

俄乌冲突背景下“一带一路”沿线原油海运网络结构特征及变化分析
|
赵鹏军(1975—),男,陕西延安人,教授,博士,研究领域包括交通地理学、交通与空间规划等,(E-mail)pengjun.zhao@pku.edu.cn。 |
收稿日期: 2023-12-20
修回日期: 2024-02-25
网络出版日期: 2024-05-08
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(42130402)
深圳市科技计划资助项目(KQTD20221101093604016)
Structural Characteristics and Changes of Crude Oil Shipping Network along the Belt and Road in the Context of the Russia-Ukraine Conflict
Received date: 2023-12-20
Revised date: 2024-02-25
Online published: 2024-05-08
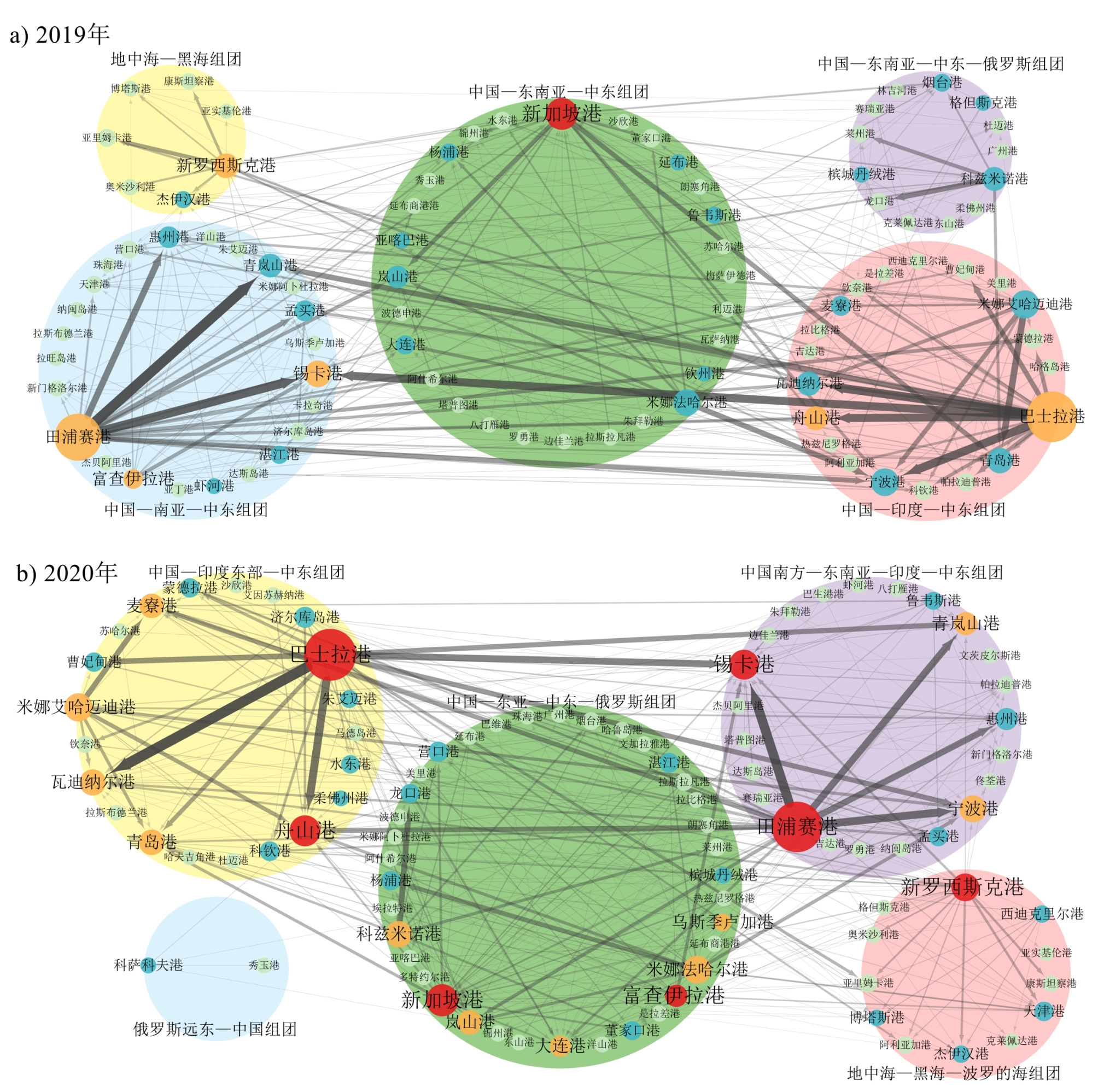
国际地缘政治对运输网络格局的影响是经济地理和交通地理的重要议题之一,探究俄乌冲突背景下“一带一路”沿线原油海运网络结构特征变化,可为该领域研究提供新的论据。文章采用AIS船舶轨迹大数据和复杂网络分析法,分析了2019—2022年“一带一路”沿线原油海运网络整体特征、节点重要性与核心边缘和组团耦合结构的变化特征,并探究了海运网络结构变化对中国原油进口稳定性的影响。结果表明:1)海运格局发生了结构性演变。港口间的联系密度、强度和网络通达性均呈现先增后减趋势;网络无标度特性不断增强,原油海运向部分主要联系集聚,出口端更加明显;俄乌冲突后中国与中东原油海运联系取代了部分中俄原油海运联系。2)海运港口重要性格局与核心边缘结构处于动态变化中。出口港综合重要性先略有降低,俄乌冲突后大幅增加;网络结构经历了单核―多核―单核的转变,俄乌冲突后国际原油市场供需格局改变,较大规模的出口港对原油海运网络中广大进口港和其他中小规模出口港的控制力明显加强。3)海运网络核心边缘与组团耦合结构前期变化稳定,后期变化突出。俄乌冲突后核心边缘与组团耦合结构在核心港、地理分布和组团规模方面发生明显变革。4)海运网络变化对中国原油进口稳定性的影响显著且具有异质性。中国原油进口网络的稳定性先增后减,俄乌冲突后的降幅远大于冲突发生前的增幅;相比环渤海湾和长三角港口,东南沿海、珠三角和西南沿海港口的原油进口稳定性受俄乌冲突影响更大。
赵鹏军 , 赵桐 , 张梦竹 , 肖婷 . 俄乌冲突背景下“一带一路”沿线原油海运网络结构特征及变化分析[J]. 热带地理, 2024 , 44(5) : 820 -837 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003867
The impact of international geopolitics on transportation network patterns is an important topic in economics and transportation geography. Previous studies have often overlooked the diversity of domestic crude oil transportation among countries due to limitations in statistical data, focusing mainly on national-level node selection. Additionally, the evolution of network characteristics is predominantly analyzed through long-term descriptive approaches, lacking specific contextual analyses of network evolution. This study investigates changes in the maritime crude oil transportation network along the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) routes against the backdrop of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, offering new evidence for research in this field. Using AIS(Automatic Identification System) ship trajectory big data and complex network analysis methods, this study analyzes the overall characteristics, node importance, core-periphery structure, and clustering of the maritime crude oil transportation network along the BRI routes from 2019 to 2022. Furthermore, it examines the impact of maritime network changes on the stability of crude oil imports to China. Our findings reveal several key points. 1) The closeness, strength, and accessibility of network connections between ports show an initial increase followed by a decreasing trend. The direction of the overall network characteristic changes in the periods 2019-2020 and 2020-2022 are opposite, with a greater magnitude in the latter period. In recent years, particularly following the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the scale-free nature of the network has continuously increased, accompanied by an increase in the concentration of crude oil shipping connections. This concentration, notably evident towards export destinations, reflects a shifting pattern in the crude oil supply demand landscape, spatially manifested as China replacing some of its crude oil shipping connections with the Middle East, thus reducing its reliance on Russian crude oil shipments. 2) The comprehensive importance of export ports has become more prominent, with a slight decrease followed by a significant increase in recent years. The importance of ports in Russia's Far East region has notably increased, reflecting a shift in Russia's crude oil export center eastward after the Russia-Ukraine conflict. The network structure transitioned from single-core to multi-core to single-core with export ports occupying more central layers. 3) Initially, there was a continuation of the core-periphery and clustering structures, but later, there was significant structural reorganization. In 2020, the core-periphery structure and clustering in terms of core ports, geographical distribution, and cluster size were largely the same as corresponding clusters in 2019; however, by 2022, a noticeable structural reorganization emerged. 4) Changes in maritime networks significantly and heterogeneously affect China's crude oil import stability. At the network level, import stability initially increases and then decreases, with the decline in the later period far exceeding that in the earlier period. At the port level, compared to ports around Bohai Bay and the Yangtze River Delta, ports along the southeastern coast, Pearl River Delta, and southwestern coast were more affected by the Russia-Ukraine conflict in terms of crude oil import stability. China responded to the risk of instability in its crude oil import network against the backdrop of the Russia-Ukraine conflict by adjusting its sources and proportions of imports from different ports. This study provides scientific evidence for a deeper understanding of the impact of geopolitical events on China's oil imports and the formulation of national energy security strategies.

图1 “一带一路”原油运输港口分布 Fig.1 Crude oil transportation ports along the Belt and Road |
表1 复杂网络主要指标公式及含义Table 1 The meaning and formula of main index of complex network |
| 类别 | 指标 | 公式 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 整体 特征 | 网络密度 | 指图中存在的边的数量; 指节点总数; 表示实际边数除以理论上最大边数 | |
| 平均度 | 为节点总数; 为节点 的度; 表示各节点直接相连的边数的平均值 | ||
| 平均加权度 | 为节点 与 之间是否有边直接连接,若有,值为1,反之,则为0; 为节点 与 之间边的权重; 表示各节点直接相连的边权重之和的平均值 | ||
| 平均路径长度 | 表示图中节点 与 之间最短路径的边数; 为节点总数; 表示任意2个节点之间的距离的平均值 | ||
| 平均聚类系数 | 为节点 与相邻节点已形成的邻边的数量; 表示网络节点总数; 表示相邻节点的数量; 表示与同一节点相连的2个节点之间相互连接的平均概率 | ||
| 节点 特征 | 加权出度 加权入度 |
| 为节点 与 之间是否有边直接连接,若有,值为1,反之,则为0; 为节点 与 之间边的权重; 或 表示有向网络中与某个节点直接相连的边权重之和 |
| 中介中心性 | 表示经过节点 ,连接 与 且为最短路径的路径数量; 表示连接 和 的最短路径的数量; 表示经过某个节点的最短路径数目 | ||
| 接近中心性 | | ||
| 组团 检测 | 模块度 |
| 为节点 与 之间边的权重; 和 分别代表节点 与 各自的权重; |
表2 “一带一路”原油海运网络特征变化Table 2 Changes in characteristics of crude oil shipping network along the Belt and Road |
| 时间 | 节点数 | 连边数 | 网络 密度 | 平均度 | 平均 加权度 | 平均路径长度 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年 | 92 | 327 | 0.078 | 3.554 | 22.315 | 2.611 | |
| 2020年 | 95 | 368 | 0.082 | 3.874 | 24.666 | 2.539 | |
| 2022年 | 96 | 318 | 0.070 | 3.312 | 21.493 | 2.625 | |
| 变化 率/% | 2019―2020年 | 3.26 | 12.54 | 5.13 | 9.00 | 10.54 | -2.76 |
| 2020—2022年 | 1.05 | -13.59 | -14.63 | -14.51 | -12.86 | 3.39 | |
表3 加权度位序分布曲线幂函数拟合Table 3 Power function fitting of weighted degree distribution curve |
| 时间 | 拟合方程 | a | b | R 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年 | y=a*x^b | 552.19 | -0.77 | 0.93 |
| 2020年 | y=a*x^b | 593.56 | -0.75 | 0.91 |
| 2022年 | y=a*x^b | 488.44 | -0.72 | 0.90 |
表4 “一带一路”原油海运网络综合重要性前10港口Table 4 The top 10 ports in terms of comprehensive importance of crude oil shipping network along the Belt and Road |
| 时间 | 港口 | 国家/地区 | 相对接近度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年 | 新加坡港 | 新加坡 | 0.82 |
| 巴士拉港 | 伊拉克 | 0.46 | |
| 拉斯坦努拉港 | 沙特阿拉伯 | 0.416 | |
| 锡卡港 | 印度 | 0.393 | |
| 新罗西斯克港 | 俄罗斯 | 0.314 | |
| 舟山港 | 中国 | 0.307 | |
| 富查伊拉港 | 阿联酋 | 0.261 | |
| 瓦迪纳港 | 印度 | 0.213 | |
| 青岛港 | 中国 | 0.205 | |
| 艾哈迈迪港 | 科威特 | 0.18 | |
| 2020年 | 新加坡港 | 新加坡 | 0.797 |
| 新罗西斯克港 | 俄罗斯 | 0.509 | |
| 巴士拉港 | 伊拉克 | 0.436 | |
| 锡卡港 | 印度 | 0.433 | |
| 舟山港 | 中国 | 0.407 | |
| 拉斯坦努拉港 | 沙特阿拉伯 | 0.395 | |
| 富查伊拉港 | 阿联酋 | 0.356 | |
| 大连港 | 中国 | 0.255 | |
| 青岛港 | 中国 | 0.242 | |
| 瓦迪纳港 | 印度 | 0.237 | |
| 2022年 | 新加坡港 | 新加坡 | 0.846 |
| 锡卡港 | 印度 | 0.396 | |
| 新罗西斯克港 | 俄罗斯 | 0.359 | |
| 舟山港 | 中国 | 0.321 | |
| 巴士拉港 | 伊拉克 | 0.275 | |
| 富查伊拉港 | 阿联酋 | 0.222 | |
| 朱阿马港 | 沙特阿拉伯 | 0.218 | |
| 艾哈迈迪港 | 科威特 | 0.206 | |
| 拉斯坦努拉港 | 沙特阿拉伯 | 0.196 | |
| 科济米诺港 | 俄罗斯 | 0.195 |

1 www.shipxy.com
赵鹏军:提出研究选题,设计研究方案,指导研究过程,撰写前言,修改论文全文,提升论文质量;
赵 桐:设计研究方案,处理分析数据,撰写论文主体及修改;
张梦竹、肖 婷:指导论文设计,提出修改意见,提升论文质量。
|
An H, Zhong W, Chen Y, Li H, and Gao X. 2014. Features and Evolution of International Crude Oil Trade Relationships: A Trading-Based Network Analysis. Energy, 74: 254-259.
|
|
An Q, Wang L, Qu D, and Zhang H. 2018. Dependency Network of International Oil Trade before and after Oil Price Drop. Energy, 165: 1021-1033.
|
|
Appiah-Otoo L. 2023. Russia-Ukraine War and US Oil Prices. Energy Research Letters, 4(1): 1-5.
|
|
Blondel V D, Guillaume J L, Lambiotte R, and Lefebvre E. 2008. Fast Unfolding of Communities in Large Networks. Journal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment, (10): 10008.
|
|
Caschili S, Medda F, Parola F, and Ferrari C. 2014. An Analysis of Shipping Agreements: The Cooperative Container Network. Networks and Spatial Economics, 14: 357-377.
|
|
程淑佳,王肇钧. 2011. 复杂网络理论下世界原油贸易空间格局演进研究. 地理科学,31(11):1342-1348.
Chen Shujia and Wang Zhaojun. 2011. Evolution of Spatial Pattern of World Crude Oil Trade Based on Complicated Network Theory. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 31(11): 1342-1348.
|
|
程淑佳,赵映慧,李秀敏. 2013. 基于复杂网络理论的原油贸易空间格局差异分析. 中国人口·资源与环境,23(8):20-25.
Chen Shujia, Zhao Yinghui, and Li Xiumin. 2013. Differences in Spatial Pattern of Main Nations' Crude Oil Trade on Complicated Network Theory. China Population, Resources and Environment, 23(8): 20-25.
|
|
陈腾瀚. 2018. “马六甲困局”再思考:被“过度解释”的风险. 东南亚研究,(6):131-146,151.
Chen Tenghan. 2018. Re-Thinking of the "Malacca Dilemma": The Risk of Being Over-Interpreted. Southeast Asian Studies, (6): 131-146, 151.
|
|
崔巍,康立成,唐丽敏. 2022. 俄乌冲突下天然气贸易网络的结构性风险分析及对中国的启示. 价格月刊,(8):37-45.
Cui Wei, Kang Licheng, and Tang Limin. 2022. Structural Risk Analysis of Natural Gas Trade Network under Russia-Ukraine Conflict and Implications for China. Prices Monthly, (8): 37-45.
|
|
崔巍,孙晓琪,唐丽敏. 2023. 俄乌冲突下亚洲进口LNG价格风险研究. 价格月刊,(2):39-45.
Cui Wei, Sun Xiaoqi, and Tang Limin. 2023. Research on the Price Risk of Imported LNG in Asia under the Russia-Ukraine Conflict. Prices Monthly, (2): 39-45.
|
|
Ducruet C and Zaidi F. 2012. Maritime Constellations: A Complex Network Approach to Shipping and Ports. Maritime Policy & Management, 39(2): 151-168.
|
|
Du R, Wang Y, Dong G, Tian L, Liu Y, Wang M, and Fang G. 2017. A Complex Network Perspective on Interrelations and Evolution Features of International Oil Trade, 2002-2013. Applied Energy, 196: 142-151.
|
|
樊建武,晁博红. 2022. 俄乌冲突对全球原油贸易的影响及中国对策研究. 价格月刊,(11):81-86.
Fan Jianwu and Chao Bohong. 2022. The Impact of Russia-Ukraine Conflict on Global Crude Oil Trade and China's Countermeasures. Prices Monthly, (11): 81-86.
|
|
冯杰. 2022. 俄乌冲突对国际贸易格局的影响及中国对策. 价格月刊,(10):84-89.
Feng Jie. 2022. The Impact of the Russia-Ukraine Conflict on the International Trade Pattern and China's Countermeasures. Prices Monthly, (10): 84-89.
|
|
富景筠. 2020. 新冠疫情冲击下的能源市场、地缘政治与全球能源治理. 东北亚论坛,29(4):99-112,128.
Fu Jingyun. 2020. Energy Market, Geopolitics, and Global Energy Governance under the Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic. Northeast Asia Forum, 29(4): 99-112, 128.
|
|
Gao C, Sun M, and Shen B. 2015. Features and Evolution of International Fossil Energy Trade Relationships: A Weighted Multilayer Network Analysis. Applied Energy, 156: 542-554.
|
|
郭建科,侯雅洁,何瑶. 2020. “一带一路”背景下中欧港口航运网络的演化特征. 地理科学进展,39(5):716-726.
Guo Jianke, Hou Yajie, and He Yao. 2020. Characteristics of Change of the China-Europe Port Shipping Network under the Belt and Road Initiative. Progress in Geography, 39(5): 716-726.
|
|
郭建科,梁木新. 2022. 中国与“21世纪海上丝绸之路”沿线国家航运网络及经贸联系的耦合特征. 地理学报,77(6):1531-1545.
Guo Jianke and Liang Muxin. 2022. The Coupling Characteristics of the Shipping Network and Trade between China and the Countries along the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road. Acta Geographica Sinica, 77(6): 1531-1545.
|
|
Gupta R, Gozgor G, Kaya H, and Demir E. 2019. Effects of Geopolitical Risks on Trade Flows: Evidence from the Gravity Model. Eurasian Economic Review, 9: 515-530.
|
|
韩梦玮,李双琳. 2020. “一带一路”海洋能源产品贸易网络结构特征及社团分布研究. 经济地理,40(10):108-117.
Han Mengwei and Li Shuanglin. 2020. Network Characteristics and Community Structure of Marine Energy Products Trade Among the Countries Along the Belt and Road. Economic Geography, 40(10): 108-117.
|
|
IEA. 2022. Oil Market Report. (2022-05-12) [2023-08-09]. https://www.iea.org/reports/oil-market-report-may-2022.
|
|
Ji Q, Zhang H Y, and Fan Y. 2014. Identification of Global Oil Trade Patterns: An Empirical Research Based on Complex Network Theory. Energy Conversion and Management, 85: 856-865.
|
|
蒋业恒,宿海颖,钱伟聪. 2022. 俄乌地缘政治冲突对全球针叶材供需格局的影响. 世界林业研究,35(4):99-106.
Jiang Yeheng, Su Haiying, and Qian Weicong. 2022. Impacts of Russia-Ukraine Geopolitical Conflict on Global Coniferous Wood Supply-Demand Pattern. World Forestry Research, 35(4): 99-106.
|
|
Korosteleva J. 2022. The Implications of Russia's Invasion of Ukraine for the EU Energy Market and Businesses. British Journal of Management, 33(4): 1678-1682.
|
|
刘建. 2013. 基于社会网络的国际原油贸易格局演化研究. 国际贸易问题,(12):48-57.
Liu Jian. 2013. Research on International Crude Oil Trade Pattern Based on Social Network Theory. Journal of International Trade, (12): 48-57.
|
|
刘卫东. 2015. “一带一路”战略的科学内涵与科学问题. 地理科学进展,34(5):538-544.
Liu Weidong. 2015. Scientific Understanding of the Belt and Road Initiative of China and Related Research Themes. Progress in Geography, 34(5): 538-544.
|
|
李晓依,许英明,肖新艳. 2022. 俄乌冲突背景下国际石油贸易格局演变趋势及中国应对. 国际经济合作,(3):10-18.
Li Xiaoyi, Xu Yingming, and Xiao Xinyan. 2022. Evolution Trend of Global Oil Trade Pattern under Russia-Ukraine Conflict and China's Countermeasures. Journal of International Economic Cooperation, (3): 10-18.
|
|
李岩. 2017. 世界石油运输网络级联失效抗毁性研究. 大连:大连海事大学.
Li Yan. 2017. Invulnerability Research of the World Oil Transportation Network Based on Cascading Failure. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University.
|
|
马远,徐俐俐. 2017. “一带一路”沿线国家天然气贸易网络结构及影响因素. 世界经济研究,(3):109-122,136.
Ma Yuan and Xu Lili. 2017. Network Structure and Influence Factors of Gas Trade about the Countries along "the Belt and Road". World Economy Studies, (3): 109-122, 136.
|
|
Michail N A and Melas K D. 2022. Geopolitical Risk and the LNG-LPG Trade. Peace Economics, Peace Science and Public Policy, 28(3): 243-265.
|
|
国家发展和改革委员会,外交部,商务部. 2015. 推动共建丝绸之路经济带和21世纪海上丝绸之路的愿景与行动. 人民日报,2015-03-29(4).
National Development and Reform Commision, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and Ministry of Commerce. 2015. Vision and Actions to Promote the Joint Construction of the Silk Road Economic Belt and 21st Century Maritime Silk Road. People's Daily, 2015-03-29(4).
|
|
National Research Council. 2010. Understanding the Changing Planet: Strategic Directions for the Geographical Sciences. Washington D C: National Academies Press.
|
|
Peng P, Cheng S, Chen J, Liao M, Wu L, Liu X, and Lu F. 2018. A Fine-Grained Perspective on the Robustness of Global Cargo Ship Transportation Networks. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 28: 881-889.
|
|
彭宇,张紫茜. 2022. 俄乌冲突对国际航运市场影响及中国因应. 航海,(3):7-12.
Peng Yu and Zhang Ziqian. 2022. The Impact of the Russia-Ukraine Conflict on International Shipping Market and China's Response. Navigation, (3): 7-12.
|
|
石泽浩,何喜军,李洪英,杨正东. 2017. “一带一路”钢铁贸易格局及演变规律研究. 国际商务(对外经济贸易大学学报),(4):27-37. [Shi Zehao, He Xijun, Li Hongying, and Yang Zhengdong. 2017. Structure and Evolution Trend of Steel Trade on Belt and Road Initiative. International Business, (4): 27-37. ]
|
|
司文,郑仪,梁建武. 2022. 俄乌冲突对全球粮食安全的影响. 现代国际关系,(5):10-19,59.
Si Wen, Zheng Yi, and Liang Jianwu. 2022. Impact of the Russia-Ukraine Conflict on Global Food Security. Contemporary International Relations, (5): 10-19, 59.
|
|
Steinbach S. 2023. The Russia-Ukraine War and Global Trade Reallocations. Economics Letters, 226: 111075.
|
|
Sun Q, Gao X, Zhong W, and Liu N. 2017. The Stability of the International Oil Trade Network from Short-Term and Long-Term Perspectives. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 482: 345-356.
|
|
孙涛,吴琳,王飞,王琪,陈昭,徐勇军. 2018. 大规模航运数据下“一带一路”国家和地区贸易网络分析. 地球信息科学学报,20(5):593-601.
Sun Tao, Wu Lin, Wang Fei, Wang Qi, Chen Zhao, and Xu Yongjun. 2018. Analysis on the Trade Networks of the Belt and Road Countries and Regions under Large Scale Shipping Data. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 20(5): 593-601.
|
|
孙天阳,陆毅,成丽红. 2022. 港口管理“放管服”改革与出口结构升级. 世界经济,45(3):134-160.
Sun Tianyang, Lu Yi, and Cheng Lihong. 2022. Port Management System Reform and Export Structural Upgrading. The Journal of World Economy, 45(3): 134-160.
|
|
孙晓蕾,杨玉英,吴登生. 2012. 全球原油贸易网络拓扑结构与演化特征识别. 世界经济研究,(9):11-17.
Sun Xiaolei, Yang Yuying, and Wu Dengsheng. 2012. Identification of Topological Structure and Evolution Properties of Global Crude Oil Trade Network. World Economy Studies, (9): 11-17.
|
|
Vakulchuk R, Overland I, Scholten D. 2020. Renewable Energy and Geopolitics: A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 122: 109547.
|
|
王列辉,叶斐,郑渊博. 2020. 中美集装箱航运网络格局演化与脆弱性评估. 经济地理,40(5):136-144.
Wang Liehui, Ye Fei, and Zheng Yuanbo. 2020. The Assessment of Sino-US Container Shipping Network Evolution and Vulnerability. Economic Geography, 40(5): 136-144.
|
|
王明利,鄢朝辉. 2022. 俄乌冲突对世界及我国食物安全的影响与应对策略. 经济纵横,(7):97-106,2.
Wang Mingli and Yan Zhaohui. 2022. The Impact of the Russia-Ukraine Conflict on Food Security in the World and China and China's Countermeasures. Economic Review Journal, (7): 97-106, 2.
|
|
王武林,龚姣,林珍. 2021. “冰上丝绸之路”沿线国家贸易网络结构特征分析. 热带地理,41(6):1199-1208.
Wang Wulin, Gong Jiao, and Lin Zhen. 2021. Structural Characteristics of Trade Network in Countries along the Polar Silk Road. Tropical Geography, 41(6): 1199-1208.
|
|
Wegge N and Keil K. 2018. Between Classical and Critical Geopolitics in A Changing Arctic. Polar Geography, 41(2): 87-106.
|
|
World Economic Forum. 2019. The Global Risks Report. (2019-01-15). [2023-08-10]. https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Global_Risks_Report_2019.pdf.
|
|
吴迪,王诺,于安琪,关雷. 2018. “丝路”海运网络的脆弱性及风险控制研究. 地理学报,73(6):1133-1148.
Wu Di, Wang Nuo, Yu An'qi, and Guan Lei. 2018. Vulnerability and Risk Management in the Maritime Silk Road Container Shipping Network. Acta Geographica Sinica, 73(6): 1133-1148.
|
|
王薇,Patrick Qiang. 2020. 丝绸之路经济带能源贸易的空间网络特征及影响因素分析. 贵州社会科学,(3):123-131.
Wang Wei and Patrick Qiang. 2020. Space and Network Features and Influential Factor in Energy Trade in the Silkroad Economy Zone. Guizhou Social Sciences, (3): 123-131.
|
|
谢昭易. 2021. 突发事件下中欧班列货运网络脆弱性研究. 成都:西南交通大学.
Xie Zhaoyi. 2021. Research on the Vulnerability of China Railway Express Freight Network Under Emergencies. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University.
|
|
杨双梅. 2022. 美国的乌克兰政策:战略目标及前景. 国际关系研究,(2):61-83.
Yang Shuangmei. 2022. The Evolution and Prospect of America's Ukraine Policy. Journal of International Relations, (2): 61-83.
|
|
杨文龙,杜德斌,马亚华,焦美琪. 2018. “一带一路”沿线国家贸易网络空间结构与邻近性. 地理研究,37(11):2218-2235.
Yang Wenlong, Du Debin, Ma Yahua, and Jiao Meiqi. 2018. Network Structure and Proximity of the Trade Network in the Belt and Road region. Geographical Research, 37(11): 2218-2235.
|
|
Yang Y, Poon J P H, Liu Y, and Bagchi-Sen S. 2015. Small and Flat Worlds: A Complex Network Analysis of International Trade in Crude Oil. Energy, 93: 534-543.
|
|
易小准,李晓,盛斌,杨宏伟,曹宝明,徐坡岭. 2022. 俄乌冲突对国际经贸格局的影响. 国际经济评论,(3):9-37,4.
Yi Xiaozhun, Li Xiao, Sheng Bin, Yang Hongwei, Cao Baoming, and Xu Poling. 2022. Impact of Russia-Ukraine Conflict on International Economic and Trade Landscape. International Economic Review, (3): 9-37, 4.
|
|
Zhang H Y, Ji Q, and Fan Y. 2014. Competition, Transmission and Pattern Evolution: A Network Analysis of Global Oil Trade. Energy Policy, 73: 312-322.
|
|
张强,苗龙,汪春雨,胡海晨. 2021. 新时代中国能源安全及保障策略研究——基于推进“一带一路”能源高质量合作视角. 财经理论与实践,42(5):116-123.
Zhang Qiang, Miao Long, Wang Chunyu, and Hu Haichen. 2021. Research on China's Energy Security and Protection Strategies in the New Era Based on the Perspective of Promoting the Belt and Road Energy High-Quality Cooperation. The Theory and Practice of Finance and Economics, 42(5): 116-123.
|
|
张永礼,朱靖源. 2022. 中美贸易战下钛供应链全球贸易网络格局动态演变研究. 中国矿业,31(12):6-14.
Zhang Yongli and Zhu Jingyuan. 2022. Research on the Dynamic Evolution of the Global Trade Network Pattern of Titanium Supply Chain under the China-US Trade War. China Mining Magazine, 31(12): 6-14.
|
|
赵亚博,刘晓凤,葛岳静. 2017. “一带一路”沿线国家油气资源分布格局及其与中国合作中的相互依赖关系. 地理研究,36(12):2305-2320.
Zhao Yabo, Liu Xiaofeng, and Ge Yuejing. 2017. Analysis of the Oil and Gas Resource Distribution Pattern along the Belt and Road and the Interdependence Relationship with China. Geographical Research, 36(12): 2305-2320.
|
|
Zhou X Y, Lu G, Xu Z, Yan X, Khu S T, Yang J, and Zhao J. 2023. Influence of Russia-Ukraine War on the Global Energy and Food Security. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 188: 106657.
|
|
祝孔超,赵媛,夏四友,夏启繁,崔盼盼. 2023. “一带一路”沿线国家石油产品贸易网络演化分析. 世界地理研究,32(6):28-38.
Zhu Kongchao, Zhao Yuan, Xia Siyou, Xia Qifan, and Cui Panpan. 2023. Evolution of the Petroleum Products Trade Network of Countries along the "Belt and Road". World Regional Studies, 32(6): 28-38.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |