

Using Cultural Flowscapes to Construct a Place Components Framework: A Case Study of Fenghuang Ancient Town
Received date: 2023-01-02
Revised date: 2023-04-13
Online published: 2024-01-20
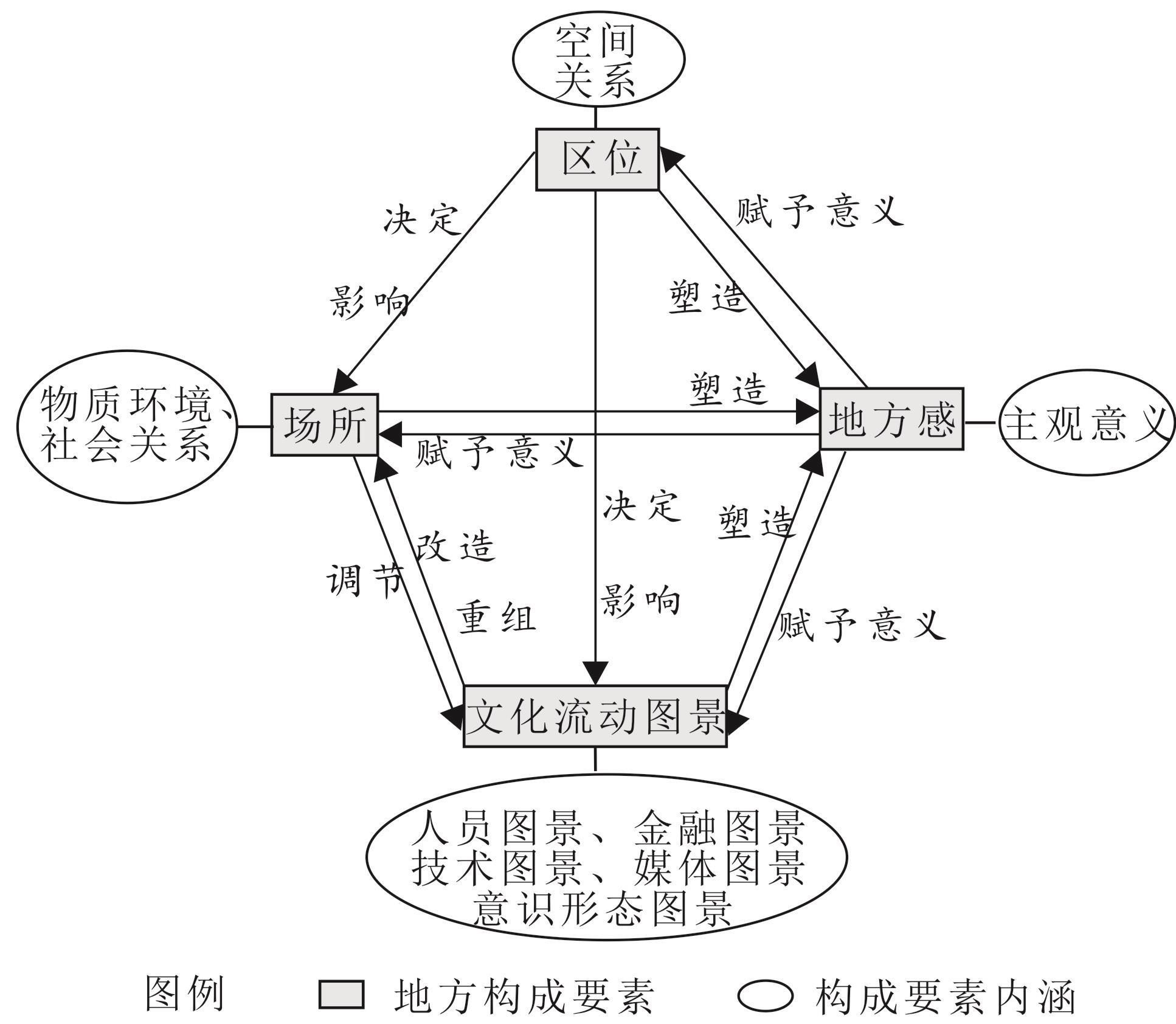
Place is a central concept and research object in cultural geography. Analyzing place components is a prerequisite for an integrated understanding of place and a core component of place theory in cultural geography. Previous studies have focused on either spatially fixed or mobile components in analytical frameworks, both of which capture different dimensions of place. However, few studies have considered both the fixed and mobile components and the interactions between them. Based on the classical framework of place components proposed by John Agnew (1987) and coupled with cultural flowscapes, this study proposes a new Analytical Framework for Place Components (AFPC) that reveals the elements of place. Taking the tourist destination of Fenghuang Ancient Town (FAT) as a case study and collecting data through observation and interviews, this study presents a preliminary empirical application of the AFPC. The results suggest that place comprises four components: location, locale, sense of place, and cultural flowscapes. Cultural flowscapes include the interrelated concepts of ethnoscapes, mediascapes, technoscapes, financescapes, and ideoscapes. The AFPC meets the scientific requirements of universality, independence, and application. It reveals the complexity of contemporary places and can be used to guide the empirical analysis of small-scale local characteristics or local specificality. The FAT case study fully reveals the multi-element features and interrelationships between the components. It was found that the location of the FAT is relatively poor, and the land-use pattern is mainly commercial. Social relationships in FAT are mainly commercial, social contact among residents is weak, and the sense of place for the different groups differed, Cultural flowscapes are dynamic and can play an active role in driving change or transformation of the locale of FAT. The locale has a mediating effect on cultural flowscapes. The location of FAT determines cultural flowscapes to some extent and partly affects the locale. Cultural flowscapes, location and locale together shape the sense of place of FAT, and the sense of place in turn gives specific meaning to the other three elements. The theoretical contributions of this study are that the AFPC considers both fixed and mobile elements of place components, and that place components are interactive, which helps enrich the theoretical perspective of place component research and expands the scope of application of place components theory. In practice, the research results can provide practical guidance for decision-makers in tourism destination development and rural revitalization, emphasizing that sustainable local development requires synergy between local and external elements.
Yongming Wang , Jingxian Tian , Lingling Jiang . Using Cultural Flowscapes to Construct a Place Components Framework: A Case Study of Fenghuang Ancient Town[J]. Tropical Geography, 2024 , 44(1) : 164 -174 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.003810

1 也有文献将后缀“scape”翻译成景观。文化景观曾是传统文化地理学研究的核心对象,是指地球表面可识别出的一块区域。而Appadurai所指的文化流动是指各类流动的现象,与文化地理学中的文化景观并没有直接联系,因此为了区分,本文翻译成“图景”。
2 该参考文献来源于凤凰县政府内部资料《凤凰历史文化名城保护规划》(2002年)。
3 https://map.baidu.com/
4 凤凰县政府官方网站“魅力凤凰”版块. http://www.fhzf.gov.cn/jrfh/。
王永明:分析框架构建及研究设计,实地调研及资料分析,论文撰写与修改;
田静娴:论文修改,文稿校对,英文翻译;
姜玲玲:图形制作,论文修改。
|
Adey P. 2006. If Mobility is Everything Then It is Nothing: Towards a Relational Politics of (IM) Mobilities. Mobilities, 1(1): 75-94.
|
|
Adey P. 2009. Mobility. London: Routledge.
|
|
Agnew J A. 1987. Place and Politics: The Geographical Mediation of State and Society. Boston M A: Allen and Unwin.
|
|
Anderson J. 2010. Understanding Cultural Geography: Places and Traces. New York: Routledge.
|
|
Appadurai A. 1996. Mordernity at Large: Cultural Dimensions of Globalization. Minneapolis: The University of Minnesota.
|
|
白凯,胡宪洋,吕洋洋,杜涛. 2017. 丽江古城慢活地方性的呈现与形成. 地理学报,72(6):1104-1117.
Bai Kai, Hu Xianyang, Lyu Yangyang, and Du Tao. 2017. Study on the Identity with Placeness of Slow Living in Lijiang. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(6): 1104-1117.
|
|
Castree N. 2003. Place: Connections and Boundaries in an Interdependent World. In: Holloway L, Rice P, and Valentine G. Key Concepts in Geography. London: Sage, 167-182.
|
|
Conner N. 2014. Global Cultural Flows and the Routes of Identity: The Imagined Worlds of Celtic FC. Social & Cultural Geography, 15(5): 525-546.
|
|
Cresswell T. 2004. Place: A Short Introduction. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing.
|
|
Cresswell T. 2006. On the Move: The Politics of Mobility in the Modern West. London: Routledge.
|
|
Cresswell T. 2011. Place: The Wiley-Blackwell Companion to Human Geography. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing.
|
|
Degen M M and Rose G. 2012. The Sensory Experiencing of Urban Design: The Role of Walking and Perceptual Memory. Urban Studies, 49(15): 3271-3287.
|
|
大卫·哈维. 2010. 正义、自然和差异地理学. 胡大平,译. 上海:上海人民出版社.
Harvey D. 2010. Justice, Nature and the Geography of Difference. Hu Daping, trans. Shanghai: Shanghai People's Publishing House.
|
|
董士鸿,梁炳琨. 2011. 建构怀旧地方——以高雄市怀旧餐厅“新台湾的原味”为例. 华冈地理学报,(27):19-35.
Tung Shih-Hung and Liang Bang-Kuen. 2011. The Construction of Nostalgic Place: A Case Study of Kaohsiung Nostalgic Restaurant "New Taiwanese Original". Geographical Journal of Huagang, (27): 19-35.
|
|
Entrikin J N. 1991. The Betweenness of Place: Toward a Geography of Modernity. London: Macmillan.
|
|
凤凰县统计局. 2001—2019. 凤凰县国民经济和社会发展统计公报(2001-2019). (2020-04-18)[2021-12-01]. [Fenghuang County Statistics Bureau. 2001-2019. Statistical bulletin of National Economic and Social Development of Fenghuang County (2001-2019). (2020-04-18)[2021-12-01]. http://www.fhzf.gov.cn/zwgk_49798/xxgkml/bmxxgkml_49803/fhxtjj/tjjgzzt/rsxx_23031/.
|
|
Gorman-Murray A and Nash C J. 2014. Mobile Places, Relational Spaces: Conceptualizing Change in Sydney's LGBTQ Neighborhoods. Environment and Planning D: Society and Space, 32(4): 622-641.
|
|
Gregory D, Johnston R, Pratt G, Watts M, and Whatmore S. 2009. The Dictionary of Human Geography. 5th Editon. Oxford: Blackwell.
|
|
高权,钱俊希. 2016. “情感转向” 视角下地方性重构研究——以广州猎德村为例. 人文地理,31(4):33-41.
Gao Quan and Qian Junxi. 2016. Negotiating Place-Restructuring from the Perspective of Emotional Geographies: A Case Study of Liede Village, Guangzhou. Human Geography, 31(4): 33-41.
|
|
Hannam K. 2008. Tourism Geographies, Tourist Studies and the Turn Towards Mobilities. Geography Compass, 2(1): 127-139.
|
|
黄嘉玲,何深静. 2014. 非洲裔移民在穗宗教场所地方感特征及其形成机制——基于广州石室圣心大教堂的实证研究. 热带地理,34(3):308-318.
Huang Jialing and He Shenjing. 2014. Profile and Determinants of African Immigrants' Sense of Place in Religious Space: A Case Study of Guangzhou Sacred Heart Cathedral. Tropical Geography, 34(3): 308-318.
|
|
Jones M. 2009. Phase Space: Geography, Relational Thinking, and Beyond. Progress in Human Geography, 33(4): 487-506.
|
|
Keating M. 2001. Rethinking the Region: Culture, Institutions and Economic Development in Catalonia and Galicia. European Urban and Regional Studies, 8(3): 217-234.
|
|
刘晨,朱竑,安宁. 2014. 文学旅游地的社会文化建构:以凤凰古城为例. 旅游学刊,29(7):68-76.
Liu Chen, Zhu Hong, and An Ning. 2014. The Sociocultural Construction of Literary Places: A Case Study of Fenghuang. Tourism Tribune, 29(7): 68-76.
|
|
Massey D. 1994. Space, Place and Gender. Cambridge: Polity.
|
|
Massey D. 2005. For Space. London & Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
|
|
Milbourne P and Kitchen L. 2014. Rural Mobilities: Connecting Movement and Fixity in Rural Places. Journal of Rural Studies, 34(4): 326-336.
|
|
Oswin N and Yeoh B S A. 2010. Introduction: Mobile City Singapore. Mobilities, 5(2): 167-175.
|
|
潘绥铭,姚星亮,黄盈盈. 2010. 论定性调查的人数问题:是“代表性”还是“代表什么”的问题——“最大差异的信息饱和法”及其方法论意义.社会科学研究,(4):108-115.
Pan Suiming, Yao Xingliang, and Huang Yingying. 2010. On the Question of the Number of Qualitative Surveys: Whether It is "Representative" or "Representative of What": Information Saturation with the Most Difference and Its Methodological Significance. Social Science Research, (4): 108-115.
|
|
Pred A. 1986. Place, Practice and Structure: Social and Spatial Transformation in Southern Sweden. Cambridge: Polity Press.
|
|
Relph E. 1976. Place and Placelessness. London: Routledge.
|
|
Sack R D. 1997. Homo Geographicus. Baltimore and London: The Johns Hopkins University Press.
|
|
Sheller M and Urry J. 2006. The New Mobilities Paradigm. Environment and Planning A, 38(2): 207-226.
|
|
Storper M and Venables A J. 2004. Buzz: Face to Face Contact and the Urban Economy. Journal of Economic Geography, 4(4): 351-370.
|
|
Su X. 2015. Urban Entrepreneurialism and the Commodification of Heritage in China. Urban Studies, 52(15): 2874-2889.
|
|
孙九霞,周一. 2015. 遗产旅游地居民的地方认同——“碉乡”符号、记忆与空间. 地理研究,34(12):2381-2394.
Sun Jiuxia and Zhou Yi. 2015. Residents' Place Identity at Heritage Sites: Symbols, Memories and Space of the "Home of Diaolou". Geographical Research, 34(12): 2381-2394.
|
|
孙九霞,庞兆玲,王学基. 2020. 现代性拓殖与地方响应:少数民族盐业旅游社区的发展实践. 经济地理,40(4):214-222.
Sun Jiuxia, Pang Zhaoling, and Wang Xueji. 2020. Modernity Colonization and Local Response: Development Practice of Minority Salt Tourism Community. Economic Geography, 40(4): 214-222.
|
|
Tuan Y F. 1977. Space and Place: The Perspective of Experience. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
|
|
魏雷,钱俊希,朱竑. 2015. 旅游发展语境中的地方性生产. 华南师范大学学报(社会科学版),(2):99-109.
Wei Lei, Qian Junxi, and Zhu Hong. 2015. The Production of Place under the Context of Tourism Development: A Case Study of Lugu Lake. Journal of South China Normal University (Social Science Edition), (2): 99-109.
|
|
吴必虎,宋治清. 2001. 一种区域旅游形象分析的技术程序. 经济地理,21(4):496-499.
Wu Bihu and Song Zhiqing. 2001. A Framework for Analysis of Regional Tourism Destination Image. Economic Geography, 21(4): 496-499.
|
|
湘西州旅游港澳外事侨务局. 2017. 凤凰棚户区改造一期工程•凤凰南华里项目正式奠基.(2017-07-14)[2020-12-01]. [Xiangxi Prefecture Bureau of Tourism, Hong Kong, Macao and Foreign Affairs and Overseas Chinese Affairs. 2017. The Foundation Stone of Fenghuang Shantytown Reconstruction Phase I Project·Fenghuang Nanhuali Project was Officially Laid. (2017-07-14) [2020-12-01]. http://whhlyt.hunan.gov.cn/news/sxxw/201909/t20190910_5473825.html.
|
|
赵振斌,褚玉杰,郝亭,张铖. 2015. 汉长安城遗址乡村社区意义空间构成. 地理学报,70(10):1606-1621.
Zhao Zhenbin, Chu Yujie, Hao Ting, and Zhang Cheng. 2015. Meaning Space Structure of Rural Community in Han Chang'an City Historical Site. Acta Geographica Sinica, 70(10): 1606-1621.
|
|
中国地图出版社. 2014. 中国地图集(地形版). 北京:中国地图出版社.
China Cartographic Publishing House. 2014. Atlas of China (Topographic Edition). Beijing: China Cartographic Publishing House.
|
|
周尚意,杨鸿雁,孔翔. 2011. 地方性形成机制的结构主义与人文主义分析:以798和M50两个艺术区在城市地方性塑造中的作用为例. 地理研究,30(9):1566-1576.
Zhou Shangyi, Yang Hongyan, and Kong Xiang. 2011. The Structuralistic and Humanistic Mechanism of Placeness: A Case Study of 798 and M50 Art Districts. Geographical Research, 30(9): 1566-1576.
|
|
周尚意,戴俊骋. 2014. 文化地理学概念、理论的逻辑关系之分析:以“学科树”分析近年中国大陆文化地理学进展. 地理学报,69(10):1521-1532.
Zhou Shangyi and Dai Juncheng. 2014. Logic Analysis of Concept and Theory of Cultural Geography: Progress in Cultural Geography in China's Mainland during the Past Decade. Acta Geographica Sinica, 69(10): 1521-1532.
|
|
周尚意,孔翔,朱华晟,朱青. 2016. 地方特性发掘方法——对苏州东山的地理调查. 北京:科学出版社.
Zhou Shangyi, Kong Xiang, Zhu Huashengshen, and Zhu Qing. 2016. The Method of Exploring Placeness: A Geographical Survey of Dongshan in Suzhou. Beijing: Science Press.
|
|
朱阿兴,闾国年,周成虎,秦承志. 2020. 地理相似性:地理学的第三定律? 地球信息科学学报,22(4):673-679.
Zhu Axing, Lv Guonian, Zhou Chenghu, and Qin Chengzhi. 2020. Geographic Similarity: Third Law of Geography? Journal of Geo-Information Science, 22(4): 673-679.
|
|
朱竑,刘博. 2011. 地方感、地方依恋与地方认同等概念的辨析及研究启示. 华南师范大学学报:自然科学版,(1):1-8.
Zhu Hong and Liu Bo. 2011. Concepts Analysis and Research Implications: Sense of Place, Place Attachment and Place Identity. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), (1): 1-8.
|
|
朱竑,李如铁,苏斌原. 2016. 微观视角下的移民地方感及其影响因素——以广州市城中村移民为例. 地理学报,71(4):637-648.
Zhu Hong, Li Rutie, and Su Binyuan. 2016. The Migrants' Sense of Place and Its Influencing Factors on a Microcosmic Perspective:A Case Study of the Migrants in the Urban Villages in Guangzhou. Acta Geographica Sinica, 71(4): 637-648.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |