

Grid Scale Measurement of Sustainable Form Elements of New Urban Districts: A Case Study of Yinzhou New Urban Districts
Received date: 2022-10-21
Revised date: 2023-04-21
Online published: 2023-10-11
After years of high-speed urbanization and rapid expansion, China's economy has gradually transformed into a "new normal," with a new people-oriented urbanization strategy emphasizing spatial quality. In this context, the disjunction between the development of medium- and high-density buildings and low-density human activity, common in the new towns and districts of China, has become increasingly prominent. From the perspective of spatial form, this study proposes that good street accessibility, suitable construction density and architectural form, and sufficient functional mixing are the bases for promoting sustainable urban development. In these studies, the spatial form elements in Yinzhou New Town in Ningbo were measured using spatial syntax, spatial matrix, and mixed function indicators. The results show that (1) the overall coordination ability of the street network in Yinzhou New Town is strong, the local spatial network and global spatial network structure are integrated, and the vitality of the street system in the central area is relatively high; (2) the architectural forms of Yinzhou New City are mainly middle-level slabs and enclosures, low-level enclosures, and high-level slabs. Analysis of density-shape correlation reveals residential areas within the low-level high coverage zones and shielded residential areas in the multi-level high coverage zones, suggesting a need to appropriately enrich multilevel slab or enclosure and high-level enclosure zones, which have strong positive effects on the vitality of New City; (3) The new urban area of Yinzhou is dominated by the single-function large-scale land development mode, with a low proportion of mixed land and only 1.73% thoroughly mixed land (H_A_W); (4) Functional mixing, accessibility, building strength, and form have a high degree of overlap. A total of 64.54% of cells with a high floor area ratio (> 2.2) were clustered in high-accessibility areas, and 50.25% and 85.71% of dual-function and multi-function mixed units, respectively, were clustered in high-accessibility areas. The effect of the mixed function-accessibility association is more obvious when mixed units include public facilities. In the future, the spatial structure represented by street accessibility should be considered the core breakthrough point. On the one hand, we should ensure good street accessibility as a whole; on the other hand, we should organize the arrangement of construction intensity and functions with high accessibility street distribution, emphasize the moderate mixing of urban land, construct diversified urban life, and improve the vitality and sustainability of urban space to simultaneously realize an agglomeration of multiple urban morphological characteristics with positive effects, and finally foster the emergence of urban spaces with high urban vitality. These sustainable spatial form investigation results are helpful for formulating policy suggestions to improve the quality of ecologically sound construction and create spatial vitality through informed planning and design.
Xiaohui Wang , Yu Ye , Lan Yang , Longsheng Wang , Qian Che , Yanhua Song , Shimou Yao . Grid Scale Measurement of Sustainable Form Elements of New Urban Districts: A Case Study of Yinzhou New Urban Districts[J]. Tropical Geography, 2023 , 43(10) : 1929 -1939 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003758
图2 空间矩阵模型(a)及城市活力分析的高-中-低值划分(b)Fig.2 Space matrix model (a) and high-medium-low value partition of urban vitality analysis (b) |
图3 基于线段模式的鄞州新城区空间句法全局(a)与局部(b)NACH值Fig.3 Spatial syntax global(a) and local(b) NACH results based on segment patterns of Yinzhou new urban district |
图4 鄞州新城区全局及局部NACH值相关性分析Fig.4 Correlation analysis of global and local NACH in Yinzhou new urban district |
图5 格网尺度下鄞州新城区街道网络可达性分析Fig.5 Analysis on the accessibility of Yinzhou new urban district street based on grid |
图6 鄞州新城区容积率(a)与建筑密度(b)格网分布Fig.6 Spatial distribution of FSI(a) and GSI(b) of Yinzhou new urban district |
图7 鄞州新城区建设类型(a)以及建设强度与建筑形态(b)空间分布Fig.7 Spatial distribution of building type(a), building intensity and building morphology(b) of Yinzhou new urban district |
图8 《城市居住区规划设计规范》与鄞州新城区住区密度-形态区间示意 Fig.8 Code of urban Residential Areas Planning & Design and density-shape interval diagram in Yinzhou new urban district |
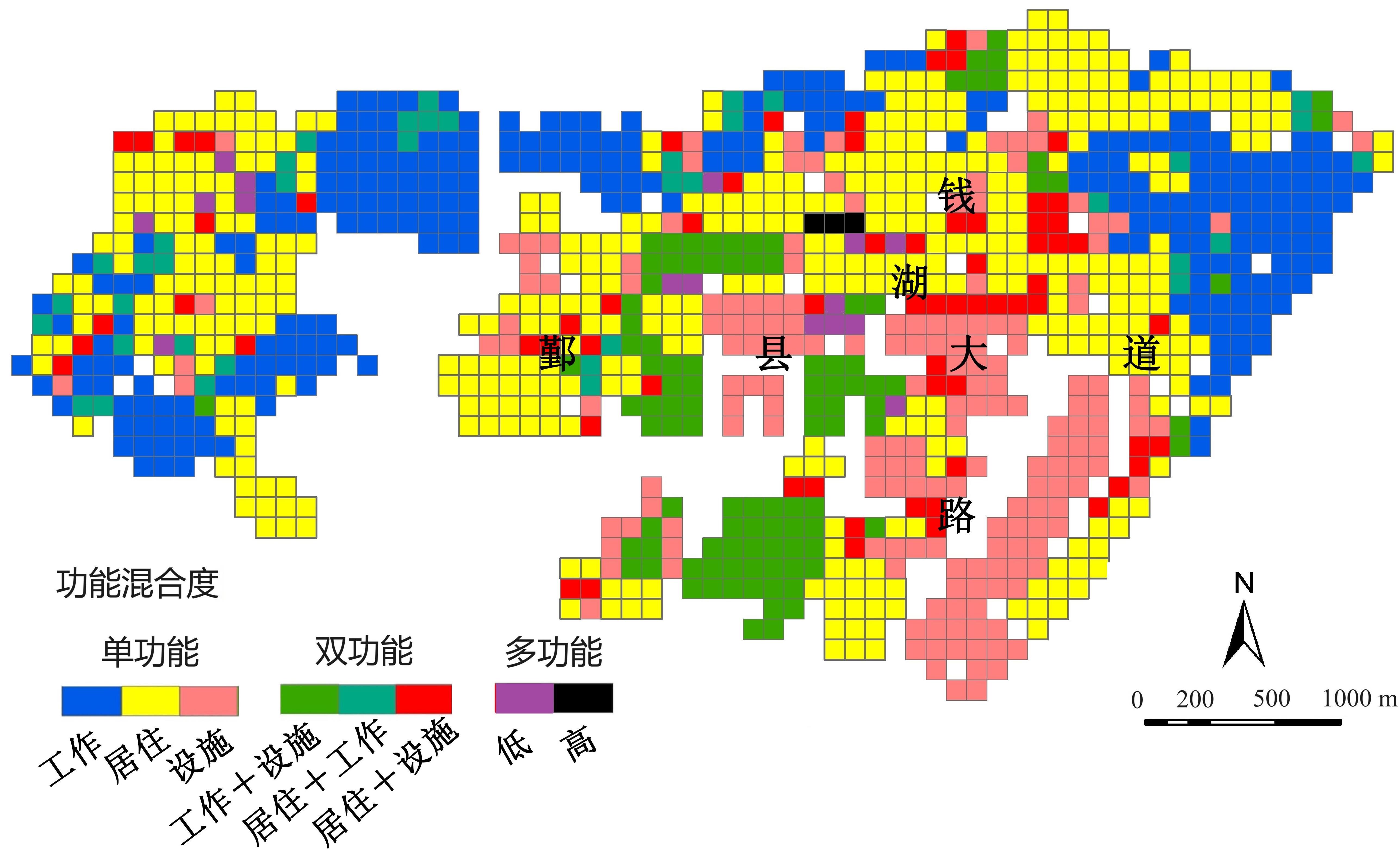
图9 鄞州新城区功能混合度空间分布Fig.9 Spatial distribution of functional mix degree in Yinzhou new urban district |
表1 空间句法分析的高、中、低值的界定Table 1 Definition of high, medium and low values in spatial syntax analysis |
| 分析方法 | 分析值 | 界定 |
|---|---|---|
| 空间句法 | 高 | 全局和局部NACH分析值均为高 |
| 全局和局部NACH分析值一为高且另一为中 | ||
| 中 | 全局和局部NACH分析值均为中 | |
| 全局和局部NACH分析值一为高且另一为低 | ||
| 低 | 全局和局部NACH分析值均为低 | |
| 全局和局部NACH分析值一为中且另一为低 |

王肖惠:主要完成论文撰写、数据处理、图片绘制;
叶 宇:论文核心思想提出及文章修改;
杨 兰:论文数据的搜集与处理;
王龙升:论文主要思路把控、部分重难点数据处理及部分图片绘制;
车 茜,宋彦华,姚士谋:主要完成文章校对修改。
|
Alberti M. 1996. Measuring Urban Sustainability. Environment Impact Assessment Review, 16: 213-221.
|
|
Berghauser Pont M, and Haupt P. 2010. Spacematrix-Space, Density and Urban Form. Rotterdam: Nai Publishers.
|
|
Cervero R. 1998. Transit Metropolis: A Global Inquiry. Washington D C: Island Press.
|
|
蔡智,唐燕,刘畅,马蒂亚斯·德米泽尔. 2021. 三维城市空间形态演进及其地表热岛效应的规划应对——以北京市为例. 国际城市规划,36(5):61-68.
Cai Zhi, Tang Yan, Liu Chang, and Matthias Demuzere. 2021. Analyzing the Transformation of 3D Urban Morphology and Corresponding Surface Heat Island Effect in Beijing. Urban Planning International, 36(5): 61-68.
|
|
曹可心,邓羽. 2021. 可持续城市更新的时空演进路径及驱动机理研究进展与展望. 地理科学进展,40(11):1942-1955.
Cao Kexin, and Deng Yu. 2021. Spatio-Temporal Evolution Path and Driving Mechanisms of Sustainable Urban Renewal: Progress and perspective. Progress in Geography, 40(11): 1942-1955.
|
|
曹小曙,梁斐雯,陈慧灵. 2019. 特大城市空间形态差异对交通网络效率的影响. 地理科学,39(1):41-51.
Cao Xiaoshu, Liang Feiwen, and Chen Huiling. 2019. Influence of Different Spatial Forms for Metropolitans on Transportation Network Efficiency. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 39(1): 41-51.
|
|
段进,殷铭. 2011. 当代新城空间发展演化规律——案例跟踪研究与未来规划思考. 南京:东南大学出版社.
Duan Jin, and Yin Ming. 2011. Spatial Evolution of Contemporary New Town in China: Case Follow-up Study and Future Planning. Nanjing: Southeast University Press.
|
|
冯奎. 2018. 中国新城新区发展报告:2018. 北京:企业管理出版社.
Feng Kui. 2018. China New City New District Development Report: 2018. Beijing: Enterprise Management Press.
|
|
He Qingsong, He Weishan, Song Yan, Wu Jiayu, Yin Chaohui, and Mou Yanchuan. 2018. The Impact of Urban Growth Patterns on Urban Vitality in Newly Built-up Areas Based on an Association Rules Analysis Using Geographical "Big Data". Land Use Policy, 78: 726-738.
|
|
Hillier B, and Hanson J. 1984. The Social Logic of Space. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
|
|
黄群芳. 2021. 城市空间形态对城市热岛效应的多尺度影响研究进展. 地理科学,41(10):1832-1842.
Huang Qunfang. 2021. Effects of Urban Spatial Morphology on Urban Heat Island Effect from Multi-Spatial Scales Perspectives. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 41(10): 1832-1842.
|
|
Lang W, Chen T, and Chan H W. 2019. Understanding Livable Dense Urban form for Shaping the Landscape of Community Facilities in Hong Kong Using Fine-Scale Measurements. Cities, 84: 34-45.
|
|
Larkin A, Gu X, Chen L, and Hystad P. 2021. Predicting Perceptions of the Built Environment Using GIS, Satellite and Street View Image Approaches. Landscape and Urban Planning, 216: 104257.
|
|
林仲煜. 2009. 近郊新城可持续形态的构建. 重庆:重庆大学.
Lin Zhongyu. 2009. Construction of Sustainable Form of Suburban New Town. Chongqing: Chongqing University.
|
|
Liu Jingming, Hou Xianhui, and Xia Chuyu. 2021. Examining the Spatial Coordination between Metrorail Accessibility and Urban Spatial Form in the Context of Big Data. Land, 6: 125-136.
|
|
Lynch K. 1981. A Theory of Good City Form. Cambridge: The MIT Press.
|
|
Jabareen Y R. 2006. Sustainable Urban Form: Their Typologies, Models and Concepts. Journal of Planning Education and Research, 26: 38-52.
|
|
Meng Yuan, and Xing Hanfa. 2019. Exploring the Relationship between Landscape Characteristics and Urban Vibrancy: A Case Study Using Morphology and Review Data. Cities, 95: 102389.
|
|
Rowley A. 1994. Definitions of Urban Design: The Nature and Concerns of Urban Design. Planning Practice and Research, 9(3): 179-197.
|
|
Rogers R. 1998. Cities for a Small Planet. Boulder: Westview Press.
|
|
Scheel A Z, and Barrientos M. 2019. Analysis of the Effects of Urban Form on Neighborhood Vitality: Five Cases in Valdivia, Southern Chile. Journal of Housing and the Built Environment, 34(3): 897-925 .
|
|
Song Yongze, Long Ying, Wu Peng, and Wang Xiangyu. 2018. "Are All Cities with Similar Urban Form or Not? Redefining Cities with Ubiquitous Points of Interest and Evaluating Them with Indicators at City and Block Levels in China". International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 32(12): 2447-2476.
|
|
隋洪鑫,杨秀,徐姗,周道静. 2020. 城市功能空间更新研究进展与新时期重点方向. 热带地理,40(6):1150-1160.
Sui Hongxin, Yang Xiu, Xu Shan, and Zhou Daojing. 2020. Progress and Hot Research on Urban Functional Space Renewal in the New Era. Tropical Geography, 40(6): 1150-1160.
|
|
Talen E. 2011. Sprawl Retrofit: Sustainable Urban Form in Unsustainable Places. Environ. Plan B, 38: 952-978.
|
|
Usman A S, and Zakri W M. 2017. Towards Sustainable Urban Form: A Comparative Analysis of Two Urban Neighborhoods in Kano, Nigeria. Advanced Science Letters, 23(7): 6367-6371.
|
|
Van N A, and Stolk E. 2012. Degrees of Sustainable Location of Railway Stations: Integrating Space Syntax and Node Place Value Model on Railway Stations in the Province Noord-Holland's Strategic Plan for 2010-2040. (2012-01-17) [2022-10-01]. http://sss8.cl/8005.pdf.
|
|
王肖惠,陈爽,姚世谋,张殷俊. 2017. 长三角新城区资源利用效率与环境可持续性评估研究. 人文地理,32(4):68-75.
Wang Xiaohui, Chen Shuang, Yao Shimou, and Zhang Yinjun. 2017. Study on the Assessment of Resource Utilization Efficiency and Environmental Sustainability of New Towns in Yangtze River Delta. Human Geography, 32(4): 68-75.
|
|
王肖惠. 2022. 长三角新城区可持续性及空间形态维度的量化研究. 北京:中国社会出版社.
Wang Xiaohui. 2022. Study on the Sustainability of New Urban Districts and Measuring in Dimension of Urban Morphology in the Yangtze River Delta.Beijing: China Social Press.
|
|
肖扬,Alain C,宋小冬. 2014. 空间句法在城市规划中应用的局限性及改善和扩展途径. 城市规划学刊,(5):32-38.
Xiao Yang, Alain C, and Song Xiaodong. 2014. Limitations of Space Syntax in Urban Planning and Ways to Improve and Expand It. Urban Planning Forum, (5): 32-38.
|
|
许赟,黄一如. 2017. 巴塞罗那扩展区围合式街区的城市更新. 住宅科技,37(10):73-78.
Xu Yun, and Huang Yiru. 2017. Urban Renewal of Enclosed Blocks in the Barcelona Expansion Area. Housing Science, 37(10): 73-78.
|
|
Ye Y, and Van N A. 2014. Measuring Urban Maturation Processes in Dutch and Chinese New Urban Districts: Combining Street Network Configuration with Building Density and Degree of Land Use Diversification through GIS. The Journal of Space Syntax, 4(1): 18-37.
|
|
Ye Y, Li D, and Liu X. 2018. How Block Density and Typology Affect Urban Vitality: An Exploratory Analysis in Shenzhen, China. Urban Geography, 39: 4, 631-652.
|
|
叶宇,庄宇,张灵珠,阿克丽丝·凡·内斯. 2016. 城市设计中活力营造的形态学探究——基于城市空间形态特征量化分析与居民活动检验. 国际城市规划,(1):26-33.
Ye Yu, Zhuang Yu, Zhang Lingzhu, and Akkelies van Nes. 2016. Designing Urban Spatial Vitality from Morphological Perspective: A Study Based on Quantified Urban Morphology and Activities' Testing. Urban Planning International, (1): 26-33.
|
|
Zhang Anqi, Xia Chang, and Li Weifeng. 2022. Relationships between 3D Urban Form and Ground-Level Fine Particulate Matter at Street Block Level: Evidence from Fifteen Metropolises in China. Building and Environment, 3: 263-275.
|
|
中华人民共和国建设部. 2002. GB50180-93城市居住区规划设计规范. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社.
Ministry of Construction of the PRC. 2002. GB50180-93 Code for Planning and Design of Urban Residential Areas. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press.
|
|
中华人民共和国原城乡建设环境保护部. 1991. 城市用地分类与规划建设用地标准:GBJ 137-90. 北京:中国计划出版社.
Former Ministry of Urban Rural Construction and Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. 1991. Urban Land Classification and Planning Construction Land Standard: GBJ 137-90. Beijing: China Planning Press.
|
|
中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 2021. 城市居住区规划设计标准(GB50180-2018). 北京:中国建筑工业出版社.
Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. 2021. Standard for Planning and Design of Urban Residential Areas (GB50180-2018).Beijing: China Building Industry Press.
|
|
周建高,王凌宇. 2013. 日本住宅统计调查的内容、特点与启示. 中国名城,(11):25-30.
Zhou Jiangao, and Wang Lingyu. The Content, Characteristics, and Enlightenment of Japan's Residential Statistical Survey. Famous Cities in China, (11): 25-30.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |