Wave Groups. Marine Science Bulletin, 43(4): 483-496.
|
|
Hardy T A and Young I R. 1996. Field Study of Wave Attenuation on an Offshore Coral Reef. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 101(C6): 14311-14326.
|
|
Hou X, Shen P, and Wang W. 2010. Method of Ocean Wave Synthesis Based on Directional Spectrum. Journal of System Simulation, 22(1): 130-134.
|
|
黄哲,掌孝永,孙加月,琚烈红,王登婷. 2024. 潜堤、挡板式透空堤组合结构合理性及消浪特性研究. 水运工程,(11):20-27,85.
Huang Zhe, Zhang Xiaoyong, Sun Jiayu, Ju liehong, and Wang Dengting. 2024. Rationality and Wave Dissipation Characteristics of Combination Structure of Submerged Breakwater and Baffle-Type Permeable Breakwater. Port & Waterway Engineering, (11): 20-27, 85.
|
|
蒋昌波,陈杰,肖政,郭杰. 2008. 斜坡床面潜堤作用下的波浪传播变形. 长沙理工大学学报(自然科学版),(3):47-51,57.
Jiang Changbo, Chen Jie, Xiao Zheng, and Guo Jie. 2008. Wave Propagation over Submerged Breakwater on a Sloping Bed. Journal of Changsha University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), (3): 47-51, 57.
|
|
Kundu P K, Cohen I M, and Dowling D R. 2012. Fluid Mechanics. Waltham, MA : Academic Press.
|
|
李鹏. 2005. 波浪在潜堤上传播和破碎. 南京:南京水利科学研究院.
Li Peng. 2005. Propagation and Breaking of Waves over Submerged Breakwaters. Nanjing:Nanjing Institute of Water Resources Science.
|
|
李玮,屈科,王超,喻仞石,张泽. 2025. 潜堤对岛礁次重力波波浪特性影响的试验研究. 热带海洋学报,1-9. DOI: 10.11978/2024199.
Li Wei, Qu Ke, Wang Chao, Yu Renshi, and Zhang Ze. 2025. Experimental Study on the Influence of Submerged Breakwater on the Wave Characteristics of Infragravity Waves on Islands and Reefs. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 1-9. DOI: 10.11978/2024199.
|
|
Lugo-Fernández A, Roberts H H, and Suhayda J N. 1998. Wave Transformations across a Caribbean Fringing-Barrier Coral Reef. Continental Shelf Research, 18(10): 1099-1124.
|
|
Metallinos A S, Klonaris G T, Memos C D, and Dimas A A. 2019. Hydrodynamic Conditions in a Submerged Porous Breakwater. Ocean Engineering, 172: 712-725.
|
|
Merrifield M A, Becker J M, Ford M, and Yao Y. 2014. Observations and Estimates of Wave‐Driven Water Level Extremes at the Marshall Islands. Geophysical Research Letters, 41(20): 7245-7253.
|
|
Nakamura M, Shiraishi H, and Sasaki Y. 1966. Wave Damping Effect of Submerged Dike. Coastal Engineering, 10: 254-267.
|
|
Pomeroy A, Lowe R, Symonds G, Dongeren A P, and Moores C. 2012. The Dynamics of Infragravity Wave Transformation over a Fringing Reef. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117: C11022.
|
|
Ranasinghe R S and Sato S. 2007. Beach Morphology behind Single Impermeable Submerged Breakwater under Obliquely Incident Waves. Coastal Engineering, 49(1): 1-24.
|
|
Salauddin M and Pearson J M. 2019. Wave Overtopping and Toe Scouring at a Plain Vertical Seawall with Shingle Foreshore: A Physical Model Study. Ocean Engineering, 171: 286-299.
|
|
Storlazzi C D, Logan J B, and Field M E. 2003. Quantitative Morphology of a Fringing Reef Tract from High-Resolution Laser Bathymetry: Southern Molokai, Hawaii. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 115(11): 1344-1355.
|
|
Storlazzi C D, Ogston A S, Bothner M H, Field M E, and Presto M K. 2004. Wave-and Tidally-Driven Flow and Sediment Flux across a Fringing Coral Reef: Southern Molokai, Hawaii. Continental Shelf Research, 24(12): 1397-1419.
|
|
Storlazzi C D, Elias E, Field M E, and Presto M K. 2011. Numerical Modeling of the Impact of Sea-Level Rise on Fringing Coral Reef Hydrodynamics and Sediment Transport. Coral Reefs, 30(Suppl. 1): 83-96.
|
|
Ting C L, Lin M C, and Cheng C Y. 2004. Porosity Effects on Non-Breaking Surface Waves over Permeable Submerged Breakwaters. Coastal Engineering, 50(4): 213-224.
|
|
王旭,屈科,门佳. 2023. 透水珊瑚岸礁亚重力波水动力特性数值研究. 海洋学报,45(9):152-167.
Wang Xu, Qu Ke, and Men Jia. 2023. Numerical Study on Infragravity Wave Hydrodynamics of Permeable Fringing Reef. Haiyang Xuebao, 45(9): 152-167.
|
|
谢天,李雪艳,彭晶,曲红红,解晓敏. 2024. 双平板与双弧板式透空堤消浪性能比较研究. 海洋湖沼通报,46(1):12-20.
Xie Tian, Li Xueyan, Peng Jing, Qu Honghong, and Xie Xiaomin. 2024. A Comparative Study on Wave Attenuation Performance of Double-Flat-Plate and Double-Arc-Plate Breakwaters. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 46(1): 12-20.
|
|
Willmott C J. 1981. On the Validation of Models. Physical Geography, 2(2): 184-194.
|
|
Yao Y, Jia M, Jiang C, Zhang Q, and Tang Z. 2020a. Laboratory Study of Wave Processes over Fringing Reefs with a Reef-Flat Excavation Pit. Coastal Engineering, 158: 103700.
|
|
Yao Y, Liu Y, Chen L, Deng Z, and Jiang C. 2020b. Study on the Wave-Driven Current around the Surf zone over Fringing Reefs. Ocean Engineering, 198: 106968.
|
|
于珍. 2023. 潜堤-双弧板组合结构水动力特性数值研究. 山东:鲁东大学.
Yu Zhen. 2023. Numerical Study on Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Submerged Breakwater-Double-arc Plate Composite Structure. Shandong: Ludong University.
|
|
“中国工程科技2035发展战略研究”海洋领域课题组. 2017. 中国海洋工程科技2035发展战略研究. 中国工程科学,19(1):108-117.
Task Force for the Research on China's Engineering Science and Technology Development Strategy 2035 Marine Research Group. 2017. Development Strategy for China's Marine Engineering Science and Technology to 2035. China Engineering Science, 19(1): 108-117.
|
|
Zhang Zhiyong, Shi Bing, Guo Yakun, and Yang Lipeng. 2013. Numerical Investigation on Critical Length of Impermeable Plate Below Underwater Pipeline under Steady Current. Science China Technological Sciences, 56: 1232-1240.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |