

The Landscape Schema of Bayu Terraced Field Human Settlements Responding to Regional Natural Features
Received date: 2021-11-20
Revised date: 2022-01-25
Online published: 2023-02-03
The Bayu terraced human settlement is an on-site living cultural heritage site that responds to natural features such as mountainous landforms and seasonal hydrology. Research into the site selection, technology, and combination of Bayu terraced human settlements can provide historical insight for the construction of resilient urban and rural developments in the southwest mountainous areas and the simultaneous protection of small and micro wetlands. Complete and representative remote sensing images of terraced fields in the Bayu area, combined with historical data analysis and field investigation using the visual landscape schema language, this study analyzed the single-terraced water conservancy technology, the spatiotemporal combination model of this technology, and the three construction characteristics of the terraced human settlement environment. As a result, the landscape schema system of the Bayu-terraced human settlement system was constructed. First, the research found that, in response to the Bayu Mountain topography and the rainfall characteristics of "spring drought and summer flood," a series of in-terrain terraced water conservancy technologies have been formed, such as winter paddy field for the autumn and spring, flushing fields for flood discharge in the summer, and hoarding paddy fields for closing water in all seasons. Second, Bayu terraced water conservancy technology forms a water resource management model of "autumn storage, winter fertility, spring ploughing, summer drainage" adapted to "spring drought and summer flooding", and a combination of "high storage, low irrigation" that conforms to the geomorphology that is formed. Finally, the terraced human settlement responds to the difference in water safety under the influence of geomorphology, presenting an "organic dispersion type" terraced human settlement pattern in low-mountainous hilly areas where the intersecting terraced base and the conservation forest and the scattered residential patches nest occlusion. The conservation forest is a "large area concentration type" terraced human settlement pattern in low-mountainous hilly areas where the intersecting terraced base and the conservation forest and the scattered residential patch nest in occlusion. In summary, Bayu terraced water conservancy technology types, combination methods, and the construction mode of terraced human settlements in mountainous topography integrate with Bayu's unique geographical geomorphology and hydrological conditions. These are important for the current low-impact development and construction of urban and rural areas and the protection of traditional construction wisdom. There are also positive references.
Wenjing Liao , Huasong Mao , Ping Luo . The Landscape Schema of Bayu Terraced Field Human Settlements Responding to Regional Natural Features[J]. Tropical Geography, 2023 , 43(1) : 155 -167 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003607
表1 巴渝梯田建设区域的地貌类型及其水文特征Table 1 Site Selection Types and Topographic and Hydrological Characteristics of Terraces In Bayu |
| 自然特征及 建设规律 | 低山丘陵区 | 中高山沟谷区 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丘陵缓坡 | 山麓 | 山腰 | 山顶 | ||
| 地形自然 环境特征 | 平行岭谷之间用地开阔、 地势起伏较缓的浅丘山区 | 地势由溪谷到山体 逐渐从缓到陡 | 单向坡面、地势较陡 | 周围小丘包围, 地势略微起伏 | |
| 建设坡度/(°) | <5 | 5~15 | 10~15 | >15 | |
| 水文特征 | 蓄水容易且不易受到山洪威胁 | 抽水困难且易受到山洪威胁 | 水源极差,蓄水极难 | 水源极差,蓄水极难 | |
| 水利设施建设 适宜性 | 适宜建造人工水利 设施堰塘、水库 | 临溪宽阔地带适宜 建设灌溉沟渠 | 不适宜建设人工水利设施 | 宽阔区域可形成 天然积水塘 | |
表2 冬水田布局位置及形态规律Table 2 Distribution Position and Form Law of Winter Paddy Field |
| 类别 | 低山丘陵区 | 中高山沟谷区 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丘陵缓坡 | 山麓 | 山腰 | 山顶 | |
| 实例 | 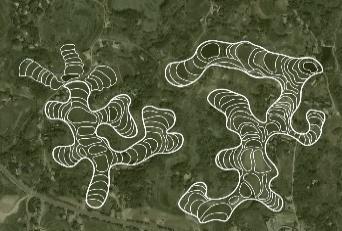 |  | 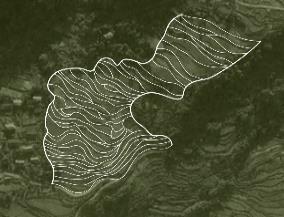 | 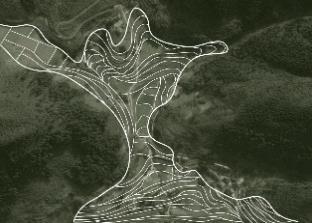 |
| 布局 位置 | 主要位于土黏泥厚的沟谷低缓区域, 蓄水性较强,较易收集秋耕余水 | 位于坡度较陡的山坡区及用地局促且抽水困难的狭长沟谷地带 | 沿山脊分水线延展 成片布置冬水田 | 顺应山体汇水方向 布置冬水田 |
| 形态规律 | 沿等高线交叉跌落型 | 汇水线两侧跌落型 | 单向成片跌落型 | 沿汇水线枝状聚集型 |
表3 冲冲田布局位置及形态规律Table 3 Layout Position and Shape Law of Alluvial Field |
| 类型 | 低山丘陵区 | 中高山沟谷区 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丘陵缓坡 | 山麓 | 山顶 | ||
| 实例 |  | 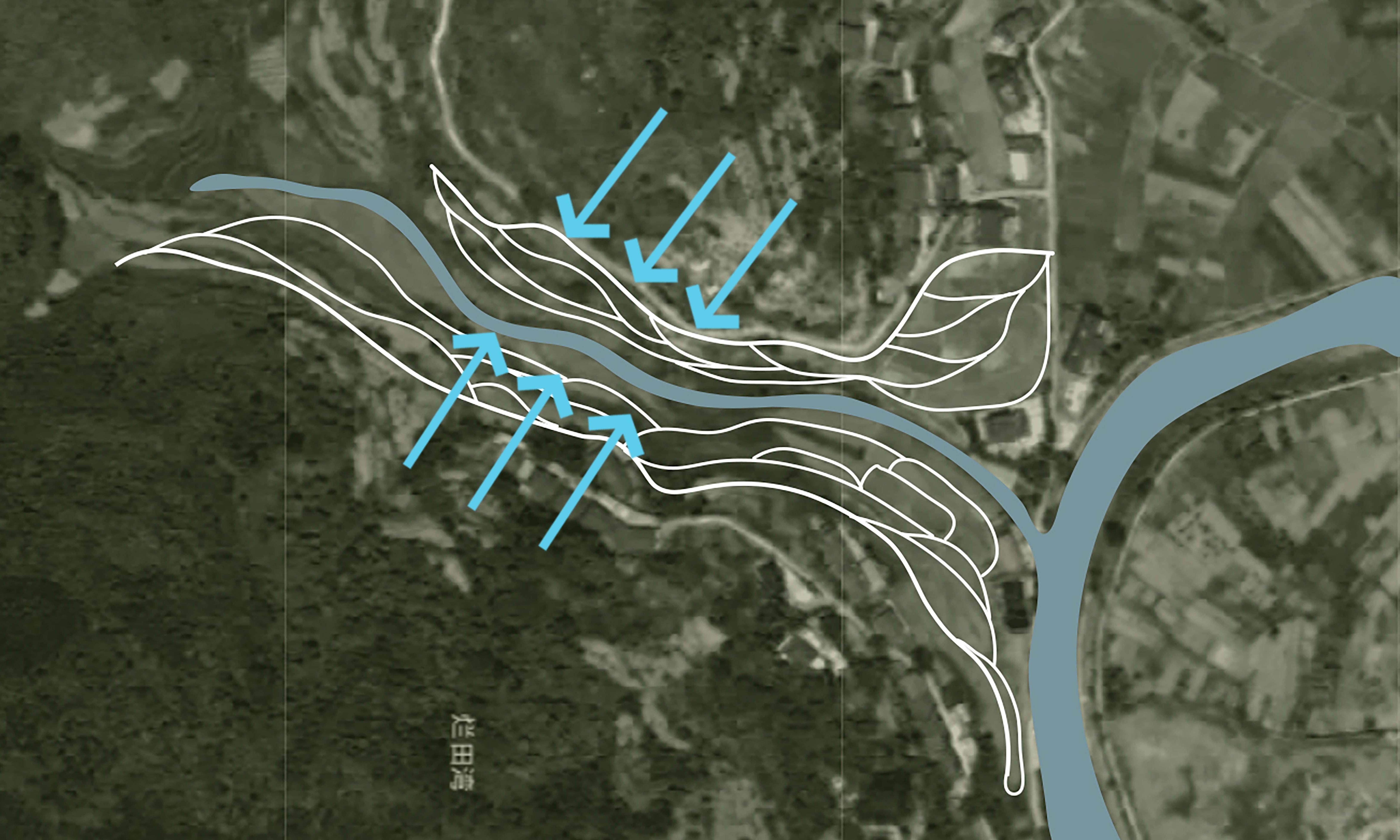 | 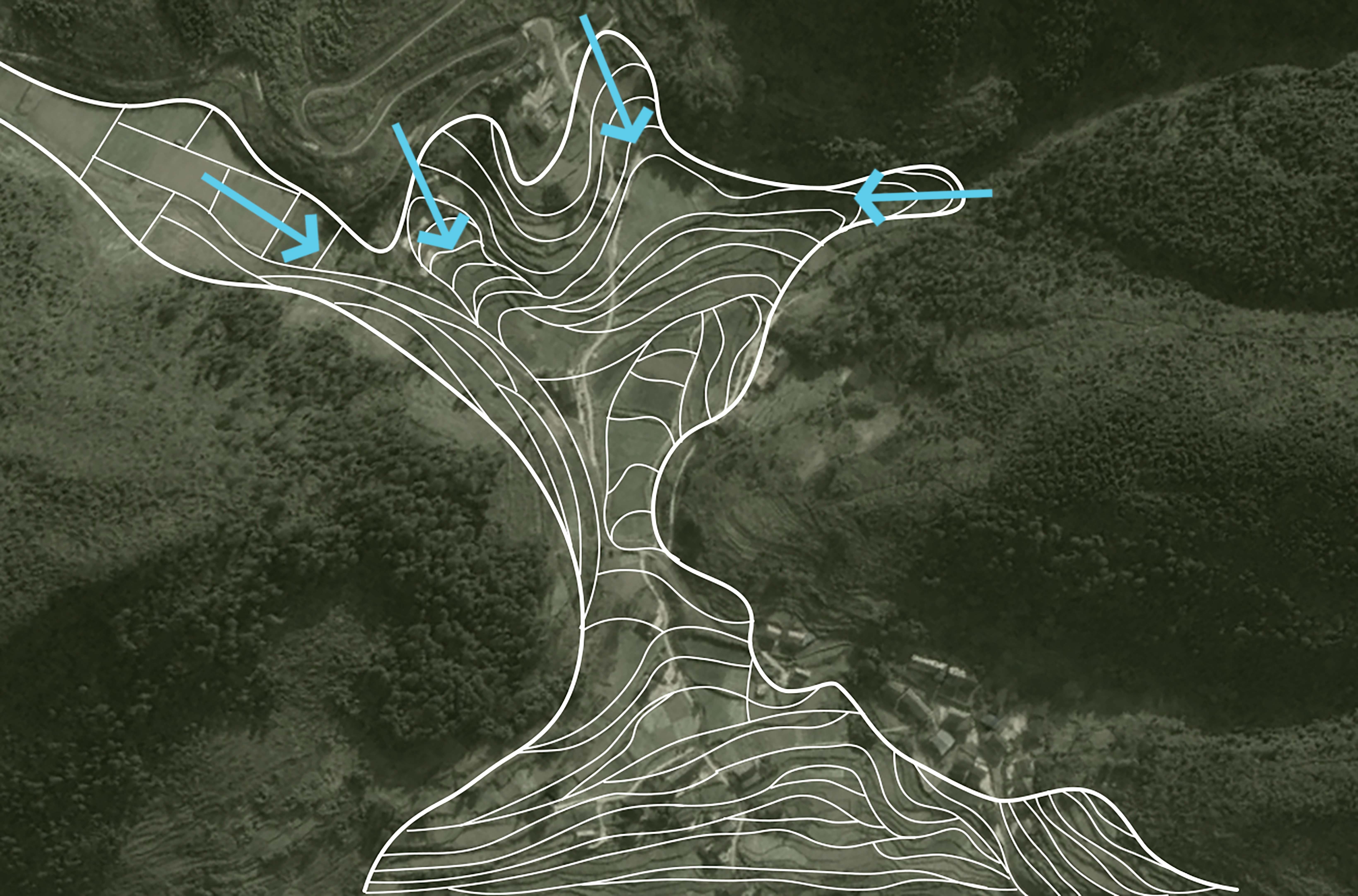 | |
| 布局位置 | 汇水区,沿丘麓坳谷等高线逐级布置, 正中为正冲,两侧为侧冲 | 沟谷较窄的地高傍山、 丘陵两侧(侧冲) | 山顶丘陵起伏的汇水区, 沿丘麓坳谷等高线逐级布置, | |
| 形态规律 | 内凹跌落型 | 两侧单向跌落型 | 内凹跌落型 | |
表4 囤水田布局位置及形态规律Table 4 Layout position and shape law of hoarding paddy fields |
| 类别 | 低山丘陵区 | 中高山沟谷区 |
|---|---|---|
| 丘陵缓坡 | 山顶缓丘 | |
| Google实例 | 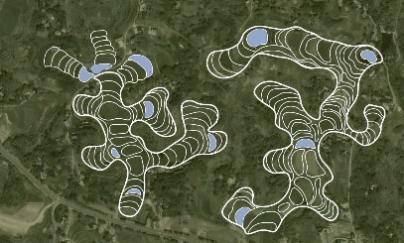 | 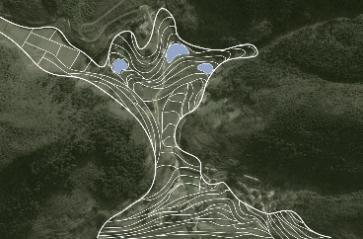 |
| 布局位置 | 两丘之间的梯田高处 | 两丘之间的梯田高处 |
| 形态规律 | 环状闭合型 | 环状闭合型 |
表5 梯田人居“田、居、林”要素布局规律及水平格局特征Table 5 The layout rules and horizontal pattern characteristics of the terraced human settlements |
| 类别 图式 分析 | 低山丘陵区 (巴南区南泉街道迎龙村) | 中高山沟谷区(南川区三泉镇) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丘陵缓坡 | 山麓 | 山腰 | 山顶 | ||
| 梯田 |  | 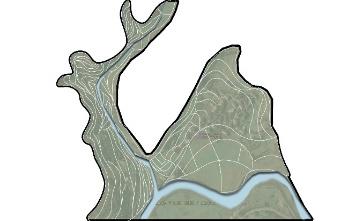 | 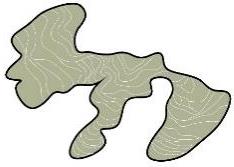 | 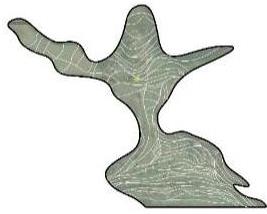 | |
| 布局 规律 | 坡度较缓的低处,交叉汇聚型 连续有机基底 | 沿溪两侧坡度相对较缓,山沟 侧面单向跌落,集中斑块 | 分水线两侧外凸坡面区域 单向跌落,集中斑块 | 山顶浅丘低洼的汇水区域 单向跌落,集中斑块 | |
| 居 | 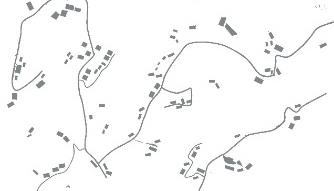 | 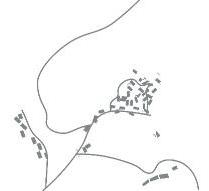 | 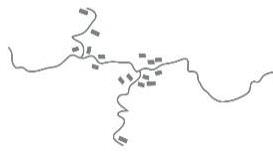 | 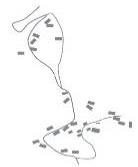 | |
| 布局 规律 | 坡度相对较陡的高处 分散斑块 | 梯田内部坡度相对较缓的区域,集中布置 | |||
| 林 |  |  |  |  | |
| 布局 规律 | 坡度相对较陡的高处 连续有机基底 | 涵养林成为连片背景基底 | |||
| 要素 叠加 |  | 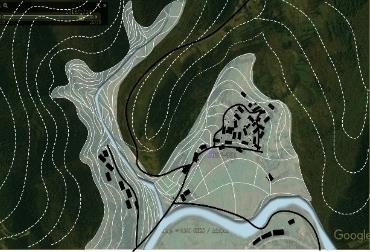 | 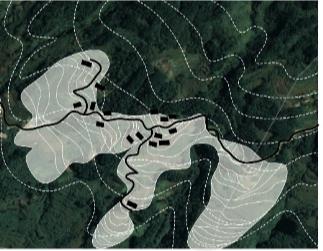 | 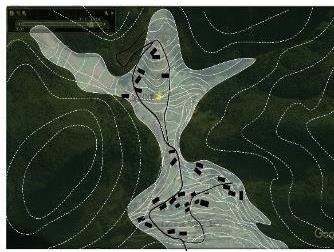 | |
| 布局 规律 | 梯田和涵养林咬合相嵌形成基底 林高田低,民居斑块分散在林间 | 涵养林为基底,聚落集中分布在梯田间坡度相对较缓的区域,梯田聚落组合为集中的大斑块 | |||
| 梯田 人居 水平 格局 | 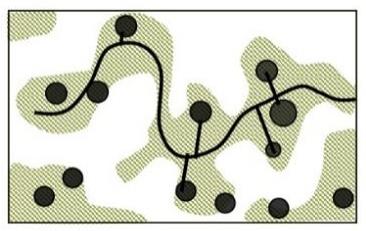 | 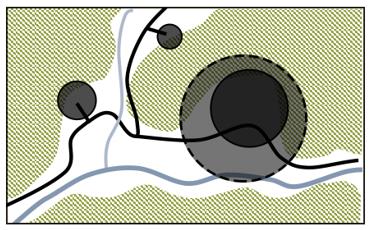 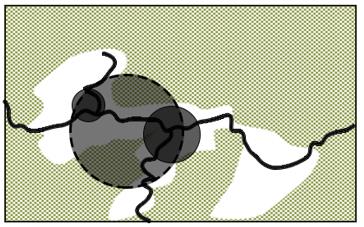 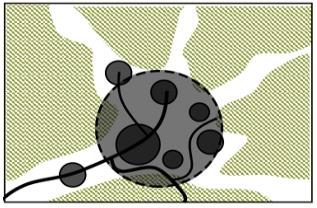 | |||
| 特征 | 有机分散型 | 大面集中型 | |||
表6 梯田人居环境区域景观水平网络的在地特征Table 6 Local characteristics of regional landscape horizontal network |
| 选址及 水平特征 | 低山丘陵区 | 中高山沟谷区 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丘陵缓坡 | 山麓 | 山腰 | 山顶 | |
| 平面 图式 |  | 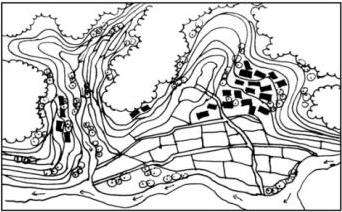 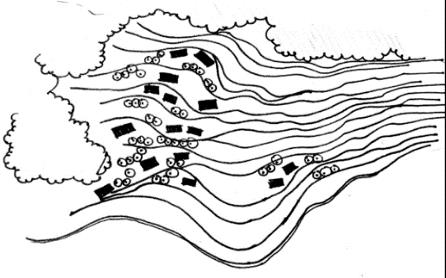 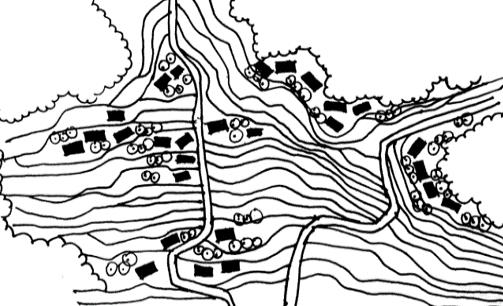 | ||
| 梯田选址特征 | 坡度相对较缓的低处 | 坡度较缓的汇水两侧安全区域或 溪水两侧坡度较缓区域 | 山腰坡度适宜的分水线 两侧外凸坡面区域 | 山顶小丘低处 汇水区 |
| 聚落选址特征 | 坡度相对较陡的高处 | 田间坡度相对较缓的区域 | ||
| 水平网络特征 | 梯田与涵养林咬合嵌套形成“ 指状嵌合型”基底小组团斑块 分散林间“有机分散型” | 涵养林成为基底单向跌落梯田及集中型聚落组成大斑块 “大面集中型” | ||

1 https://wenku.baidu.com/view/2d57935ca717866fb84ae45c3b3567ec102ddcf5.html?_wkts_=1673402838481&bdQuery
廖文静:案例选取、图表绘制、内容撰写、结果讨论及校对修改;
毛华松:选题方向及研究框架、创新点总结、进度管理及校对修改;
罗 评:调研分析、综述梳理、内容讨论及校对修改。
|
Antrop M. 2006. Sustainable Landscapes: Contradiction, Fiction or Utopia. Urban Plan, 75: 187-197.
|
|
Andersen Erling. 2017. The Farming System Component of European Agricultural Landscape. European Journal of Agronomy, 82: 282-291.
|
|
Bizoza A R. 2014. Three-Stage Analysis of the Adoption of Soil and Water Conservation in the Highlands of Rwanda. Land Degradation & Development, 25(4): 360-372.
|
|
陈蝶,卫伟,陈利顶. 2017. 梯田景观的历史分布及典型国际案例分析. 应用生态学报,28(2):689-698.
Chen Die, Wei Wei and Chen Liding. 2017. History and Distribution of Terraced Landscapes and Typical International Cases Analysis. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 28(2): 689-698.
|
|
陈桂权. 2013. 冬水田技术的形成与传播——以四川为中心的考察. 中国农史,(4):3-13.
Chen Guiquan. 2013. The Formation and Propagation of the Winter Paddy Field Technology: Research Focused on the Sichuan Province's Historical Facts. Agricultural History of China, (4): 3-13.
|
|
陈桂权. 2018. 稻作与环境:清代以来四川冬水田的历史变迁与技术选择. 自然科学史研究,37(4):461-471.
Chen Guiquan. 2018. Rice and Environment: Historical Changes in Winter Flooded Paddy Fields and Technical Choice since the Qing Dynasty. Studies in the History of Natural Sciences, 37(4): 461-471.
|
|
戴芹芹. 2013. 地方知识在水安全格局识别中的作用——以重庆御临河流域龙兴、石船镇为例. 北京:北京大学.
Dai Qinqin. 2013. The Role of Local Knowledge in the Identification of Water Safety Patterns-Take Chongqing's Imperial River Basin Longxing and Stone Boat Town as Examples. Beijing: Beijing University.
|
|
戴芹芹,王志芳. 2015. 重庆堰塘—冲冲田系统对现代水资源管理的启示. 中国水利,(1):34-37.
Dai Qinqin and Wang Zhifang. 2015. China Water Resources, (1): 34-37.
|
|
Federico Preti, Enrico Guastini, Daniele Penna, Andrea Dani and Giorgio Cassiani. 2018. Conceptualization of Water Flow Pathways in Agricultural Terraced Landscapes. Land Degradation & Development, 29(3): 651-662.
|
|
关兴. 2013. 四川省盆周山区冬水田利用的生态农业模式的现状调查研究——以旺苍县木门镇为例. 四川:四川农业大学.
Guan Xing. 2013. Investigation on The Current Situation of Ecological Agriculture Model of Winter Paddy Field Utilization in The Mountainous Areas around the Basin of Sichuan Province:Taking Mumen Town,Wangcang County as an Example. Sichuan: Sichuan Agricultural University.
|
|
官加杰,周静. 2021. 贵州从江加榜梯田国家湿地公园生态旅游开发初步研究. 贵州林业科技,49(2):51-54.
Guan Jiajie and Zhou Jing. 2021. A Preliminary Study on Eco-Tourism Development of Congjiang Jiabang Terrace National Wetland Park in Guizhou Province. Guizhou Forestry Science and Technology, 49(2): 51-54.
|
|
Guido Paliaga, Fabio Luino, Laura Turconi, Francesco Faccini. Terraced Landscapes on Portofino Promontory (Italy): Identification, Geo-Hydrological Hazard and Management. Water, 12: 435.
|
|
何灿. 2019. 重庆市丘陵区小型蓄水工程研究. 重庆:西南大学.
He Can. 2019. Study on Small Water Storage Project in Hilly Area of Chongqing City. Chongqing: Southwest University.
|
|
贺冉. 2018. 基于小流域水文过程的山地城市水系空间规划对策研究——以巴中市经济技术开发区水系规划为例. 重庆:重庆大学.
He Ran. 2018. Research on Spatial Planning of Mountain Urban Water System Based on Hydrological Process of Small Watershed: Taking the Water System Planning of Bazhong City Economic and Technological Development Zone as an Example. Chongqing: Chongqing University.
|
|
何晓珊,马俊. 2019. 西南地域聚落建筑发展浅析. 居舍,(17):11.
He Xiaoshan and Ma Jun. 2019. On the Development of Settlement Architecture in Southwest China. Jushe, (17): 11.
|
|
何杨,杨宇亮,角媛梅. 2019. 空间与机制:元阳县多民族稻作聚落的垂直分异现象对比. 住区,(2):116-125.
He Yang, Yang Yuliang and Jue Yuanmei. 2019.Space and Mechanism: A Comparison of Vertical Differentiation of Multi-ethnic Rice Settlements in Yuanyang County. Community Design, (2): 116-125.
|
|
黄国勤. 2019. 江西崇义客家梯田系统的特征、价值与保护. 古今农业,(4):81-93.
Huang Guoqin. 2019. Characteristics, Value and Protection of Chongyi Hakka Terrace System in Jiangxi Province. Ancient and Modern Agriculture, (4): 81-93.
|
|
角媛梅,邱应美,杨宇亮,李亚,李宏,赵冬梅,刘澄静,张娟. 2021. 哈尼族典型聚落的民居分布格局及其演变机理——以云南省元阳县全福庄中寨为例. 地域研究与开发,40(5):40-50.
Jue Yuanmei, Qiu Yingmei, Yang Yuliang, Li Ya, Li Hong, Zhao Dongmei, Liu Chengjing and Zhang Juan. 2021. Residential Distribution Pattern and Evolution Mechanism of Typical Hani Settlement: A Case Study of Quanfuzhuang Middle Village in Yuanyang County, Yunnan Province. Areal Research and Development, 40(5): 40-50.
|
|
Katharina Heider, Emanuele Quaranta, José María García Avilés, Juan Miguel Rodriguez Lopez, Andrea L Balbo and Jürgen Scheffran. 2021. Reinventing the Wheel: the Preservation and Potential of Traditional Water Wheels in The Terraced Irrigated Landscapes of The Ricote Valley, Southeast Spain. Agricultural Water Management, 259(1): 107240.
|
|
李禾尧,贺献林. 2019. 河北涉县旱作梯田系统的特征、价值与保护实践. 遗产与保护研究,4(1):39-43.
Li Heyao and He Xianlin. 2019. The Characteristics, Values and Conservation Practice of Dryland Terraces System in She County, Hebei Province. Research on Heritages and Preservation, 4(1): 39-43.
|
|
李明英. 2016. 基于生态基础设施的山地城市滨河公共空间规划研究. 重庆:重庆大学.
Li Mingying. 2016. Study on Planning of Riverside Space in Mountainous City Based on the Ecological Infrastructure. Chongqing: Chongqing University.
|
|
李仕华. 2011. 梯田水文生态及其效应研究. 西安:长安大学.
Li Shihua. 2011. Reaserch on Hydro: Ecology of Terrace and Its Effect. Xi'an: Changan University.
|
|
李笑寒. 2017. 重庆都市近郊区农田植物多样性研究. 重庆:重庆大学.
Li Xiaohan. 2017. Research of the Farmland Plant Diversity in the Suburban Area of Chongqing. Chongqing: Chongqing University.
|
|
刘迪,王志芳,俞孔坚. 2015. 基于雨洪调蓄的城市新区湿地保护规划——以重庆两江新区为例. 中国水利,(19):28-34.
Liu Di, Wang Zhifang and Yu Kongjian. 2015. Wetland Protection Planning of New Urban District Based on Rainwater Storage: Taking Liangjiang New District of Chongqing as an Example. China Water Resources, (19): 28-34.
|
|
刘宗滨,宋维峰. 2019. 基于GIS空间数据的红河县哈尼梯田分布规律研究. 亚热带水土保持,31(3):7-11.
Liu Zongbin and Song Weifeng. 2019. Study on the Spatial Distribution Rules of Hani Terrace in Honghe County Based on GIS Spatial Data. Subtropical Soil and Water Conservation, 31(3): 7-11.
|
|
Melissa Goodman-Elgar. 2008. Evaluating Soil Resilience in Long-Term Cultivation: A Study of Pre-Columbian Terraces from the Paca Valley, Peru. Journal of Archaeological Science, 35(12): 3072-3086.
|
|
马焱. 2018. 黔西南喀斯特地貌区农耕村落居住环境优化研究. 重庆:重庆大学.
Ma Yan. 2018. Research on the Living Environment Optimization of Farming Villages in Karst Landform Area. Chongqing: Chongqing University.
|
|
Pabitra Banik, Ashim Midya, Sharon Fajardo and Suan Pheng Kam. 2008. Natural Resource Inventory of Luppi Village, Eastern Plateau of India: Implications for Sustainable Agricultural Development. Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 28(2): 85-100.
|
|
Sam Turner, Jordi Bolòs and Tim Kinnaird. 2018. Changes and Continuities in A Mediterranean Landscape: A New Interdisciplinary Approach to Understanding Historic Character in Western Catalonia. Landscape Research,43(7):922-938.
|
|
Shimbahri Mesfin, Lucas Allan Almeida Oliveira, Eyasu Yazew, Elena Bresci and Giulio Castelli. 2019. Spatial Variability of Soil Moisture in Newly Implemented Agricultural Bench Terraces in the Ethiopian Plateau. Water, 11(10): 2134.
|
|
温莉,周廷刚,刘晓璐,吴浪. 2019. 地形对重庆市土地利用动态变化影响分析. 人民长江,50(4):76-80.
Wen Li, Zhou Tinggang, Liu Xiaolu and Wu Lang. 2019. Impact Analysis of Landform for Land Use Dynamic Change of Chongqing. Yangtze River, 50(4): 76-80.
|
|
王云才. 2009. 传统地域文化景观之图式语言及其传承. 中国园林,25(10):73-76.
Wang Yuncai. 2009. The Pattern Language and Its Inheritance of Traditional local Cultural landscape. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 25(10): 73-76.
|
|
王云才,孟晓东,邹琴. 2016. 传统村落公共开放空间图式语言及应用. 中国园林,(11):44-49.
Wang Yuncai, Meng Xiaodong and Zou Qin. 2016. The Pattern Language and Its Application in Public Open Space in Traditional Village. Chinese Landscape Architecture, (11): 44-49.
|
|
辛儒鸿,曾坚,黄友慧. 2018. 基于生态智慧的西南山地传统村落保护研究. 中国园林,35(9):95-99.
Xin Ruhong, Zeng Jian and Huang Youhui. 2018. Study on the Protection of Traditional Villages in Southwest Mountainous Areas Based on Ecological Wisdom. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 35(9): 95-99.
|
|
杨建辉,周庆华. 2018. 陕北传统雨水场地的生态智慧对现代海绵城市建设的启示. 中国园林,34(7):64-68.
Yang Jianhui and Zhou Qinghua. 2018. Enlightenment of Ecological Wisdom of Traditional Stormwater Site in Northern Shaanxi to the Construction of Sponge City. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 34(7): 64-68.
|
|
袁梦. 2019. 哈尼梯田湿地水文特征研究. 绿色科技,10(5):16-20.
Yuan Meng. 2019. Study on Hydrological Characteristics of Hani Terrace Wetland. Green Science and Technology, 10(5): 16-20.
|
|
张苗苗. 2014. 清代重庆地区农田水利与主要粮食作物种植研究. 重庆:重庆师范大学.
Zhang Miaomiao. 2014. The Research on Irrigation and Water Conservancy and Main Grain Crops of Chongqing in Qing Dynasty. Chongqing:Chongqing Normal University.
|
|
张涛. 2017. 基于流域生态安全理念的多尺度城市防洪排涝研究——以嘉陵江流域为例. 重庆:重庆大学.
Zhang Tao. 2017. The Research on Multi-Scale Urban Flood Control and Storm Drainage Based on Economical Security of River Basin: Taking Jialing River Basin as the Example. Chongqing:Chongqing University.
|
|
郑文俊,张贝贝,吴忠军. 2019. 桂林龙脊人居环境适应的营造智慧. 中国园林,35(9):20-24.
Zhen Wenjun, Zhang Beibei and Wu Zhongjun. 2019. Construction Wisdom of Longji Settlement Environmental Adaptation in Guilin. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 35(9): 20-24.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |