

High-Quality Development Path of the "Enclave Economy" from the Perspective of Symbiosis: A Case Study of Guangqing Economic Cooperation Zone (Guangde Park)
Received date: 2023-06-14
Revised date: 2023-08-04
Online published: 2023-12-15
The "enclave economy" is an important governance tool for promoting regional integration. Guangdong Province occupies the leading position in exploring the "enclave economy" model in China, which has effectively promoted the development of the east and northwest of Guangdong Province through the "point to area" approach. However, certain problems that are associated with the "enclave economy" concept, including a weak level of industrial relatedness, disconnection with the development of the local urban system, and inadequate interest driving mechanisms, need to be urgently addressed. The article aims to explore the high-quality development path of the "enclave economy" in the new era, taking advantage of the symbiosis theory. Based on field research and semi-structured interview methods, the present study attempts to not only probe into the cooperative relationship and mutually beneficial symbiosis mechanism among different actors in the "enclave economy" but also explore a more sustainable and mutually beneficial development "enclave economy" model. With respect to theoretical contribution, based on the symbiosis theory and the characteristics of the "enclave economy", this study facilitates a better understanding of the high-quality development logic of the "enclave economy" from the perspective of symbiosis in particular and establishes a theoretical framework comprising the "industrial symbiosis network-industrial symbiosis unit-interest symbiosis mechanism" components. Empirically, this study takes the Guangqing Economic Cooperation Zone (Guangde Park) as the case study; reveals the development process and problems of the "enclave economy", including the isolation of industry transplantation, fragmentation of industry-city units, and locking of interests and mismatch between rights and responsibilities; and proposes high-quality development strategies, such as establishing a cross-regional "enclave economic circle", a resource-linking platform between industry and city, and a community of interests in industrial parks and towns, to form a more sustainable symmetric and mutually beneficial symbiotic mechanism. The key contribution of this study lies in the theoretical framework for the high-quality development of the "enclave economy" through the lens of symbiosis, which enriches the ways of analysis and cognitive logic of the "enclave economy" and advances cross-regional cooperation and "enclave economy" research. It enhances the cross-territorial geographic thinking of regional cooperation and "enclave economy" research, holding the potential to provide decision-making references for the promotion of regional coordinated development in Guangdong Province in the new period. It also has practical application value for relieving the pressure of unbalanced and insufficient regional development in China by promoting cross-municipal and cross-provincial cooperation.
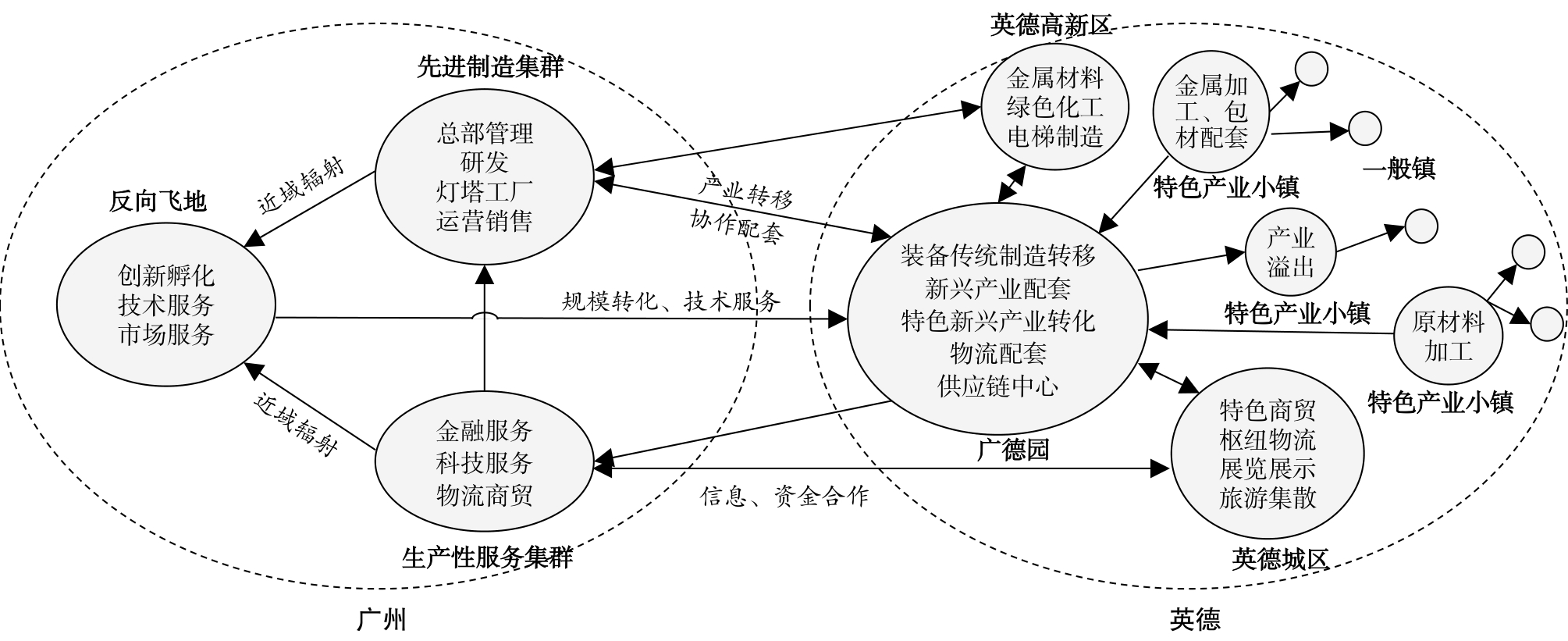
Xianfeng Xu , Jili Xu , Jiangchun Yao , Jialing Huang , Sicong Hu . High-Quality Development Path of the "Enclave Economy" from the Perspective of Symbiosis: A Case Study of Guangqing Economic Cooperation Zone (Guangde Park)[J]. Tropical Geography, 2023 , 43(12) : 2263 -2273 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003782
表1 广东省重要飞地经济基本情况Table 1 Important enclaves in Guangdong Province |
| 名称 | 合作方 | 开始时间 | 合作内容 | 共生模式 | 飞地面积/km2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 广清经济特别合作区 | 广州—清远 | 2010年 | 以“三园一城”为主体,双方合作共同推进产业协同、交通连接、空间发展等各方面。 | 由不成功的对称互惠共生转向非对称互惠共生(飞入地受益更高),未来逐步向对称互惠共生发展 | 127.9 |
| 深汕特别合作区 | 深圳—汕尾 | 2011年 | 4个街镇行政区范围,深圳全面接管合作区各项事务。 | 非对称互惠共生(飞出地受益更高) | 68.3 |
| 莞韶园 | 东莞—韶关 | 2016年 | 以莞韶园为主体,产业转移和帮扶为主要内容。 | 偏利共生(主要是飞入地受益) | 8.6 |
| 佛云园、云浮新兴新成产业园 | 佛山—云浮 | 2013年 | 以佛云园、云浮新兴新成产业园为主体,产业转移和帮扶为主要内容。 | 偏利共生(主要是飞入地受益) | 51.7 |
| 广州(梅州)产业转移工业园 | 广州—梅州 | 2008年 | 包含北区(东升工业园)与南区(畲江工业园),穗梅对口帮扶的重要举措,广州提供部分无偿建设资金、共建公益性设施,并推动产业转移 | 偏利共生(主要是飞入地受益) | 12.9 |
表2 主要访谈对象信息Table 2 Information of main interviewees |
| 类型 | 编号 | 单位 | 访谈时间 | 访谈形式 | 访谈内容 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 企业管理 人员 | A | 园区企业甲 | 2021年 9月 | 面对面访谈 | 企业产值、员工规模、供应链分布等基本情况;企业选择转移的原因;转移后企业发展的主要问题 |
| B | 园区企业乙 | ||||
| 行政管理 人员 | C | 广德园管委会 | 2023年 5月 | 电话访谈 | 园区发展历程;产业合作成效;行政管理机制、利益分配机制、规划建设协同等方面的成效与问题 |
| D | |||||
| E | 英德市自然资源和规划局 | 面对面访谈 | |||
| 规划设计 人员 | F | 广州市城市规划勘测 设计研究院 | 2023年 4月 | 面对面访谈 | 园区区位、用地、空间布局、公共服务设施布局、规划协同等方面的基本情况与主要问题 |
| G |
“顺德企业一开始扩大生产规模比较大,但在考察并签约转移后,由于经济形势发生了比较大的变化,扩产需求几乎没有了,以RS电器为首的13家家电上下游企业最终均未投产,成体系转移顺德家电产业集群的设想没有实现。”
“2017年广东省委主要领导视察了园区,做出了由广州市承接园区对口共建任务的批示;2018年黄埔区代表广州市全面承接园区开发建设工作。”
“我们企业有很强的物流需求,但是主要还是通过外包给珠三角的物流企业解决,园区在供应链服务方面的配套还非常不足。”
表3 广德园、周边镇区规划用地结构与规划标准对照 (%)Table 3 Comparison of the planned land use structure and planning standards of the Guangde Industrial Park and the surrounding townships |
| 用地类型 | 广德园 | 英红镇区 | 横石塘镇区 | 规划城市建设用地标准 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 居住用地 | 13.5 | 30.2 | 44.0 | 20~32 |
| 公共管理与公共服务设施用地 | 2.2 | 2.8 | 9.0 | 5~8 |
| 商业服务业设施用地 | 9.5 | 2.7 | 11.4 | - |
| 工业用地 | 54.5 | 33.4 | 0 | 15~30 |
| 物流仓储用地 | 1.6 | 4.8 | 0 | - |
| 道路与交通设施用地 | 10.7 | 17.6 | 19 | 10~25 |
| 公用设施用地 | 2.9 | 0.5 | 0.56 | - |
| 绿地与广场用地 | 5.3 | 7.9 | 15.7 | 10~15 |
表4 飞地园区参与产业分工的重点环节与模式引导Table 4 Key aspects and models of industrial park participation in industrial division of labor in enclave economy |
| 重点协作领域 | 价值链环节 | 合作模式 | 产业分工 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 广州黄埔区 | 广德园 | |||
| 精细化工 | 精细石油化工、化学制药、工业气体、电子化学品 | 日化美妆、绿色涂料、日化产品包材生产等 | 总部+生产 | 飞入地:后台生产 飞出地:总部管理+技术研发+运营销售(反向飞地) |
| 新材料 | 高分子材料、化工新材料、生物新材料等 | 新型建材、锂电池材料、稀有金属新材料 | 研发+转化 | 飞入地:转化基地 飞出地:研发孵化 |
| 汽车及先进 装备制造 | 新能源整车、核心零部件 | 锂电池组装、动力系统、轮毂等非核心零部件 | 总装+配套 | 飞入地:配套零部件 飞出地:总部管理与总装 |

许险峰:负责整体研究框架、飞地经济高质量发展理论模式和实证案例研究;
许吉黎:负责共生理论和区域协调发展理论研究;
姚江春:负责飞地经济实证案例调研、发展历程和问题分析;
黄嘉玲:参与共生理论视角下的飞地经济高质量发展理论模式研究;
胡思聪:参与实证案例调研和实证案例广德园飞地经济高质量发展路径研究。
|
陈诣博,薛聪聪,万国伟. 2022. 浙江乡村“飞地”抱团的发展现状、主要模式与经验启示. 农村经济与科技,33(7):95-97,106.
Chen Zhibo, Xue Chongchong, and Wang Guowei. 2022. The Development Status, Main Model and Experience Enlightenment of Rural Enclaves in Zhejiang Province. Journal of Rural Economy and Science and Technology, 33(7): 95-97, 106.
|
|
邓祥征,金贵,何书金,王成新,李兆华,王占岐,宋马林,杨庆媛,张安录,陈建成. 2020. 发展地理学研究进展与展望. 地理学报,75(2):226-239.
Deng Xiangzheng, Jin Gui, He Shujin, Wang Chengxin, Li Zhaohua, Wang Zhangqi, Song Malin, Yang Qingyuan, Zhang Anlu, and Chen Jiancheng. 2020. Research Progress and Prospect on Development Geography. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(2): 226-239.
|
|
付桂军,齐义军. 2013 .“飞地经济”研究综述. 经济纵横,(12):113-116.
Fu Guijun, and Qi Yijun. 2013. Summary of Research on "Enclave Economy". Economic Review, (12): 113-116.
|
|
高幸,任冬林. 2023. 我国飞地经济内涵的界定与完善. 北方经贸,(3):53-55.
Gao Xing, and Ren Donglin. 2023. Defining and Perfecting the Connotation of China's Enclave Economy. Northern Economy and Trade, (3): 53-55.
|
|
胡航军,张京祥. 2022. 创新型反向飞地——飞地经济模式的跨梯度创新发展. 城市规划,46(9):30-39.
Hu Hangjun, and Zhang Jingxiang. 2022. Innovative Reverse Enclaves-Cross Gradient Innovative Development of Enclave Economy Model. Urban Planning, 46 (9): 30-39.
|
|
李琰. 2021. 飞地经济中地方政府的竞争与合作. 武汉:华中师范大学. DOI:10.27159/d.cnki.ghzsu.2021.002175.
Li Yan. 2021. Competition and Cooperation between Local Governments in Enclave Economy.Wuhan:Central China Normal University. DOI: 10.27159/d.cnki.ghzsu.2021.002175.
|
|
刘佳宁,王茜. 2023. 推动广东区域协调发展的理论分析和实践探讨——基于人均财政收入视角. 新经济,(6):50-60.
Liu Jianing, and Wang Qian. 2023. Theoretical Analysis and Practical Exploration of Promoting Coordinated Regional Development in Guangdong: Based on the Perspective of Per Capita Fiscal Income. New Economy, (6): 50-60.
|
|
刘荣增. 2006. 共生理论及其在我国区域协调发展中的运用. 工业技术经济,(3):19-21.
Liu Rongzeng. 2006. Symbiosis Theory and Its Application in Regional Coordinated Development in China. Industrial Technology and Economy, (3): 19-21.
|
|
何悦,胡品平. 2017. 广东省产业转移园发展现状、问题与梯度转移布局研究. 广东经济,(5):49-53.
He Yue, and Hu Pingping. 2017. Research on the Development Status, Problems and Gradient Transfer Layout of Industrial Transfer Parks in Guangdong Province. Guangdong Economy, (5): 49-53.
|
|
Johnson C M. 2009. Cross-Border Regions and Territorial Restructuring in Central Europe: Room for More Transboundary Space. European Urban and Regional Studies, 16(2): 177-191.
|
|
Perkmann M. 2007. Construction of New Territorial Scales: A Framework and Case Study of the EUREGIO Cross-Border Region, Regional Studies. Taylor & Francis Journals, 41(2): 253-266.
|
|
Pikner T. 2008. Reorganizing Cross-Border Governance Capacity: The Case of the Helsinki-Tallinn Euregio. European Urban and Regional Studies, 15(3): 211-227.
|
|
Robinson G W S. 1959. Exclaves. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 49(3): 283-295.
|
|
孙久文,苏玺鉴. 2020. 新时代区域高质量发展的理论创新和实践探索. 经济纵横,(2):6-14,2.
Sun Jiuwen, and Su Xijian. 2020. Theoretical Innovation and Practical Exploration of Regional High-Quality Development in the New Era. Economic Review, (2): 6-14, 2.
|
|
王绍博,罗小龙,唐蜜,刘峻峰. 2019. 基于共生理论的临京临沪地区跨界融合发展对比研究. 地理科学,39(11):1681-1690.
Wang Shaobo, Luo Xiaolong, Tang Mi, and Liu Junfeng. 2019. Development of Cross-Border Integration of Beijing and Shanghai Based on Symbiosis Theory. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 39(11): 1681-1690.
|
|
文欣中. 2004. 诸侯经济寻破局——从开发区到“飞地经济”. 中国高新区,(4):20-21.
Wen Xinzhong. 2004. The Breakdown of vassal Economy: From Development Zone to "Enclave Economy". Science & Technology Industry PAarks, (4): 20-21.
|
|
许吉黎,叶玉瑶,罗子昕,张虹鸥,王长建,吴康敏. 2022. 新发展格局下粤港澳大湾区高科技产业多尺度空间联系与政策启示. 地理科学进展,41(9):1592-1605.
Xu Jili, Ye Yuyao, Luo Zixin, Zhang Hong'ou, Wang Changjian, and Wu Kangmin. 2022. Multi-Scalar Spatial Linkages Initiated by High-Tech Industries in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and Policy Implications Against the Backdrop of China's New Development Paradigm. Progress in Geography, 41(9): 1592-1605.
|
|
许树辉,王利华. 2015. 区域产业转移与欠发达地区产业结构升级研究综述. 热带地理,35(2):284-290.
Xu Shuhui, and Wang Lihua. 2015. Review of the Study on Relationship between industry Transfer and Industry Structural Update in Developing Regions. Tropical Geography, 35(2): 284-290.
|
|
许树辉. 2017. 产业转移下的广东省制造业空间集聚与区际分工演变——基于2005―2014年统计数据. 热带地理,37(3):347-355.
Xu Shuhui. 2017. Evolution of Spatial Agglomeration of Manufacturing Industry and Regional Division of Labor Driven in Guangdong Province under the Industrial Transfer: Based on the Analysis of Statistical Data during 2005-2014. Tropical Geography, 37(3): 347-355.
|
|
许闻博,李福映. 2019. 大都市区域合作的“飞地”模式特征初探——以深圳为例// 中国城市规划学会. 中国城市规划年会论文集.北京:中国建筑工业出版社,9. DOI:10.26914/c.cnkihy.2019.045999.
Xu Wenbo, and Li Fuying. 2019. A Preliminary Study on the Characteristics of the "Enclave" Mode of Regional Cooperation in Metropolises: Take Shenzhen as an Example. In: Urban Planning Society of China. Proceedings of the 2019 China Urban Planning Annual Conference. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 9. DOI: 10.26914/c.cnkihy. 2019. 045999.
|
|
徐蕴清,窦西其,陈雪. 2022. 国际知识转移视角下的跨区域飞地合作——苏州工业园区从飞入到飞出的知识转移和迭代. 城市发展研究,29(12):62-71.
Xu Yunqing, Dou Xiqi, and Chen Xue. 2022. Cross Regional Enclave Cooperation from the Perspective of International Knowledge Transfer-Knowledge Transfer and Iteration from Flying in to Flying out of Suzhou Industrial Park. Urban Development Research, 29 (12): 62-71.
|
|
杨玲丽. 2014.超越“嵌入性”约束,共建产业园——苏州工业园“飞地经济”促产业转移. 经济体制改革,(3):105-109.
Yang Lingli. 2014. Beyond the "Embeddedness" Constraint, to Build an Industrial Park: Suzhou Industrial Park "Enclave Economy" to Promote Industrial Transfer. Journal of Economic System Reform, (3): 105-109.
|
|
姚江春,朱江,姜浩,李翔. 2023. 基于生态产品价值实现的生态型地区城乡融合路径研究——以粤北生态发展区为例. 自然资源学报,38(8):2169-2183.
Yao Jiangchun, Zhu Jiang, Jiang Hao, and Li Xiang. 2023. Research on the Path of Urban-Rural Integration in Ecological Areas Based on the Realization of the Value of Ecological Products. Journal of Natural Resources, 38(8): 2169-2183.
|
|
姚远,周博雅. 2021. “飞地经济”何以为继——基于主体关系研究视角. 中共青岛市委党校 青岛行政学院学报,(6):43-49.
Yao Yuan, and Zhou Boya. 2021. How Does Enclave Economy Continue: A Perspective on Subject Relations. Journal of the Party School of C.P.C. Qingdao Municipal Committee and Qingdao Administrative Institute, (6): 43-49.
|
|
姚丹燕,刘云刚. 2019. 从域外领土到飞地社区:人文地理学中的飞地研究进展. 人文地理,34(1):20-27.
Yao Danyan, and Liu Yungang. 2019. From Overseas Territory to Enclave Community: Research on Transmutation of Enclave in Human Geography. Human Geography, 34(1): 20-27.
|
|
于代松,肖雅丽,赵佳伟,兰虹. 2020. “飞地经济”共赢发展的基本条件:一个初步的分析框架——以成都甘孜共建成甘工业园区为例. 西华大学学报(哲学社会科学版),39(2):74-83.
Yu Daisong, Xiao Yali, Zhao Jiawei, and Lan Hong. 2020. Basic Conditions for Win-Win Development of "Enclave Economy": A Preliminary Analytical Framework: Take the Example of Chengdu Ganzi to Jointly Build Gansu Industrial Park. Journal of Xihua University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), 39(2): 74-83.
|
|
张日波,钱姝凡. 2023. 飞地经济中的“猎鹿困境”及其消解——基于博弈分析的视角. 浙江树人大学学报,23(2):30-39.
Zhang Ribo, and Qian Shufan. 2023. Dilemma and Resolution of the Stag Hunt Game in Enclave Economy: Based on the Perspective of Game Theory Model. Journal of Zhejiang Shuren University, 23(2): 30-39.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |