

Study on the Renewal Satisfaction of Urban Villages in Megacities from the Perspective of Dependence: A Case Study of Wuhan City
Received date: 2024-03-29
Revised date: 2024-06-03
Online published: 2024-08-09
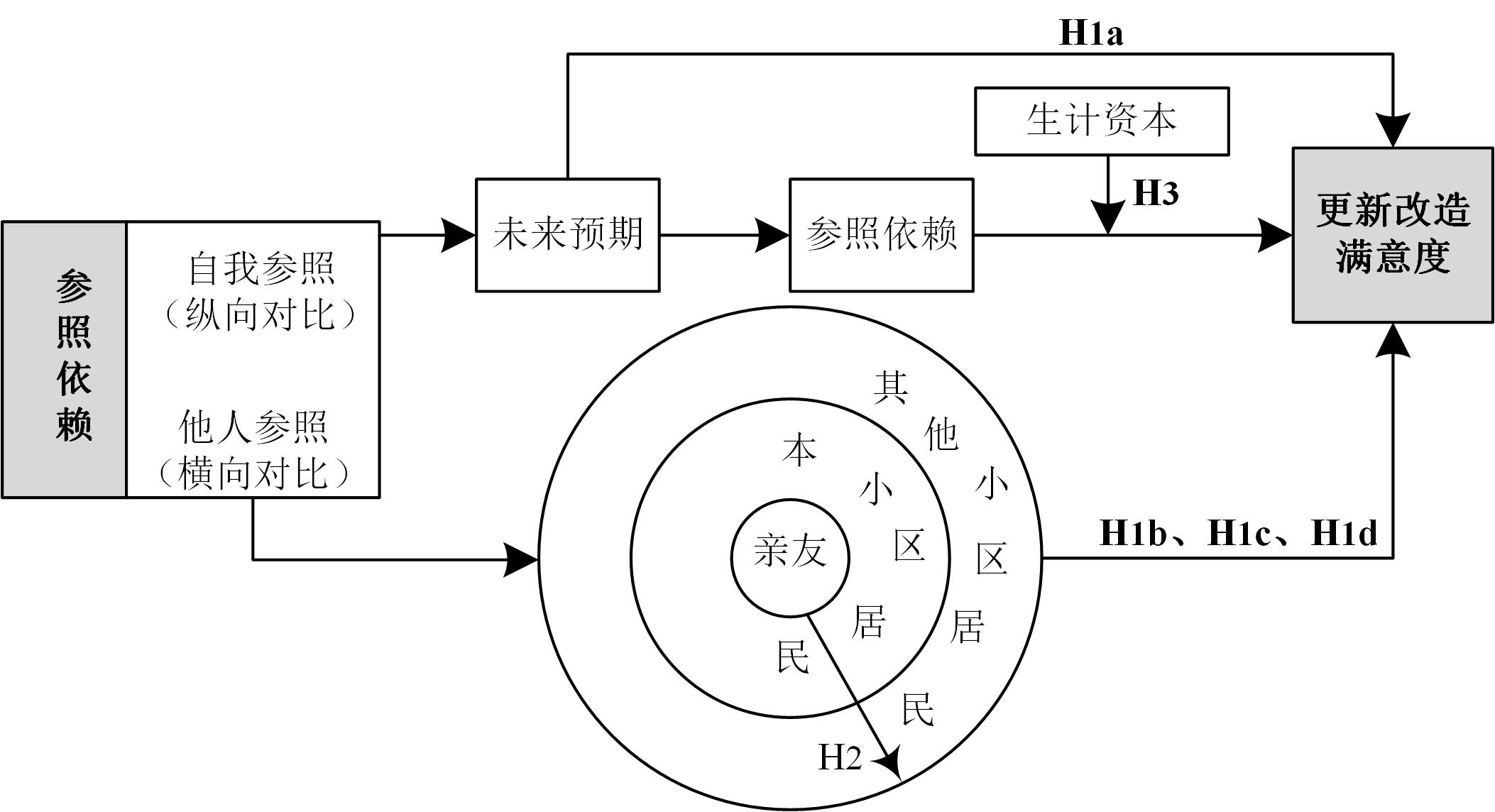
As a unique phenomenon in China's dualistic urban-rural system, the renewal of urban villages, along with the continuous advancement of urbanization, has attracted much attention, because it involves changes in land ownership, compensation for house demolition and relocation, environmental construction, and social security, among other aspects. Resident satisfaction in urban villages is directly related to the issues of policy strengths and weaknesses, resident happiness, and social fairness, and has been widely researched in academia. However, few studies have explored the influence mechanism of satisfaction in urban village renewal from the perspective of reference dependence and have neglected to compare the differences in the levels of different proximity reference points and livelihood capitals. From the perspective of reference dependence, this study analyzes the influence of different proximity reference points on the satisfaction with urban village renewal based on the theory of differential order patterns and tests the moderating effect of livelihood capital on this mechanism. Based on 413 valid samples from two typical urban village renewal areas in Wuhan, this study explored the mechanisms of reference dependence, livelihood capital, and satisfaction with urban village renewal and reconstruction in megacity urban villages using an ordered logistic regression model, a moderating effect model, and other methods. The study found that: 1) reference dependence positively and significantly affected the satisfaction of urban village resettlement residents with renewal and reconstruction; 2) the proximity of the object of reference dependence to one's own relationship was positively correlated with the degree of influence; and 3) livelihood capital positively moderated the relationship between reference dependence and satisfaction with renewal and reconstruction. Policy implications: The design of demolition and relocation compensation policy should strengthen the public participation of villagers, formulate reasonable standards for the identification of legal property rights of housing, and take into account efficiency and fairness by adapting to the local conditions. Efforts should be made to eliminate the influence of the differences in livelihood capital, and improve the cultural quality and skills of resettled villagers through training to reduce the "cultural lag" brought about by the change of identity. Monitoring groups should be set up to oversee the implementation of urban village renewal. This study helps to further elucidate the influence mechanism of satisfaction with urban village renewal and enriches the theoretical application of reference dependence theory in the field of behavioral economics. The findings provide practical experience for reducing social conflicts and public opinion impacts and provides a reference for megacities to actively and steadily implement urban village renewal, thereby improving people's livelihoods, expanding domestic demand, and promoting high-quality urban development.
Qing Yang , Shuzhuo Wang , Yinying Cai . Study on the Renewal Satisfaction of Urban Villages in Megacities from the Perspective of Dependence: A Case Study of Wuhan City[J]. Tropical Geography, 2024 , 44(8) : 1387 -1399 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20240187
表1 2019年武汉市2处更新改造社区调研样本的基本特征Table 1 Basic characteristics of the research sample of two renewal and rehabilitation communities in Wuhan in 2019 |
| 特征 | 类别 | 频数/人 | 比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | 男 | 252 | 61 |
| 女 | 161 | 39 | |
| 年龄/岁 | <35 | 5 | 1.2 |
| 35~45 | 11 | 2.7 | |
| 46~55 | 41 | 9.9 | |
| 56~65 | 165 | 40 | |
| >65 | 191 | 46.2 | |
| 政治面貌 | 中共党员 | 42 | 10.2 |
| 非党员 | 371 | 89.8 | |
| 家庭月收入/元 | <3 000 | 50 | 12.1 |
| [3 000~6 000) | 144 | 34.9 | |
| [6 000~10 000] | 119 | 28.8 | |
| >10 000 | 100 | 24.2 | |
| 受教育年限/a | <6 | 34 | 13.9 |
| 6~8 | 183 | 43.1 | |
| 9~11 | 132 | 28.8 | |
| 12~15 | 56 | 12.3 | |
| ≥16 | 8 | 1.9 | |
| 是否分户 | 是 | 162 | 39.23 |
| 否 | 243 | 60.78 |
表2 拆迁安置村民生计资本评估指标及赋权情况Table 2 Indicators for assessing the livelihood capital of villagers who have been demolished and resettled and their empowerment |
| 一级指标 | 二级指标 | 三级指标 | 指标含义或赋值 | 权重/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 生 计 资 本 | 人力 资本 | 家庭劳动力人数 | 反映家庭劳动能力 | 23.31 |
| 家庭人均受教育年限 | 家庭总受教育年限/家庭成员数 | 4.02 | ||
| 物质 资本 | 人均住房面积 | 家庭住房面积/家庭成员数 | 26.89 | |
| 基础和配套实施状况 (黄海艳 等,2019) | 周边道路交通、停车位数量、教育、商城超市、医疗、供水、供电基础配套设施状况平均值:非常差=1,比较差=2,一般=3,比较好=4,非常好=5 | 8.15 | ||
| 金融资本 | 家庭年总收入 | 通过房屋商铺出租、劳务工作或股份分红等取得的收入 | 18.55 | |
| 社会 资本 | 与街坊邻居之间的关系 | 非常和睦=1,比较和睦=2,一般=3,不太和睦=4,很不和睦=5 | 5.51 | |
| 家庭成员中是否有人任村干部或 城镇干部 | 有=1,没有=2 | 3.40 | ||
| 亲戚朋友中是否有人任村干部或 城镇干部 | 有=1,没有=2 | 5.11 | ||
| 家庭成员中是否有人负责或 参与拆迁改造工作 | 有=1,没有=2 | 1.94 | ||
| 是否有亲戚朋友负责或参与拆迁改造工作 | 有=1,没有=2 | 3.12 |
表3 变量含义及描述性统计分析Table 3 Meaning of variables and descriptive statistical analysis |
| 变量名 | 变量说明 | 变量赋值 | MIN | MAX | MEAN | DV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | 更新改造满意度 | 非常不满意—非常满意=1~5 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 2.76 | 1.03 |
| RD1 | 相比于自身预期的补偿 | 非常差—非常好=1~5 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 2.64 | 0.75 |
| RD2 | 相比于亲戚朋友的补偿 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 2.75 | 0.65 | |
| RD3 | 相比于本小区居民的补偿 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 2.57 | 0.74 | |
| RD4 | 相比于其他小区居民的补偿 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 2.54 | 0.77 | |
| LC | 总生计资本 | 以熵值法赋值 | 0.14 | 0.59 | — | — |
| X 1 | 性别 | 男=0;女=1 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.390 | 0.238 |
| X 2 | 年龄 | 35岁以下= 1;35~45岁= 2;46~55岁= 3;56~65岁= 4;65岁以上=5 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 4.27 | 0.84 |
| X 3 | 政治面貌 | 党员=0;非党员=1 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.900 | 0.092 |
| X 4 | 拆迁实施主体的强势程度 | 非常不强势—非常强势=1~5 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 3.74 | 0.88 |
表4 参照依赖与更新改造满意度相关性分析Table 4 Analysis of the correlation between reference dependence and satisfaction with renewal and reconstruction |
| 变量 | Y | RD1 | RD2 | RD3 | RD4 | X 1 | X 2 | X 3 | X 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y | 1 | ||||||||
| RD1 | 0.708*** | 1 | |||||||
| RD2 | 0.536*** | 0.729*** | 1 | ||||||
| RD3 | 0.570*** | 0.715*** | 0.761*** | 1 | |||||
| RD4 | 0.559*** | 0.629*** | 0.669*** | 0.700*** | 1 | ||||
| X 1 | -0.118** | -0.135*** | -0.145*** | -0.209*** | -0.171*** | 1 | |||
| X 2 | 0.052 | -0.002 | -0.032 | -0.014 | -0.014 | 0.041 | 1 | ||
| X 3 | -0.041 | -0.044 | -0.057 | -0.054 | -0.087* | 0.170*** | -0.053 | 1 | |
| X 4 | -0.476*** | -0.350*** | -0.299*** | -0.338*** | -0.349*** | 0.094* | 0.006 | 0.019 | 1 |
|
表5 模型估计结果Table 5 Model estimation results |
| 变量 | 模型1 | 模型2 | 模型3 | 模型4 | 模型5 | 模型6 | 模型7 | 模型8 | 模型9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RD1 | - | 2.793***(0.042) | - | - | - | 2.942***(0.061) | - | - | - |
| RD2 | - | - | 1.684***(0.064) | - | - | - | 1.739***(0.065) | - | - |
| RD3 | - | - | - | 1.652***(0.057) | - | - | - | 1.632***(0.076) | - |
| RD4 | - | - | - | - | 1.501***(0.055) | - | - | - | 1.581***(0.042) |
| LC | - | - | - | - | - | -0.456(0.513) | -0.969(0.598) | -0.959(0.587) | -0.748(0.592) |
| LC×RD1 | - | - | - | - | - | 6.052*(0.578) | — | - | - |
| LC×RD2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 7.588**(0.772) | - | - |
| LC×RD3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 9.662**(0.699) | - |
| LC×RD4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 9.277***(0.672) |
| X 1 | -0.257*(0.091) | 0.035(0.468) | -0.055(0.083) | 0.023(0.072) | -0.033(0.023) | -0.036(0.071) | -0.065(0.083) | 0.004(0.083) | -0.039(0.082) |
| X 2 | 0.045(0.074) | 0.068*(0.041) | 0.085*(0.047) | 0.042(0.073) | 0.099(0.033) | 0.064(0.041) | 0.074(0.047) | 0.067(0.047) | 0.080*(0.047) |
| X 3 | -0.045(0.121) | 0.019(0.123) | -0.007(0.133) | -0.047(0.236) | 0.031(0.312) | -0.014(0.114) | -0.019(0.132) | -0.039(0.130) | 0.012(0131) |
| X 4 | -0.535***(0.011) | 0.571*** (0.051) | -0.407***(0.047) | -0.678***(0.076) | -0.378***(0.081) | -0.300***(0.041) | -0.393***(0.048) | -0.359***(0.048) | -0.348***(0.048) |
| R² | 0.456 | 0.551 | 0.395 | 0.471 | 0.399 | 0.568 | 0.413 | 0.431 | 0.415 |

杨 青:研究框架设计、数据采集、文稿修改;
望舒卓:数学建模,撰写论文初稿;
蔡银莺:提供研究经费和课题支撑,提供指导性意见。
|
蔡银莺,张小珲,杨青. 2021. 城中村更新住房补偿基底选取及村民政策满意度研究. 华中农业大学学报(社会科学版),(5):138-146,198.
Cai Yinying, Zhang Xiaohui, and Yang Qing. 2021. The Selection of Housing Compensation Base for Urban Village Renewal and Its Impacton Villagers PolicySatisfaction. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University(Social Sciences Edition), (5): 138-146, 198.
|
|
陈凯仁,龙茂乾,李贵才. 2017. 城中村利益相关者改造意愿影响因素——以深圳市上步村为例. 城市问题,(8):96-103.
Chen Kairen, Long Maoqian, and Li Guicai. 2017. Factors Influencing Stakeholders' Willingness to Renovate in Urban Villages: The Case of Shangbu Village in Shenzhen City. Urban Problems, (8): 96-103.
|
|
Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky. 2014. Prospective Theory: An Analysis of Decision under Risk. Estudios de Psicología, 47(2): 263-292.
|
|
DFID. 1999. Sustainable Livelihoods Guidance Sheets. Emergency Nutrition Network, 445: 710.
|
|
Durlauf S and Fafchamps M. 2003. Empirical Studies of Social Capital: A Critical Survey. Journal of Chemical Physics, 92: 3359-3376.
|
|
甘臣林,陈璐,陈银蓉,张苗. 2018. 基于农户满意度的农地转出绩效影响因素分析——以武汉、鄂州两地典型调查样本为例. 资源科学,40(11):2225-2235.
Gan Chenlin, Chen Lu, Chen Yinrong, and Zhang Miao. 2018. Analysis on the Factors That Affect the Farmland Transfer Performance Based on Farmers' Satisfaction: A Typical Survey in Wuhan and Ezhou. Resources Science, 40(11): 2225-2235.
|
|
耿云,黄志基,戴晓冕. 2023. 基层协商视角下城中村改造实施机制优化研究——以广州市X村为例. 城市发展研究,30(10):134-140.
Gen Yun, Huang Zhiji, and Dai Xiaomian. 2023. Research on the Optimization of the Implementation Mechanism of the Urban Village Renewal from the Perspective of Grassroots Consultative Democracy: A Case Study on X Village in Guangzhou. Urban Development Studies, 30(10): 134-140.
|
|
郭瑞. 2017. 城中村改造居民满意度的影响因素——以开封市为例. 城市问题,(7):35-41.
Guo Rui. 2017. Influencing Factors of Residents' Satisfaction in Urban Village Reconstruction:Take Kaifeng City as an example. Urban Problems, (7): 35-41.
|
|
胡安宁. 2019. 主观变量解释主观变量:方法论辨析. 社会,39(3):183-209.
Hu Anning. 2019. Explaining One Subjective Variable with Another: A Methodological Clarification. Chinese Journal of Sociology, 39(3): 183-209.
|
|
黄海艳,蔡银莺. 2019. 城中村拆迁还建居民家庭生计资本的流动特征——以武汉市两个拆迁安置小区为例. 城市问题,(6):86-93.
Huang Haiyan and Cai Yinying. 2019. Characteristics of the Mobility of Household Livelihood Capital of Residents of Urban Villages Who Were Demolished and Relocated for Reconstruction:A Case Study of Two Demolished and Relocated Resettlement Neighbourhoods in Wuhan City. Urban Problems, (6): 86-93.
|
|
Huang Xu, He Dongsheng, Tang Shuangshuang, and Li Xin. 2020. Compensation, Housing Situation and Residents' Satisfaction with the Outcome of Forced Relocation: Evidence from Urban China. Cities, 96C:102436-102436.
|
|
刘守英,王一鸽. 2018. 从乡土中国到城乡中国——中国转型的乡村变迁视角. 管理世界,34(10):128-146,232.
Liu Shouying and Wang Yige. 2018. From Native Rural China to Urban-Rural China: The Rural Transition Perspective of China Transformation. Journal of Management World, 34(10): 128-146, 232.
|
|
孟俊红. 2013. 试论城中村改造中拆迁补偿利益主体的缺位与错位. 中国土地科学,27(2): 28-32,96.
Meng Junhong. 2013. Discussing on the Absence and Misplacement of the Beneficiary of Land Compensation for Reconstructing Villages Within Urban Areas. China Land Science, 27(2): 28-32, 96.
|
|
Nicholas Mukisa, Ramon Zamora, and Tek Tjing Lie. 2020. Assessment of Community Sustainable Livelihoods Capitals for the Implementation of Alternative Energy Technologies in Uganda -Africa. Renewable Energy, 160: 886-902.
|
|
Ordóñez Lisa D, Connolly Terry, and Coughlan Richard. 2000. Multiple Reference Points in Satisfaction and Fairness Assessment. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 133: 329-344.
|
|
Panas Epaminondas Efst. 2013. Homeorhesis and Indication of Association Between Different Types of Capital on Life Satisfaction: The Case of Greeks Under Crisis. Social Indicators Research, 1101: 171-186.
|
|
庞洁,徐珂,靳乐山. 2021. 湿地生态补偿对农户生计策略和收入的影响研究——以鄱阳湖区调研数据为例. 中国土地科学,35(4):72-80,108.
Pang Jie, Xu Ke, and Jin Leshan. 2021. Research on the Impact of Wetland Eco-Compensation on Farmers' Livelihood Strategies and Income: An Empirical Analysis of Poyang Lake Governance Modes for Coordinated Rural Construction Land Transfer. China Land Science, 35(4): 72-80, 108.
|
|
仇叶. 2021. 公平博弈与拆迁秩序——基于两种拆迁补偿模式的比较分析. 中国农村经济,(9):127-144.
Qiu Ye. 2021. Fair Gambling and Demolition Order: A Comparative Analysis Based on Two Demolition Compensation M. Chinese Rural Economy, (9): 127-144.
|
|
Punya P Regmi and Karl E Weber, 1996. Sustainable Agricultural Development for Small Farmers in Nepal: Myth or Reality. Outlook on Agriculture, 25(2): 89-94.
|
|
孙敬水,蔡培培. 2018. 资本异质性与居民收入分配公平满意度——基于人力资本、物质资本、政治资本与社会资本的微观证据. 商业经济与管理,(11):74-87.
Sun Jingshui and Cai Peipei. 2018. Capital Heterogeneity and Residents' Satisfaction of Income Distribution Justice: Based on Micro Evidence of Human Capital, Physical Capital Political Capital and Social Capital. Journal of Business Economics, (11): 74-87.
|
|
谈林沂,郭贯成,唐鹏,王俊龙,孙昊. 2024. 生计资本对农户宅基地退出意愿的影响——基于水平和结构的双重视角. 中国土地科学,38(3):26-37.
Tan Linyi, Guo Guancheng, Tang Peng, Wang Junlong, and Sun Hao. 2024. Impact of Livelihood Capital on Farmers' Willingness to Withdraw from Rural Residential Land: From the Dual Perspectives of Level and Structure. China Land Science, 38(3): 26-37.
|
|
Tan Yongzhong, He Ju, Han Haoying, and Zhang Weiwen. 2019. Evaluating Residents' Satisfaction with Market-Oriented Urban Village Transformation: A Case Study of Yangji Village in Guangzhou, China. Cities, 95: 102394-102394.
|
|
陶然,王瑞民. 2014. 城中村改造与中国土地制度改革:珠三角的突破与局限. 国际经济评论,(3):26-55,24-25.
Tao Ran and Wang Ruimin. 2014. Urban Village Rehabilitation and China's Land System Reform: Breakthroughs and Limitations in the Pearl River Delta. International Economic Review, (3): 26-55, 24-25.
|
|
田莉,陶然,梁印龙. 2020. 城市更新困局下的实施模式转型:基于空间治理的视角. 城市规划学刊,(3):41-47.
Tian Li, Tao Ran, and Liang Yinlong. 2020. Transition of Implementation Pattern in the Predicament of Urban Renewal: A Perspective of Spatial Governance. Urban Planning Forum, (3): 41-47.
|
|
王娟. 2015. 基于村民满意度的城中村改造评价——以郑州市1425份村民调查样本为例. 规划师,31(S2):268-271.
Wang Juan. 2015. Evaluation Of Urban Village Reconstruction Based On The Villagers Satisfaction: 1425 Villagers' Survey Samples in Zhengzhou. Planners, 31(S2): 268-271.
|
|
汪明峰,林小玲,宁越敏. 2012. 外来人口、临时居所与城中村改造——来自上海的调查报告. 城市规划,36(7):73-80.
Wang Mingfeng, Lin Xiaoling, and Ning Yuemin. 2012. Migrant Populations, Temporary Residence, and Urban Villages Renovation:A Survey of Migrant Settlements in Shanghai City Planning Review, 36(7): 73-80.
|
|
王伟军,赵雪雁,李花. 2022. 易地扶贫搬迁对贫困山区农户生计空间的影响机理——以陇南山区为例. 经济地理,42(5):165-174.
Wang Weijun, Zhao Xueyan, and Li Hua. 2022. The Impact Mechanism of Poverty Alleviation Relocation on Farmers' Livelihood Space in Poor Mountainous Areas: A Case of Longnan Mountainous Area. Economic Geography, 42(5): 165-174.
|
|
王跃敏,李建权. 2009. 从“文化堕距”理论看城中村村民的社会化——以太原市城中村改造为例. 理论探索,(3):95-97.
Wang Yuemin and Li Jianquan. 2009. From the Theory of "Cultural Depravity": Socialisation of Villagers in Urban Villages. Theoretical Exploration, (3): 95-97.
|
|
温忠麟,侯杰泰,张雷. 2005. 调节效应与中介效应的比较和应用. 心理学报,(2):268-274.
Wen Zhonglin, Hou Jietai, and Zhang Lei. 2005. A Comparison of Moderator and Mediator and Their Applications. Acta Psychologica Sinica, (2): 268-274.
|
|
新华社. 2021. 中华人民共和国国民经济和社会发展第十四个五年规划和2035年远景目标纲要. (2021-03-13)[2024-07-28]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-03/13/content_5592681.htm.
Xinhua News. 2021. Outline of the 14th Five Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of the People's Republic of China and the Long Range Objectives for 2035. (2021-03-13) [2024-07-28]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-03/13/content_5592681.htm.
|
|
新华社. 2022. 高举中国特色社会主义伟大旗帜 为全面建设社会主义现代化国家而团结奋斗——在中国共产党第二十次全国代表大会上的报告. (2022-10-25)[2024-07-28]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-10/25/content_5721685.htm.
Xinhua News. 2022. Hold High the Great Banner of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics and Work in Unity for the Comprehensive Construction of a Socialist Modernized Country: Report on the 20th National Congress of the CPC. (2022-10-25) [2024-07-28]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-10/25/content_5721685.htm.
|
|
新华社. 2023. 在超大特大城市积极稳步推进城中村改造工作部署电视电话会议在京召开 何立峰出席会议并讲话. (2023-07-28)[2024-07-28]. http://www.news.cn/2023-07/28/c_1129774376.htm. [Xinhua News. 2023. A Teleconference was Held in Beijing to Actively and Steadily Promote the Renovation of Urban Villages in Mega Cities. He Lifeng Attended the Meeting and Delivered a Speech. (2023-07-28) [2024-07-28]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2021-03/13/content_5592681.htm. ]
|
|
武汉市自然资源和城乡建设局. 2004. 市人民政府办公厅转发市体改办等部门关于落实市委市人民政府积极推进“城中村”综合改造工作意见的通知. (2004-09-15)[2024-07-28]. https://zrzyhgh.wuhan.gov.cn/zwgk_18/zcfgyjd/gtzyl/202001/t20200107_594973.shtml.
Wuhan Municipal Bureau of Natural Resources and Urban-Rural Development. 2004. General Office of the Municipal People's Government forwarded to the Municipal Reform Office and Other Departments on the Implementation of the Municipal Party Committee and the Municipal People's Government to Actively Promote the Comprehensive Transformation of the “Village in the City” Notice of the Views of the Work (2004-09-15) [2024-07-28]. https://zrzyhgh.wuhan.gov.cn/zwgk_18/zcfgyjd/gtzyl/202001/t20200107_594973.shtml.
|
|
武汉市统计局. 2023. 2022年武汉市国民经济和社会发展统计公报. (2023-03-30)[2024-07-26]. https://tjj.wuhan.gov.cn/tjfw/tjgb/202303/t20230330_2177979.shtml.
Wuhan Municipal Bureau of Statistics. 2023. Wuhan National Economic and Social Development Statistics Bulletin. 2022. (2021-03-30) [2023-07-26]. https://tjj.wuhan.gov.cn/tjfw/tjgb/202303/t20230330_2177 979.shtml.
|
|
伍薇,刘锐金,何长辉,杨琳,占达儒. 2024. 基于生计资本的农户可持续生计研究——以滇琼天然橡胶主产区为例. 热带地理,44(4):746-760.
Wu Wei, Liu Ruijing, He Changhui, Yang Lin, and Zhan Daru. 2024. Research on the Sustainable Livelihoods of Rural Households Based on Livelihood Capital: Evidence from the Natural Rubber Production Area in Hainan and Yunnan Provinces. Tropical Geography, 44(4): 746-760.
|
|
严金海,阮彦钦. 2016. 参照依赖、现状偏见与拆迁安置满意度——基于福建省厦门市的经验分析. 中国土地科学,30(8):3-11.
Yan Jinhai and Ruan Yanqin. 2016. Reference Dependence, Status Quo Bias and Satisfaction Degree of Resettlement: Taking Xiamen City in Fujian Province as an Example. China Land Science, 30(8): 3-11.
|
|
杨娟娟. 2023. 城中村改造重启 万亿级规模市场来袭. (2023-09-05)[2024-07-26]. https://new.qq.com/rain/a/20230905A02AXC00.
Yang Juanjuan. 2023. Urban Village Renovation Restarted, Trillions of Dollars of Scale Market is Coming. (2023-09-05) [2024-07-26]. https://new.qq.com/rain/a/20230905A02AXC00.
|
|
杨青,蔡银莺. 2018. 城中村拆迁对原住民社会阶层变化的影响——以武汉市为例. 中国土地科学,32(10):36-42.
Yang Qing and Cai Yinying. 2018. The Impact of Demolition on the Social Class Change of Indigenous Villagers in Urban Villages: A Case Study of Wuhan City. China Land Science, 32(10): 36-42.
|
|
Yang Qing and Cai Yinying. 2020a. Housing Property Redistribution and Elite Capture in the Redevelopment of Urban Villages: A Case Study in Wuhan, China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 262: 121192.
|
|
Yang Qing, Song Yan and Cai Yinying. 2020b. Blending Bottom-Up and Top-Down Urban Village Redevelopment Modes: Comparing Multidimensional Welfare Changes of Resettled Households in Wuhan, China. Sustainability, 12(18): 7447.
|
|
Yang Qing and Zhang Chaozheng. 2023. How Does the Renewal of Urban Villages Affect the Resettled Villagers' Subjective Well-Being? A Case Study in Wuhan, China. Land, 128.
|
|
叶裕民. 2015. 特大城市包容性城中村改造理论架构与机制创新——来自北京和广州的考察与思考. 城市规划,39(8):9-23.
Ye Yumin. 2015. Theoretical Framework and Mechanism Innovation of the Inclusive Urban Village Renovation in Chinese Megacities: Study and Reflection on Beijing and Guangzhou. City Planning Review, 39(8): 9-23.
|
|
殷宇超,蔡银莺. 2020. 城中村拆迁还建居民家庭住房租赁与生计能力提升——以武汉市汉阳区八个拆迁安置小区为例. 城市问题,(9):86-93,103.
Yin Yuchao and Cai Yinying. 2020. Improvement of Housing Rental and Livelihood Capacity of Households of Residents of Urban Villages Demolished and Relocated for Reconstruction: An Example of Eight Demolition and Resettlement Neighbourhoods in Hanyang District, Wuhan City. Urban Problems, (9): 86-93, 103.
|
|
张理政,叶裕民. 2021. 前景理论视角下城中村村民更新意愿研究——基于广州市25村问卷调查. 现代城市研究,(12):19-26.
Zhang Lizheng and Ye Yumin. 2021. Villagers' Willingness to Urban Village Redevelopment from the Perspective of Prospect Theory:A Study Based on Questionnaire Survey of 25 Urban Villages in Guangzhou. Modern Urban Research, (12): 19-26.
|
|
赵雪雁. 2011. 生计资本对农牧民生活满意度的影响——以甘南高原为例. 地理研究,30(4):687-698.
Zhao Xueyan. 2011. The Impact of Livelihood Capital on the Life Satisfaction of Peasants and Herdsmen: A Case of Gannan Plateau. Geographical Research, 30(4): 687-698.
|
|
周娟. 2019. 农村征地拆迁中“钉子户”的产生机制及其治理. 华南农业大学学报(社会科学版),18(3):35-43.
Zhou Juan. 2019. Production Mechanism and Treatment of Nail Households in Rural Land Acquisition and Demolition. Journal of South China Agricultural University(Social Science Edition), 18(3): 35-43.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |