

改革开放40年深圳海岸线变化的遥感监测
|
卫诗韵(1998—),女,广东东莞人,硕士研究生,主要从事海洋遥感与GIS技术研究,(E-mail)v162802sy@163.com; |
收稿日期: 2021-11-22
修回日期: 2022-02-16
网络出版日期: 2023-06-13
基金资助
广东省教育厅创新强校工程项目(2019KZDXM019)
南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(湛江)资助项目(ZJW-2019-08)
广东海洋大学高水平海洋学科团队项目(0002026002009)
Remote Sensing Monitoring of Shenzhen Coastline Changes over the Past 40 Years
Received date: 2021-11-22
Revised date: 2022-02-16
Online published: 2023-06-13
探讨改革开放近40年来深圳海岸线的变化有利于揭示其时空演变过程及驱动机制,可为岸线资源的保护和利用提供参考。文章筛选1979—2019年16景深圳区域Landsat遥感影像,基于遥感(RS)与地理信息系统(GIS)方法进行岸线提取,在保证配准精度以及提取精度达到研究要求的基础上,对深圳岸线演变时空特征、速率及驱动因素进行探讨。结果表明:1)40年间深圳海岸线长度呈现持续增加趋势,总长度增加41.52 km,平均每年增加1.04 km。其中,自然岸线总降幅达56.61%,人工岸线所占比例持续上升。2)海岸线类型主要由早期的粉砂淤泥质和砂质岸线向围垦养殖和工程建设岸线转变。3)海岸线变化经历了起始、加速和合理约束3个阶段,岸线扩张显著的地区分布在宝安国际机场、前海合作区、后海深圳湾、盐田区和龙岐湾近岸。西岸的岸线最高端点变化速率(EPR)达到422.19 m/a,出现在2004—2008年蛇口半岛的向海扩建时期;东岸的EPR最高达到449.65 m/a,出现在1994—1998年的盐田港开发建设期间。4)人类活动、特区政策和自然因素是深圳岸线变化的主要驱动因素。
卫诗韵 , 付东洋 , 刘大召 , 徐华兵 , 李高聪 , 程阳艳 . 改革开放40年深圳海岸线变化的遥感监测[J]. 热带地理, 2023 , 43(5) : 986 -1004 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003589
Since the reform and opening-up, the ecological environment of the coastline of Shenzhen has been under pressure from high-intensity human exploitation activities. Additionally, the structure, type, and length of the coastline has undergone significant changes. Studying the changes of the Shenzhen coastline over the past 40 years is helpful to reveal its spatial and temporal evolutionary processes and driving mechanisms to provide a reference for the protection and utilization of coastline resources. This study screened 16 scenes of the Shenzhen regional Landsat remote sensing images from 1979 to 2019, and performed a coastline extraction using Remote Sensing (RS) and Geographic Information System (GIS) methods to ensure alignment, accuracy, and extraction precision to meet the research requirements. Based on four coastline evaluation indexes (End Point Rates, Linear Regression Rates, Coastline-type Diversity Index, and Comprehensive Index of Coastline Utilization), the spatiotemporal characteristics of the coastline length, structure, types, and rate of change were analyzed to explore the factors driving the spatio-temporal evolution of the Shenzhen coastline. The results found that over the past 40 years, (1) the length of the Shenzhen coastline has experienced a continuously increasing trend, with a total increase of 41.52 km, and an average annual growth of 1.04 km. All the natural coastlines within the coastal area of Shenzhen decreased significantly to varying degrees, with a total decrease of 56.61%, while the proportion of artificial coastlines increased rapidly. (2) The change in coastline type in Shenzhen is mainly from the early muddy and sandy coastline to the farming reclamation and engineering construction coastline, i.e., the transition from natural to artificial shore. Among them, coastline length increased the most from 1979 to 1988. The most drastic coastline change was observed from 1979 to 1994, and the peak period of land reclamation was from 1994 to 2008. After 2008, Shenzhen coastline development gradually entered a sustainable and rational stage. (3) The spatial vicissitudes of the Shenzhen coastline have progressed through the stages of initiation, acceleration, and rational restriction. Areas with significant coastline expansion were located in Bao'an International Airport, Qianhai Cooperation Zone, Shenzhen Bay of Houhai, Yantian District, and near Longqi Bay. The change in the west coast of Shenzhen is more drastic than that of the east coast. The maximum rate of change (EPR) on the west coast reaches 422.19 m/a, which occurred during the Shekou Peninsula seaward extension period from 2004 to 2008. The EPR on the east coast reached the highest level of 449.65 m/a during the development and construction of Yantian Port from 1994 to 1998; and (4) the Shenzhen coastline change is a dynamic and a continuous process of change. Human activities, special zone policies, and natural factors were the main driving forces of the coastline changes. The special zone policy is the core driving force for Shenzhen's population expansion, urban sprawl, and the fundamental reason for the reduction in natural coastlines and the growth of artificial coastlines. This study provides important guidance for future sustainable urban development in Shenzhen.
表1 研究区遥感影像数据参数信息Table 1 Parameters of the remote sensing image data for the study area |
| 序号 | 卫星 | 传感器 类型 | 轨道号 | 成像时间 | 空间 分辨率/m | 云量/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Landsat3 | MSS | 130/44 | 1979-10-18 | 79 | 0.00 |
| 2 | Landsat3 | MSS | 131/44 | 1979-10-19 | 79 | 0.00 |
| 3 | Landsat5 | TM | 121/44 | 1988-12-19 | 30 | 0.02 |
| 4 | Landsat5 | TM | 122/44 | 1988-11-24 | 30 | 7.49 |
| 5 | Landsat5 | TM | 121/44 | 1994-10-01 | 30 | 0.04 |
| 6 | Landsat5 | TM | 122/44 | 1994-10-24 | 30 | 0.20 |
| 7 | Landsat5 | TM | 121/44 | 1998-09-26 | 30 | 3.10 |
| 8 | Landsat5 | TM | 122/44 | 1998-11-04 | 30 | 0.48 |
| 9 | Landsat5 | TM | 121/44 | 2004-10-12 | 30 | 0.03 |
| 10 | Landsat5 | TM | 122/44 | 2004-10-19 | 30 | 0.12 |
| 11 | Landsat5 | TM | 121/44 | 2008-12-10 | 30 | 0.12 |
| 12 | Landsat5 | TM | 122/44 | 2008-12-01 | 30 | 0.28 |
| 13 | Landsat8 | OLI | 121/44 | 2013-10-05 | 15 | 0.01 |
| 14 | Landsat8 | OLI | 122/44 | 2013-12-31 | 15 | 0.14 |
| 15 | Landsat8 | OLI | 121/44 | 2019-11-23 | 15 | 4.00 |
| 16 | Landsat8 | OLI | 122/44 | 2019-11-14 | 15 | 0.23 |
表2 深圳海岸线解译标志及确定原则Table 2 Interpretation mark and determination principle of Shenzhen coastline |
| 岸线类型 | 利用方式 | 确定原则 | 解译标志 | 岸线类型 | 利用方式 | 确定原则 | 解译标志 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然 岸线 | 基岩 岸线 | 经过长期海水侵蚀和波浪冲刷所形成,多在岬湾相间地带,由坚硬岩石组成,岸线弯曲复杂,水边线不平整 |  | 自然 岸线 | 自然 过渡 河口 岸线 | 河口区域由海向陆若无桥梁等人工建筑物,则以河口突然展宽处的河流两岸连线为岸线位置所在 |  |
| 砂质 岸线 | 影像中一般呈现亮白色的长条带状,常常堆积成一条与岸平行的脊状砂质沉积 |  | 人工 岸线 | 围垦 养殖 岸线 | 一般呈现规则的方形片状分布在淤泥质岸线附近 | 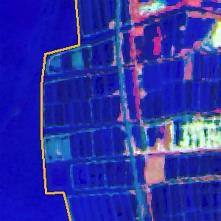 | |
| 生物 岸线 | 分布在河口附近的潮滩或者海岸沼泽区,其空间分布具有向海延伸的特征。影像中表现为红色,比陆地植被要暗,纹理平滑 |  | 工程 建设 岸线 | 主要为人工建筑所形成的 岸线,在影像上具有明显的几何特征,棱角分明 |  | ||
| 粉砂 淤泥质 岸线 | 主要分布在一些隐蔽的港湾和平原的外端,影像表现为海底处颜色偏暗 |  | 人工 分界 河口 岸线 | 通常以河口区域由海向陆 所遇到的第一人工建筑(道路、桥梁或者闸门)确定 |  |
表3 深圳区域不同岸线类型的人力作用强度指数Table 3 Intensity index of human action of different shoreline types in Shenzhen |
| 岸线类型 | 利用方式 | 人力作用强度指数 |
|---|---|---|
| 自然岸线 | 基岩岸线 | 1 |
| 砂质岸线 | 1 | |
| 生物岸线 | 1 | |
| 粉砂淤泥质岸线 | 1 | |
| 自然过渡河口岸线 | 1 | |
| 人工岸线 | 围垦养殖岸线 | 2 |
| 工程建设岸线 | 3 | |
| 人工分界河口岸线 | 2 |
图3 1979—2019年深圳市海岸线空间变化Fig.3 Spatial change of Shenzhen coastline from 1979 to 2019 |
图4 深圳市不同类型海岸线的空间分布Fig.4 Spatial distribution of different coastline types in Shenzhen |
表4 近40年来深圳不同海岸类型的岸线长度 (km)Table 4 Coastline length of different coastal types in Shenzhen in recent 40 years |
| 岸线类型 | 利用方式 | 1979年 | 1988年 | 1994年 | 1998年 | 2004年 | 2008年 | 2013年 | 2019年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 自然海岸线 | 基岩岸线 | 106.49 | 86.88 | 82.24 | 81.93 | 74.68 | 74.46 | 67.90 | 61.50 |
| 砂质岸线 | 39.65 | 33.00 | 27.16 | 22.19 | 25.49 | 23.00 | 22.20 | 22.83 | |
| 粉砂淤泥质岸线 | 51.84 | 21.54 | 17.39 | 12.57 | 8.71 | 6.51 | 5.98 | 4.73 | |
| 生物岸线 | 8.02 | 5.43 | 7.10 | 5.16 | 5.95 | 6.99 | 8.61 | 9.66 | |
| 自然过渡河口岸线 | 0.52 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.17 | |
| 总计 | 206.52 | 147.05 | 134.08 | 122.03 | 115.03 | 111.16 | 104.85 | 98.89 | |
| 人工海岸线 | 围垦养殖岸线 | 0.00 | 41.62 | 43.97 | 28.56 | 35.81 | 17.77 | 16.65 | 15.24 |
| 工程建设岸线 | 11.54 | 41.06 | 63.43 | 92.41 | 94.74 | 123.07 | 136.23 | 144.35 | |
| 人工分界河口岸线 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.47 | 0.60 | 1.10 | |
| 总计 | 11.54 | 83.18 | 107.76 | 121.27 | 130.62 | 141.31 | 153.48 | 160.69 | |
| 总计 | 218.06 | 230.23 | 241.84 | 243.30 | 245.65 | 252.47 | 258.33 | 259.58 | |
图7 东宝河河口—大铲湾岸线变迁速率(a. 线性回归速率LRR空间分布;b. LRR分布统计;c. EPR分布统计)Fig.7 The coastline change rate of Dongbao River estuary-Dachan Bay [a. spatial distribution of Linear Regression Rates (LRR); b. Linear Regression Rates (LRR) distribution statistics; c. End Point Rates (EPR) distribution statistics] |
图8 大铲湾—深圳河河口岸线变迁速率(a. 线性回归速率LRR空间分布;b. LRR分布统计;c. EPR分布统计)Fig.8 The coastline change rate of Dachan Bay-Shenzhen River port line [a. Spatial distribution of Linear Regression Rates (LRR); b. Linear Regression Rates (LRR) distribution statistics; c. End Point Rates (EPR) distribution statistics] |
图9 沙头角—大鹏湾东岸岸线变迁速率(a. 线性回归速率LRR空间分布;b. LRR分布统计;c. EPR分布统计)Fig.9 Change rate of the eastern shoreline of Sha Tau Kok - Dapeng Bay [a. Spatial distribution of Linear Regression Rates (LRR); b. Linear Regression Rates (LRR) distribution statistics; c. End Point Rates (EPR) distribution statistics] |
图10 大鹏湾东岸—大亚湾西岸岸线变迁速率(a. 线性回归速率LRR空间分布;b. LRR分布统计;c. EPR分布统计)Fig.10 The coastline change rate of the eastern coast of Dapeng Bay and the western coast of Daya Bay [a. spatial distribution of Linear Regression Rates (LRR); b. Linear Regression Rates (LRR) distribution statistics; c. End Point Rates (EPR) distribution statistics] |
表5 人为扩张热点地区主要扩张过程Table 5 The expansion process of key artificial sites |
| 时间 | 宝安国际机场 | 前海合作区 | 后海深圳湾 | 盐田区近岸 | 龙岐湾近岸 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1979年 |  |  |  |  |  |
| 1988年 |  |  |  |  |  |
| 1994年 |  |  |  |  |  |
| 1998年 | 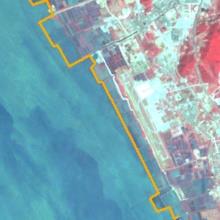 | 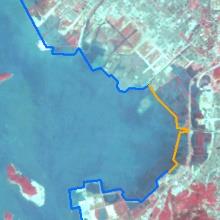 |  |  | 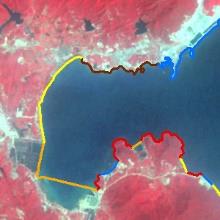 |
| 2004年 | 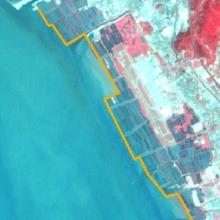 | 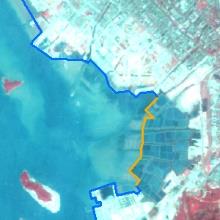 |  | 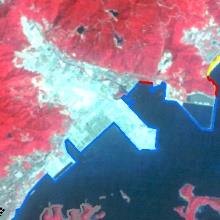 | 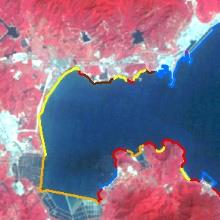 |
| 2008年 |  |  |  |  |  |
| 2013年 |  |  |  | 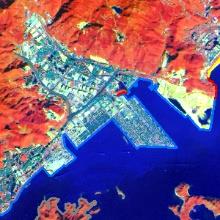 | 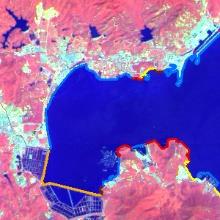 |
| 2019年 |  |  |  |  |  |
表6 人为扩张热点地区主要发展历程Table 6 The main development history of hot spots of artificial expansion |
| 地点 | 时间段 | 事件 |
|---|---|---|
| 宝安国际机场 | 1991年 | 建设完成,正式通航 |
| 1994—1998年 | 续建货运站,航站楼扩建 | |
| 2004—2008年 | B号候机楼扩建,飞行区扩建,机场南停机坪扩建 | |
| 2008—2013年 | T3航站楼扩建 | |
| 2013—2019年 | 航站区与跑滑系统扩建,三跑道扩建 | |
| 前海合作区 | 2010年 | 合作区建成 |
| 2013年 | 产业准入 | |
| 2013—2019年 | 前海合作区和前海蛇口自贸片区“双扩区” | |
| 后海深圳湾 | 1980—1988年 | 集中在蛇口半岛南部的填海开发 |
| 1995—2000年 | 扩建南山商业文化中心区、滨海大道、赤湾码头、蛇口码头 | |
| 2001—2005年 | 后海中心区初步形成 | |
| 2013—2019年 | CBD超级基地形成 | |
| 盐田区近岸 | 1989年 | 盐田港建设完成 |
| 1999年 | 大梅沙海滨公园竣工 | |
| 2013—2019年 | 万科天琴湾建成 | |
| 龙岐湾近岸 | 2013—2019年 | 龙岐湾1号建成、桔钓沙旅游片区、较场尾沿岸民宿小镇兴起 海滨路—滨海养殖区绿岛规划建设 |

卫诗韵:数据收集处理,制图分析并撰写初稿;
付东洋:框架确定,全程指导并修改;
刘大召、徐华兵、李高聪:参与文章指导;
程阳艳:协助初期数据收集。
|
Aedla R, Dwarakish G S, and Reddy D V. 2015. Automatic Shoreline Detection and Change Detection Analysis of Netravati-Gurpurrivermouth Using Histogram Equalization and Adaptive Thresholding Techniques. Aquatic Procedia, 4: 563-570.
|
|
Ai B, Zhang R, Zhang H, Ma C, and Gu F. 2019. Dynamic Process and Artificial Mechanism of Coastline Change in the Pearl River Estuary. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 30: 100715.
|
|
Bamunawala J, Ranasinghe R, Van Der Spek A, Maskey S, and Udo K. 2018. Assessing Future Coastline Change in the Vicinity of Tidal Inlets via Reduced Complexity Modelling. Journal of Coastal Research, 85: 636-640.
|
|
毕京鹏. 2019. 海岸线时空变迁遥感监测与分析——以泰国和马六甲海峡为例. 青岛:山东科技大学.
Bi Jingpeng. 2019. Remote Sensing Monitoring and Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Changes of Coastlines: A Case Study of Thailand and Malacca Strait. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology.
|
|
Boak E H, and Turner I L. 2005. Shoreline Definition and Detection: A Review. Journal of Coastal Research, 21(214): 688-703.
|
|
卜心国,王仰麟,吴健生. 2008. 深圳快速城市化中地形对景观垂直格局的影响. 地理学报,63(1):75-82.
Bu Xinguo, Wang Yanglin, and Wu Jiansheng. 2008. The Effect of Topography on Landscape Vertical Pattern in Rapid Urbanization of Shenzhen. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 63(1): 75-82.
|
|
陈金月. 2017. 基于GIS和RS的近40年珠江三角洲海岸线变迁及驱动因素研究. 成都:四川师范大学.
Chen Jinyue. 2017. Study on Shoreline Changes and Driving Factors of Pearl River Delta in Recent 40 Years Based on GIS and RS. Chengdu: Sichuan Normal University.
|
|
陈俊侠. 2003. 岸线规划的一个案例——深圳西海岸线的现状与未来. 中外房地产导报,(9):28-29.
Chen Junxia. 2003. A Case of Shoreline Planning: The Present Situation and Future of Shenzhen West Shoreline. Real Estate Guide at Home and Abroad, (9): 28-29.
|
|
Chen S S, Chen L F, Liu Q H, Li X, and Tan Q Y. 2005. Remote Sensing and Gis-Based Integrated Analysis of Coastal Changes and Their Environmental Impacts in Lingding Bay, Pearl River Estuary, South China. Ocean & Coastal Management, 48(1): 65-83.
|
|
丁小松. 2019. 渤海海岸线和沿岸栖息地破碎化的时空变化研究. 上海:上海海洋大学.
Ding Xiaosong. 2019. Temporal and Spatial Changes of Coastline and Coastal Habitat Fragmentation in Bohai Sea. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University.
|
|
Dolan R, Fenster M S, and Holme S J. 1991. Temporal Analysis of Shoreline Recession and Accretion. Journal of Coastal Research, 7: 723-744.
|
|
Fan Q D, Liang L K, Liang F, and Sun X F. 2020. Research Progress on Coastline Change in China. Journal of Coastal Research, 99: 289-295.
|
|
高梅,曾辉. 2012. 深圳市1986―2020年间海岸线动态变化特征及成因分析. 热带地理,32(3):274-279.
Gao Mei, and Zeng Hui. 2012. Characteristics and Causes of Coastal Dynamic Change in Shenzhen from 1986 to 2020. Tropical Geography, 32(3): 274-279.
|
|
古希婷. 2016. 深圳市大鹏新区第三产业集群升级中的政府责任分析. 武汉:华中师范大学.
Gu Xiting. 2016. Analysis of Government Responsibility in the Upgrading of Tertiary Industry Cluster in Dapeng New District, Shenzhen. Wuhan: Central China Normal University.
|
|
郭伟,李书恒,朱大奎. 2007. 深圳东部海岸地貌环境与可持续发展. 地理学报,62(4):377-386.
Guo Wei, Li Shuheng, and Zhu Dakui. 2007. Geomorphological Environment and Szustainable Development of the Eastern Coast of Shenzhen. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 62(4): 377-386.
|
|
国家发展改革委和国家海洋局. 2017. 全国海洋经济发展“十三五”规划 (发改地区 [2017] 861号). (2017-05-10)[2021-10-08]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fzggw/jgsj/dqs/sjdt/201705/P020190909487471217145.pdf.
National Development and Reform Commission and State Oceanic Administration. 2017. The 13th Five-Year Plan for Global Marine Economy Development (Development and Reform Region [2017] No. 861). (2017-05-10) [2021-10-08]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fzggw/jgsj/dqs/sjdt/201705/P020190909487471217145.pdf.
|
|
国家海洋局. 2008. 关于改进围填海造地工程平面设计的若干意见 (国海管字〔2008〕37号). (2008-08-14)[2021-10-09]. http://gc.mnr.gov.cn/201806/t20180615_1796672.html.
State Oceanic Administration. 2008. The Land Reclamation Works on Improving Reclamation of Graphic Design Several Opinions (Sealand Tube Word [2008] No. 37). (2008-08-14) [2021-10-09]. http://gc.mnr.gov.cn/201806/t20180615_1796672.html.
|
|
国务院. 1981. 国务院批转国家水产总局关于当前水产工作若干问题的请示报告的通知. (1981-05-04)[2021-10-07]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2016-10/18/content_5120779.htm.
State Council. 1981. Notice of The State Council Approving and Transferring to the State Fisheries Administration the Request Report on Some Problems in the Current Work of Aquatic Products. (1981-05-04) [2021-10-07]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2016-10/18/content_5120779.htm.
|
|
国务院. 1988. 国务院关于深圳市在国家计划中实行单列的批复 (国函〔1988〕121号). (1988-10-03)[2021-10-08]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2011-11/15/content_5083.htm.
State Council. 1988. Reply of The State Council Concerning the Implementation of Separate Listing in the State Plan of Shenzhen (State Letter [1988] No. 121). (1988-10-03) [2021-10-08]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2011-11/15/content_5083.htm.
|
|
国务院. 2019. 中共中央国务院关于支持深圳建设中国特色社会主义先行示范区的意见. (2019-08-09)[2021-10-07]. http://www.mofcom.gov.cn/article/b/g/201909/20190902900710.shtml.
State Council. 2019. Opinions of the CPC Central Committee and The State Council on Supporting Shenzhen in Building a Pilot Demonstration Zone of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics. (2019-08-09) [2021-10-07]. http://www.mofcom.gov.cn/article/b/g/201909/20190902900710.shtml.
|
|
国家海洋局908专项办公室. 2005a. 908全国海岸线调查技术规程. 北京:海洋出版社.
Special Office of the State Oceanic Administration. 2005a. 908 Technical Regulations for National Coastline Survey. Beijing: China Ocean Press.
|
|
国家海洋局908专项办公室. 2005b. 我国近海海洋综合调查与评价专项海岸带调查技术规程. 北京:海洋出版社.
State Oceanic Administration 908 Special Office. 2005b. Technical Regulation of Coastal Zone Investigation for Marine Comprehensive Survey and Evaluation. Beijing: China Ocean Press.
|
|
侯西勇,徐新良. 2011. 21世纪初中国海岸带土地利用空间格局特征. 地理研究,30(8):1370-1379.
Hou Xiyong, and Xu Xinliang. 2011. Spatial Pattern of Land Use in Coastal Zone of China in the Early 21st Century, China. Geographical Research, 30(8): 1370-1379.
|
|
Huang F, Xu Y, Tan Z, Wu Z, Xu H, Shen L, Xu X, Han Q, Guo H, and Hu Z. 2018. Assessment of Pollutions and Identification of Sources of Heavy Metals in Sediments from West Coast of Shenzhen, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25: 3647-3656.
|
|
贾明明,刘殿伟,王宗明,汤旭光,董张玉. 2013. 面向对象方法和多源遥感数据的杭州湾海岸线提取分析. 地球信息科学学报,15(2):262-269.
Jia Mingming, Liu Dianwei, Wang Zongming, Tang Xuguang, and Dong Zhangyu. 2013. Coastline Extraction and Analysis of Hangzhou Bay Using Object-Oriented Method and Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 15(2): 262-269.
|
|
Kermani S, Boutiba M, Guendouz M, Guettouche M S, and Khelfani D. 2016. Detection and Analysis of Shoreline Changes Using Geospatial Tools and Automatic Computation: Case of Jijelian Sandy Coast (East Algeria). Ocean & Coastal Management, 132: 46-58.
|
|
李清泉,卢艺,胡水波,胡忠文,李洪忠,刘鹏,石铁柱,汪驰升,王俊杰,邬国锋. 2016. 海岸带地理环境遥感监测综述. 遥感学报,20(5):1216-1229.
Li Qingquan, Lu Yi, Hu Shuibo, Hu Zhongwen, Li Hongzhong, Liu Peng, Shi Tiezhu, Wang Chisheng, Wang Junjie, and Wu Guofeng. 2016. Overview of Remote Sensing Monitoring of Coastal Geographical Environment. Journal of Remote Sensing, 20(5): 1216-1229.
|
|
Li X, and Damen M C J. 2010. Coastline Change Detection with Satellite Remote Sensing for Environmental Management of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Journal of Marine Systems, 82: S54-S61.
|
|
李孝娟,傅文辰,繆迪优,苏广明. 2019. 陆海统筹指导下的深圳海岸带规划探索. 规划师,35(7):18-24.
Li Xiaojuan, Fu Wenchen, Miao Diyou, and Su Guangming. 2019. Coastal Zone Planning and Exploration in Shenzhen Under the Guidance of Land-Sea Coordination. Planners, 35(7): 18-24.
|
|
李薛,付东洋,张莹,刘大召,丁又专,王文芳,栾虹,蒋城飞. 2016. 超强台风“威马逊”对南海西北海域海洋环境的影响. 热带海洋学报,35(6):19-28.
Li Xue, Fu Dongyang, Zhang Ying, Liu Dazhao, Ding Youzhuan, Wang Wenfang, Luan Hong, and Jiang Chengfei. 2016. Effects of Super Typhoon Rammasun on Marine Environment in Northwestern South China Sea. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 35(6): 19-28.
|
|
李猷,王仰麟,彭建,吴健生,吕晓芳. 2009. 深圳市1978年至2005年海岸线的动态演变分析. 资源科学,31(5):875-883.
Li You, Wang Yanglin, Peng Jian, Wu Jianshen, and Lyu Xiaofang. 2009. Dynamic Evolution of Shenzhen Coastline from 1978 to 2005. Resources Science, 31(5): 875-883.
|
|
林逸涛. 2018. 深圳市生态系统补偿体制机制研究. 武汉:武汉大学.
Lin Yitao. 2018. Study on Ecosystem Compensation System and Mechanism in Shenzhen City. Wuhan: Wuhan University.
|
|
Liu C, Wu X, Cao X, and Wu G. 2017. Analysis of Coastline Changes and the Socio-Economic Driving Mechanisms in Shenzhen, China. Marine Geodesy, 40(6): 378-403.
|
|
刘鹏,王庆,战超,王昕,杜国云,李雪艳. 2015. 基于DSAS和FA的1959—2002年黄河三角洲海岸线演变规律及影响因素研究. 海洋与湖沼,46(3):585-594.
Liu Peng, Wang Qing, Zhan Chao, Wang Xin, Du Guoyun, and Li Xueyan. 2015. Study on Shoreline Evolution and Influencing Factors of Yellow River Delta from 1959 to 2002 Based on DSAS and FA. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 46(3): 585-594.
|
|
申家双,翟京生,郭海涛. 2009. 海岸线提取技术研究. 海洋测绘,29(6):74-77.
Shen Jiashuang, Zhai Jingsheng, and Guo Haitao. 2009. Study on Coastline Extraction Technology. Marine Surveying and Mapping, 29(6): 74-77.
|
|
深圳市规划和自然资源局. 2018. 深圳市海岸带综合保护与利用规划(2018—2035). (2018-09-07)[2021-10-07]. http://pnr.sz.gov.cn/ywzy/ghzs/content/post_5841608.html.
Shenzhen City Planning and Natural Resource Bureau. 2018. Shenzhen Comprehensive Protection and Utilization of Coastal Zone Planning (2018-2035). (2018-09-07) [2021-10-07]. http://pnr.sz.gov.cn/ywzy/ghzs/content/post_5841608.html.
|
|
深圳市人民政府. 2019. 深圳经济特区海域使用管理条例. (2019-12-31)[2021-10-28]. http://sf.sz.gov.cn/fggzsjcx/content/post_7260475.html.
Shenzhen City People's Government. 2019. Waters Using the Management Regulations of Shenzhen Special Economic Zone. (2019-12-31) [2021-10-28]. http://sf.sz.gov.cn/fggzsjcx/content/post_7260475.html.
|
|
深圳市政协人资环委课题组. 2020. 推进深圳全球海洋中心城市建设. 特区实践与理论,(2):70-78.
Research Group of Human Resources and Environment Committee of Shenzhen CPPCC. 2020. Promoting the Construction of Shenzhen as a Global Marine Center City. Special Zone Practice and Theory, (2): 70-78.
|
|
苏奋振. 2015. 海岸带遥感评估. 北京:科学出版社.
Su Fenzhen. 2015. Remote Sensing Evaluation of Coastal Zone. Beijing: Science Press.
|
|
Sui L, Wang J, Yang X, and Wang Z. 2020. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Coastline Changes in Indonesia from 1990 to 2018. Sustainability, 12: 3242.
|
|
孙伟富,马毅,张杰,刘善伟,任广波. 2011. 不同类型海岸线遥感解译标志建立和提取方法研究. 测绘通报,(3):41-44.
Sun Weifu, Ma Yi, Zhang Jie, Liu Shanwei, and Ren Guangbo. 2011. Research on the Establishment and Extraction Methods of Different Types of Coastline Remote Sensing Interpretation Markers. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (3): 41-44.
|
|
孙永光,李秀珍,何彦龙,贾悦,马志刚. 2010. 长江口不同区段围垦区土地利用/覆被变化的时空动态. 应用生态学报,21(2):434-441.
Sun Yongguang, Li Xiuzhen, He Yanlong, Jia Yue, and Ma Zhigang. 2010. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Land Use/Cover Change in Different Reclamation Areas of the Yangtze River Estuary. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 21(2): 434-441.
|
|
Thoai D T, Dang A N, and Oanh N T K. 2019. Analysis of Coastline Change in Relation to Meteorological Conditions and Human Activities in Ca mau cape, Viet Nam. Ocean & Coastal Management, 171: 56-65.
|
|
Valeyev A, Karatayev M, Abitbayeva A, Uxukbayeva S, Bektursynova A, and Sharapkhanova Z. 2019. Monitoring Coastline Dynamics of Alakol Lake in Kazakhstan Using Remote Sensing Data. Geosciences, 9: 404.
|
|
毋亭. 2016. 近70年中国大陆岸线变化的时空特征分析. 烟台:中国科学院烟台海岸带研究所.
Wu Ting. 2016. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Shoreline Changes in China during the Past 70 Years. Yantai: Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
|
|
Wu X, Liu C, and Wu G. 2017. Spatial-Temporal Analysis and Stability Investigation of Coastline Changes: A Case Study in Shenzhen, China. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 11(1): 45-56.
|
|
徐涵秋. 2005. 利用改进的归一化差异水体指数(MNDWI)提取水体信息的研究. 遥感学报,(5):589-595.
Xu Hanqiu. 2005. Study on Water Information Extraction Using Improved Normalized Difference Water Index (MNDWI). Journal of Remote Sensing, (5): 589-595.
|
|
Xu N, Gao Z, and Ning J. 2016. Analysis of the Characteristics and Causes of Coastline Variation in the Bohai Rim (1980–2010). Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(8): 719.
|
|
闫秋双. 2014. 1973年以来苏沪大陆海岸线变迁时空分析. 青岛:国家海洋局第一海洋研究所.
Yan Qiushuang. 2014. Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Shoreline Changes in Jiangsu and Shanghai Mainland Since 1973. Qingdao: First Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration.
|
|
杨桂山. 2001. 中国海岸环境变化及其区域响应. 南京:中国科学院研究生院(南京地理与湖泊研究所).
Yang Guishan. 2001. Coastal Environmental Change and Regional Response in China. Nanjing: Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology).
|
|
杨玉娣,边淑华. 2001. 海岸线及其划定方法探讨. 海洋开发与管理,(3):34-35
Yang Yudi, and Bian Shuhua. 2001. Discussion on Coastline and Its Demarcation Methods. Ocean Development and Management, (3): 34-35.
|
|
于海波,莫多闻,吴健生. 2009. 深圳填海造地动态变化及其驱动因素分析. 地理科学进展,28(4):584-590.
Yu Haibo, Mo Duowen, and Wu Jiansheng. 2009. Dynamic Change of Land Reclamation in Shenzhen and Its Driving Factors. Progress in Geography, 28(4): 584-590.
|
|
Zhang K, Douglas B C, and Leatherman S P. 2004. Global Warming and Coastal Erosion. Climatic change, 64(1): 41-58.
|
|
Zhang Y, and Hou X. 2020. Characteristics of Coastline Changes on Southeast Asia Islands from 2000 to 2015. Remote Sensing, 12: 519.
|
|
张怡. 2014. 近40年来珠江口海岸线变迁遥感分析. 呼和浩特:内蒙古师范大学.
Zhang Yi. 2014. Remote Sensing Analysis of Shoreline Changes of Pearl River Estuary in Recent 40 Years. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Normal University.
|
|
周凯,王壮雄. 2012. 强化深圳海岸和海域管理 科学利用海洋资源. 海洋开发与管理,29(3):35-37.
Zhou Kai, and Wang Zhuangxiong. 2012. Strengthening the Management and Scientific Utilization of Marine Resources in Shenzhen Coast and Sea Area. Ocean Development and Management, 29(3): 35-37.
|
|
庄大方,刘纪远. 1997. 中国土地利用程度的区域分异模型研究. 自然资源学报,(2):10-16.
Zhuang Dafang, and Liu Jiyuan. 1997. Study on Regional Differentiation Model of Land Use Degree in China. Journal of Natural Resources, (2): 10-16.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |