

Toward the Third Space: Emotional Dynamics and Heterogeneous Identities in Heritage Communities during Urban Renewal
Received date: 2023-11-16
Revised date: 2024-03-05
Online published: 2024-08-09
This research delved into the complex dynamics of heritage communities during urban renewal, navigating the tension between preserving local heritage and embracing modernization. This study centered on Hangzhou's Mantoushan community and utilized a combination of fieldwork, participatory observation, semi-structured interviews, and online text analysis to investigate the interplay between spatial transformation and the construction of local identity in the context of urban development. This study aimed to dissect the multifaceted effects of urban renewal on the physical and emotional fabric of heritage spaces, with a particular focus on the microhistorical perspective. The methodology involved a comprehensive approach, capturing the voices of residents, tracking changes in spatial usage, and analyzing digital narratives to provide a nuanced understanding of the community's evolution. The results of this study underscore the dual impact of urban renewal. On one hand, it has led to improvements in the built environment and public amenities, fostering a renewed sense of community pride and attachment among residents. On the other hand, the process has been instrumental in the creation of a second space, as envisioned by authoritative bodies, which in turn, has given rise to a third space characterized by commercial, productive, and recreational functions. This transformation has been marked by diverse actors' reconstruction of the third space influenced by their varied perceptions and aspirations, which has led to a sense of dislocation and internal community division. The conclusions drawn from this study highlight the importance of recognizing the uneven and unstable nature of the transition towards a third space. It advocates for a more inclusive approach to urban renewal that acknowledges and addresses the diverse needs and aspirations of community members. This study also emphasizes the critical role of emotional connections and empathy in the sustainable development of heritage communities, cautioning against the illusion of a second space that overlooks the complex realities of community life. This study provides a compelling argument for a more nuanced understanding of the impacts of urban renewal on heritage communities. It calls for a balanced approach that respects the historical significance of these spaces, while embracing the potential for modernization, ensuring that the process of renewal is one that enhances rather than erodes the communities' sense of identity and belonging. The insights gained from this study are not only relevant to the Mantoushan community, but also offer valuable lessons for urban planners and policymakers worldwide, as they grapple with the challenges of integrating heritage conservation with the demands of contemporary urban life.
Chengcheng Yang . Toward the Third Space: Emotional Dynamics and Heterogeneous Identities in Heritage Communities during Urban Renewal[J]. Tropical Geography, 2024 , 44(8) : 1410 -1422 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20230885
图1 馒头山社区与各遗产(a. 南宋皇城遗址;b. 西湖文化景观;c. 京杭大运河)的叠压情况 Fig.1 The overlapping of the Mantoushan Community and heritage sites (a. Southern Song Dynasty Imperial City Site; b. West Lake Cultural Landscape of Hangzhou; c. The Grand Canal) |
表1 馒头山社区半结构访谈对象基本信息Table 1 Basic information of semi-structured interviewees in the Mantoushan Community |
| 访谈对象 | 编号 | 性别 | 职业 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原住 居民 | Y01 | 女 | 包子店老板 |
| Y02 | 女 | 包子店工人 | |
| Y03 | 男 | 国营厂退休员工 | |
| Y04 | 男 | 私营厂退休员工 | |
| Y05 | 男 | 社区食堂厨师 | |
| Y06 | 男 | 面馆经营者 | |
| Y07 | 女 | 铁路退休员工 | |
| 外来 务工 租户 | W01 | 男 | 收废品从业者 |
| W02 | 女 | 收废品从业者 | |
| W03 | 女 | 无业 | |
| W04 | 女 | 全职母亲 | |
| W05 | 女 | 酒店服务员 | |
| W06 | 男 | 快递员 | |
| W07 | 男 | 外卖骑手 | |
| W08 | 女 | 社区保洁员 | |
| 创意 工作者 | C01 | 女 | 广告公司从业者 |
| C02 | 女 | 摄影公司从业者 | |
| C03 | 女 | 原创服装设计者 | |
| C04 | 男 | 咖啡店店长 | |
| C05 | 男 | 书店店长 | |
| C06 | 男 | 中古杂货店店长 | |
| 社区 管理者 | S01 | 男 | 邻里中心工作人员 |
| S02 | 女 | 邻里中心社工 | |
| S03 | 女 | 志愿者 | |
| S04 | 女 | 退休书记 | |
| 游客 | Y01 | 女 | 零散游客 |
| Y02 | 女 | 零散游客 | |
| Y03 | 女 | 探店网红 | |
| Y04 | 女 | 摄影网红 | |
| Y05 | 男 | City Walk游客 | |
| Y06 | 男 | 建筑学专业学生 |
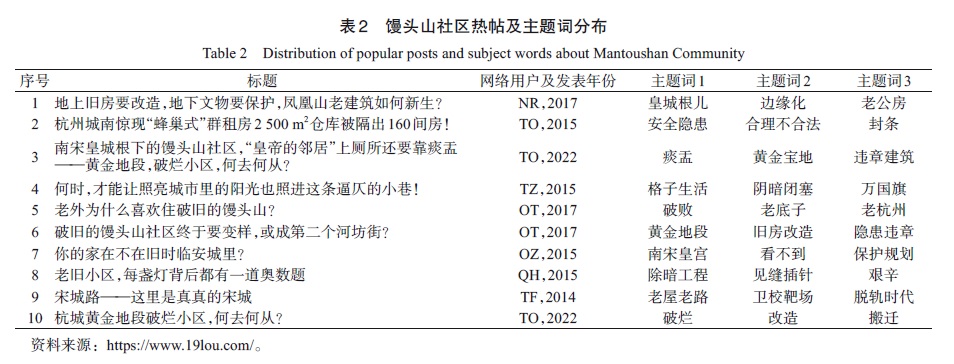
表2 馒头山社区热帖及主题词分布Table 2 Distribution of popular posts and subject words about Mantoushan Community |
| 序号 | 标题 | 网络用户及发表年份 | 主题词1 | 主题词2 | 主题词3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 地上旧房要改造,地下文物要保护,凤凰山老建筑如何新生? | NR,2017 | 皇城根儿 | 边缘化 | 老公房 |
| 2 | 杭州城南惊现“蜂巢式”群租房2 500 m2仓库被隔出160间房! | TO,2015 | 安全隐患 | 合理不合法 | 封条 |
| 3 | 南宋皇城根下的馒头山社区,“皇帝的邻居”上厕所还要靠痰盂——黄金地段,破烂小区,何去何从? | TO,2022 | 痰盂 | 黄金宝地 | 违章建筑 |
| 4 | 何时,才能让照亮城市里的阳光也照进这条逼仄的小巷! | TZ,2015 | 格子生活 | 阴暗闭塞 | 万国旗 |
| 5 | 老外为什么喜欢住破旧的馒头山? | OT,2017 | 破败 | 老底子 | 老杭州 |
| 6 | 破旧的馒头山社区终于要变样,或成第二个河坊街? | OT,2017 | 黄金地段 | 旧房改造 | 隐患违章 |
| 7 | 你的家在不在旧时临安城里? | OZ,2015 | 南宋皇宫 | 看不到 | 保护规划 |
| 8 | 老旧小区,每盏灯背后都有一道奥数题 | QH,2015 | 除暗工程 | 见缝插针 | 艰辛 |
| 9 | 宋城路——这里是真真的宋城 | TF,2014 | 老屋老路 | 卫校靶场 | 脱轨时代 |
| 10 | 杭城黄金地段破烂小区,何去何从? | TO,2022 | 破烂 | 改造 | 搬迁 |
资料来源:https://www.19lou.com/。 |
表3 馒头山社区内创意园区Table 3 Creative park in the Mantoushan Community |
| 创意园区 | 运营管理主体 | 改造前身 | 性质 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOMO创意谷 | 杭州商旅资产管理有限公司 | 火柴厂仓库 | 国有 |
| 凤山·拾遗 | 更换中 | 杭州电焊条厂 | 未确定 |
| 凤凰御元 | 杭州丰平控股集团 | 浙江省军区后勤部综合仓库 | 民营 |
| 凤凰1138 | 杭州丰平控股集团 | 浙江省军区后勤部综合宿舍 | 民营 |
| 凤凰公社 | 杭州筑巢文化创意有限公司 | 杭州华东医药中成药品仓库 | 民营 |
|
表4 馒头山社区City Walk路线特征对比Table 4 Comparison of City Walk route characteristics in the Mantoushan Community |
| 特征 | 社区江南民居 | 创意产业园区 |
|---|---|---|
| 环境特点 | 老树、古井、白墙黛瓦 | 文创园区、潮流店铺、色彩丰富 |
| 社区活动 | 打牌聊天、洗衣、家常谈话 | 拍照打卡、探店、咖啡手作 |
| 生活氛围 | 传统市井风情 老人们围坐打牌聊天,孩子们嬉戏 | 文化艺术氛围 咖啡对谈、花店购物、展览参观 |
| 文化氛围 | 传统市井文化,生活气息浓厚 | 装饰精美洋气,艺术感浓郁 |

1 资料来源:杭州城市建设档案馆. 馒头山社区主要单位统计表(内部资料),2023。
|
Bell S L. 2017. The Role of Fluctuating Soundscapes in Shaping the Emotional Geographies of Individuals Living with Ménière's Disease. Social & Cultural Geography, 18(6): 831-850.
|
|
Berta M, Bottero M, and Ferretti V. 2018. A Mixed Methods Approach for the Integration of Urban Design and Economic Evaluation: Industrial Heritage and Urban Regeneration in China. Environment and Planning B: Urban Analytics and City Science, 45(2): 208-232.
|
|
Canclini N. 1995. Hybrid Cultures: Strategies for Entering and Leaving Modernity. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
|
|
Carrera L. 2022. Designing Inclusive Urban Places. Italian Sociological Review, 12(1): 141.
|
|
Clark W A V, Duque-Calvache R, and Palomares-Linares I. 2017. Place Attachment and the Decision to Stay in the Neighborhood: Place Attachment and Staying in the Neighborhood. Population Space and Place, 23(2): e2001.
|
|
陈宏萍,裘梦洁,金丹丹,胡元勇. 2016. 一场皇城根下的渐变,钱江晚报,2016-02-26(A1、A3、A6).
Chen Hongping, Qiu Mengjie, Jin Dandan, and Hu Yuanyong. 2016. A Gradual Change at the Foot of the Imperial City. Qianjiang Evening News,2016-02-26 (A1, A3, A6).
|
|
陈忠,爱德华·索亚. 2012. 空间与城市正义: 理论张力和现实可能. 苏州大学学报(哲学社会科学版),33(1):1-6,191.
Chen Zhong and Edward Soja. 2012. Space and Urban Justice: Theoretical Tensions and Realistic Possibilities. Journal of Soochow University (Philosophy & Social Sciences Edition), 33(1): 1-6, 191.
|
|
翟斌庆,伍美琴. 2009. 城市更新理念与中国城市现实. 城市规划学刊,(2):75-82.
Zhai Binqing and Wu Meiqin. 2009. The Concept of Urban Renewal and the Reality of Chinese Cities. Urban Planning Journal, (2): 75-82.
|
|
丁凡,伍江. 2017. 城市更新相关概念的演进及在当今的现实意义. 城市规划学刊,(6):87-95.
Ding Fan and Wu Jiang. 2017. The Evolution of Concepts Related to Urban Renewal and Their Current Practical Significance. Urban Planning Journal, (6): 87-95.
|
|
段义孚,志丞,左一鸥. 2006. 人文主义地理学之我见. 地理科学进展,25(2):1-7. [Duan Yifu, Zhi Cheng, and Zuo Yi'ou. 2006. My View on Humanistic Geography. Progress in Geography, 25(2): 1-7.]
|
|
Figueiredo Y D, Prim M A, and Dandolini G A. 2022. Urban Regeneration in the Light of Social Innovation: A Systematic Integrative Literature Review. Land Use Policy, 113: 105873.
|
|
方创琳. 2009. 改革开放30年来中国的城市化与城镇发展. 经济地理,29(1):19-25.
Fang Chuanglin. 2009. Urbanization and Urban Development in China Over the Past 30 Years of Reform and Opening-Up. Economic Geography, 29(1): 19-25.
|
|
González Martínez Plácido. 2022. The 'Preservation by Relocation' of Huizhou Vernacular Architecture: Shifting Notions on the Authenticity of Rural Heritage in China. International Journal of Heritage Studies, 28(2): 200-215.
|
|
格诺特·波默. 2018. 气氛美学. 贾红雨,译. 北京:中国社会科学出版社.
Gernot Böhme. 2018. The Aesthetics of Atmospheres. Jia Hongyu, Trans. Beijing: China Social Sciences Press.
|
|
Harvey D. 1985. The Geopolitics of Capitalism. In: Gregory D and Urry J Palgrave. Social Relations and Spatial Structures: Critical Human Geography. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
|
|
Huston S, Rahimzad R, and Parsa A. 2015. Smart Sustainable Urban Regeneration: Institutions, Quality and Financial Innovation. Cities, 48: 66-75.
|
|
韩顺法,纪小美,陶卓民. 2018. 创意城市发展模式类型的适应性评价. 地理科学,38(9):1458-1465.
Han Shunfa, Ji Xiaomei, and Tao Zhuomin. 2018. Adaptability Evaluation of Creative City Development Models. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 38(9): 1458-1465.
|
|
杭州市人民政府. 2018. 杭州市人民政府关于印发杭州市之江文化产业带建设推进计划(2018—2022年)的通知. (2018-11-20)[2023-11-10]. http://www.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2019/1/16/art_1620754_4491.html
Hangzhou Municipal Government. 2018. Notice of the Hangzhou Municipal Government on Issuing the Implementation Plan for the Construction of the Zhijiang Cultural Industry Belt in Hangzhou (2018-2022). (2018-11-20) [2023-11-10]. http://www.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2019/1/16/art_1620754_4491.html.
|
|
杭州市发展和改革委员会. 2021. 杭州市“十二五”文化创意产业发展规划. (2021-07-02)[2023-11-10]. https://www.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2021/7/2/art_1229541472_3894833.html.
Hangzhou Development and Reform Committee. 2021. Hangzhou's Twelfth Five-Year Plan for Cultural and Creative Industry Development. (2021-07-02) [2023-11-10] https://www.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2021/7/2/art_1229541472_3894833.html.
|
|
黄经南,陈舒怡,王存颂,张媛媛. 2017. 从“光辉城市”到“美丽乡村”——荷兰Bijlmermeer住区兴衰对我国新农村规划的启示. 国际城市规划,32(1):116-122.
Huang Jingnan, Chen Shuyi, Wang Cunsong, and Zhang Yuanyuan. 2017. From "Radiant City" to "Beautiful Countryside": Lessons from the Rise and Fall of Bijlmermeer Residential Area in the Netherlands for China's New Rural Planning. Urban Planning International, 32(1): 116-122.
|
|
黄怡,吴长福,谢振宇. 2015. 城市更新中地方文化资本的激活——以山东省滕州市接官巷历史街区更新改造规划为例. 城市规划学刊,(2):110-118.
Huang Yi, Wu Changfu, and Xie Zhenyu. 2015. Activating Local Cultural Capital in Urban Renewal: A Case Study of the Regeneration Planning of Jieguan Alley Historic District in Tengzhou City, Shandong Province. Urban Planning Forum,(2): 110-118.
|
|
Krueger R and Savage L. 2007. City-Regions and Social Reproduction: A 'Place' for Sustainable Development? International Journal of Urban and Regional Research, 31(1): 215-223.
|
|
Lai L Y, Said I, and Kubota A. 2013. The Roles of Cultural Spaces in Malaysia's Historic Towns: The Case of Kuala Dungun and Taiping. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 85: 602-625.
|
|
Lefebvre Henri. 1991. The Production of Space. Oxford: Blackwell.
|
|
赖亚妮,桂艺丹. 2019. 城中村土地发展问题:文献回顾与研究展望. 城市规划,43(7):108-114.
Lai Yani and Gui Yidan. 2019. Land Development Issues in Urban Villages: Literature Review and Research Prospects. City Planning Review, 43(7): 108-114.
|
|
林铭亮,高川秀,林元城,王敏. 2020. 旅游地品牌化:唐诗“第三空间”的旅游体验与地方想象的建构. 旅游学刊,35(5):98-107.
Lin Mingliang, Gao Chuanxiu, Lin Yuancheng, and Wang Min. 2020. Tourism Destination Branding: The Construction of Tourist Experience and Local Imagination in the "Third Space" of Tang Poetry. Tourism Tribune, 35(5): 98-107.
|
|
刘伯霞,刘杰,王田,程婷. 2022. 国外城市更新理论与实践及其启示. 中国名城,36(1):15-22.
Liu Boxia, Liu Jie, Wang Tian, and Cheng Ting. 2022. Foreign Urban Renewal Theory and Practice and Its Enlightenment. China Ancient City, 36(1): 15-22.
|
|
MacCannell Dean. 2008. 旅游者休闲阶层新论. 张晓萍,译. 桂林:广西师范大学出版社. [MacCannell Dean. 2008. The Tourist Leisure Class New Theory. Zhang Xiaoping, Trans. Guilin: Guangxi Normal University Press.]
|
|
Massey D. 1994. Space, Place and Gender. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
|
|
Roberts P. 2000. Evolution, Definition and Purpose of Urban Regeneration. In: Roberts P and Sykes H. Urban Regeneration: A Handbook. London: SAGE Publications, 9-36.
|
|
任杲,宋迎昌,蒋金星. 2019. 改革开放40年中国城市化进程研究. 宁夏社会科学,(1):23-31.
Ren Gao, Song Yingchang, and Jiang Jinxing. 2019. A Study on the Urbanization Process in China over the Past 40 Years of Reform and Opening Up. Ningxia Social Sciences, (1): 23-31.
|
|
Smith L. 2006. Uses of Heritage. London: Routledge.
|
|
Soja E W. 1996. Third Space: Journeys to Los Angeles and Other Real-and-Imagined Places. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell.
|
|
Soja Edward W. 2005. 第三空间 去往洛杉矶和其他真实和想象地方的旅程. 陆扬,译. 上海:上海教育出版社.
Soja Edward W. 2005. The Third Space: Journeys to Los Angeles and Other Real-and-Imagined Places. Lu Yang, Trans. 2005. Shanghai: Shanghai Education Publishing House.
|
|
苏俊杰. 2021. 文化遗产旅游中的真实性概念:从分离到互动. 西南民族大学学报(人文社会科学版),42(11):44-51.
Su Junjie. 2021. The Concept of Authenticity in Cultural Heritage Tourism: From Separation to Interaction. Journal of Southwest University for Nationalities (Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 42(11): 44-51.
|
|
Tuan Y F. 1979. Landscapes of Fear. Minnesota, MN: University of Minnesota Press.
|
|
田汝成. 2012. 西湖游览志馀. 陈志明,校. 北京:东方出版社.
Tian Rucheng. 2012. Xihu Youlan Zhiyu. Chen Zhiming, Proofreading. Beijing: Oriental Publishing House.
|
|
谭其骧. 1982. 中国历史地图集(第六册). 北京:中国地图出版社.
Tan Qichang. 1982. Historical Atlas of China (Volume VI). Beijing: China Map Publishing House.
|
|
United Nations Education Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). 2011. West Lake Cultural Landscape of Hangzhou. (2011-12-06) [2023-11-11]. https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1334.
|
|
United Nations Education Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). 2016. The Grand Canal. (2016-09-18) [2023-11-11] https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1443/maps/. [UNESCO. 2016. The Grand Canal. (2016-09-18) [2023-11-11]. https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1443/maps/.]
|
|
王笛. 2022. 碌碌有为:微观历史视野下的中国社会与民众. 北京:中信出版社集团.
Wang Di. 2022. Busy Being Productive: Chinese Society and the People from a Micro-Historical Perspective. Beijing: CITIC Press Group.
|
|
徐琴. 2011. 有机更新:历史文化名城走出保护性衰败与建设性破坏困境之路. 城市观察,(3):62-69.
Xu Qin. 2011. Organic Renewal: A Way Out of the Dilemma of Protective Decay and Constructive Destruction for Historic and Cultural Cities. Urban Insight,(3): 62-69.
|
|
徐玉梅,王朝辉,张婷婷,张伟,刘娟. 2019. 国内外旅游绅士化研究综述与展望. 人文地理,34(2):8-16,104.
Xu Yumei, Wang Chaohui, Zhang Tingting, Zhang Wei, and Liu Juan. 2019. A Review and Prospect of Domestic and Foreign Research on Tourism Gentrification. Human Geography, 34(2): 8-16, 104.
|
|
阳建强,杜雁,王引,段进,李江,杨贵庆,杨利,王嘉,袁奇峰,张广汉,朱荣远,王唯山,陈为邦. 2016. 城市更新与功能提升. 城市规划,40(1):99-106.
Yang Jianqiang, Du Yan, Wang Yin, Li Jiang, Yang Guiqing, Yang Li, Wang Jia, Yuan Qifeng, Zhang Guanghan, Zhu Rongyuan, Wang Weishan, and Chen Weibang. 2016. Urban Renewal and Functional Upgrading. City Planning Review, 40(1): 99-106.
|
|
杨程程. 2020. 城市“失落空间”更新的理论观照——以上海徐汇滨江区域的更新为例. 江南论坛,(5):33-35.
Yang Chengcheng. 2020. Theoretical Observation on the Renewal of Urban "Lost Space": Taking the Renewal of Xuhui Binjiang Area in Shanghai as an Example. Jiangnan Forum, (5): 33-35.
|
|
Zhu Y and González Martínez Plácido. 2022. Heritage, Values and Gentrification: The Redevelopment of Historic Areas in China. International Journal of Heritage Studies, 28(4): 476-494.
|
|
Zukin S. 2020. Seeing Like a City: How Tech Became Urban. Theory and Society, 49(5): 941-964.
|
|
曾涛,刘红升. 2021.中国文化创意产业区域发展水平测度.统计与决策,37(1):55-59.
Zeng Tao and Liu Hongsheng. 2021. Measurement of Regional Development Level of China's Cultural and Creative Industries. Statistics and Decision Making, 37(1): 55-59.
|
|
张卫良. 2020. 杭州城市空间蔓延与区域发展逻辑. 杭州师范大学学报(社会科学版),42(5):111-120.
Zhang Weiliang. 2020. Urban Spatial Sprawl and Regional Development Logic in Hangzhou. Journal of Hangzhou Normal University (Social Science Edition), 42(5): 111-120.
|
|
张瑛,汲忠娟,曾仁辉,盘霄远. 2016. “旅游绅士化”与农耕文化遗产地可持续发展——以联合国教科文组织(UNESCO)世界遗产地元阳梯田为例. 中央民族大学学报(哲学社会科学版),43(6):75-81.
Zhang Ying, Ji Zhongjuan, Zeng Renhui, and Pan Xiaoyuan. 2016. "Tourism Gentrification" and Sustainable Development of Agricultural Cultural Heritage Sites: Taking the Yuanyang Terraced Fields, A UNESCO World Heritage Site, as an Example. Journal of Central University for Nationalities (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), 43(6): 75-81.
|
|
张志庆,刘佳丽. 2019. 爱德华·索亚第三空间理论的渊源与启示. 现代传播(中国传媒大学学报),41(12):14-20.
Zhang Zhiqing and Liu Jiali. 2019. The Origin and Enlightenment of Edward Soja's Thirdspace Theory. Modern Communication (Journal of Communication University of China), 41(12): 14-20.
|
|
浙江省人民政府. 2018. 浙江省人民政府关于印发之江文化产业带建设规划的通知. (2018-06-11)[2023-11-10]. https://zjjcmspublic.oss-cn-hangzhou-zwynet-d01-a.internet.cloud.zj.gov.cn/jcms_files/jcms1/web3096/site/attach/0/1a087b0dda7c4f5eb212cbdfe273c1b0.pdf.
Zhejiang Provincial Government. 2018. Notice of the Zhejiang Provincial Government on Issuing the Zhijiang Cultural Industry Belt Construction Plan. (2018-06-11) [2023-11-10]. https://zjjcmspublic.oss-cn-hangzhou-zwynet-d01-a.internet.cloud.zj.gov.cn/jcms_files/jcms1/web3096/site/attach/0/1a087b0dda7c4f5eb212cbdfe273c1b0.pdf.
|
|
朱竑,高权. 2015. 西方地理学“情感转向”与情感地理学研究述评. 地理研究,34(7):1394-1406.
Zhu Hong and Gao Quan. 2015. A Review of "Emotional Turn" in Western Geography and Research on Emotional Geography. Geographical Research, 34(7): 1394-1406.
|
|
朱要龙. 2018. 土地制度安排与半城镇化问题研究: 分野、论争及引申. 中国人口·资源与环境,28(11):29-36.
Zhu Yaolong. 2018. Research on Land Institutional Arrangements and Semi-urbanization Issues: Divisions, Debates, and Extension. China Population, Resources and Environment, 28(11): 29-36.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |