

Analysis of Coastline Changes in Zhanjiang Bay from 1973 to 2023
Received date: 2023-11-09
Revised date: 2024-03-28
Online published: 2024-11-07
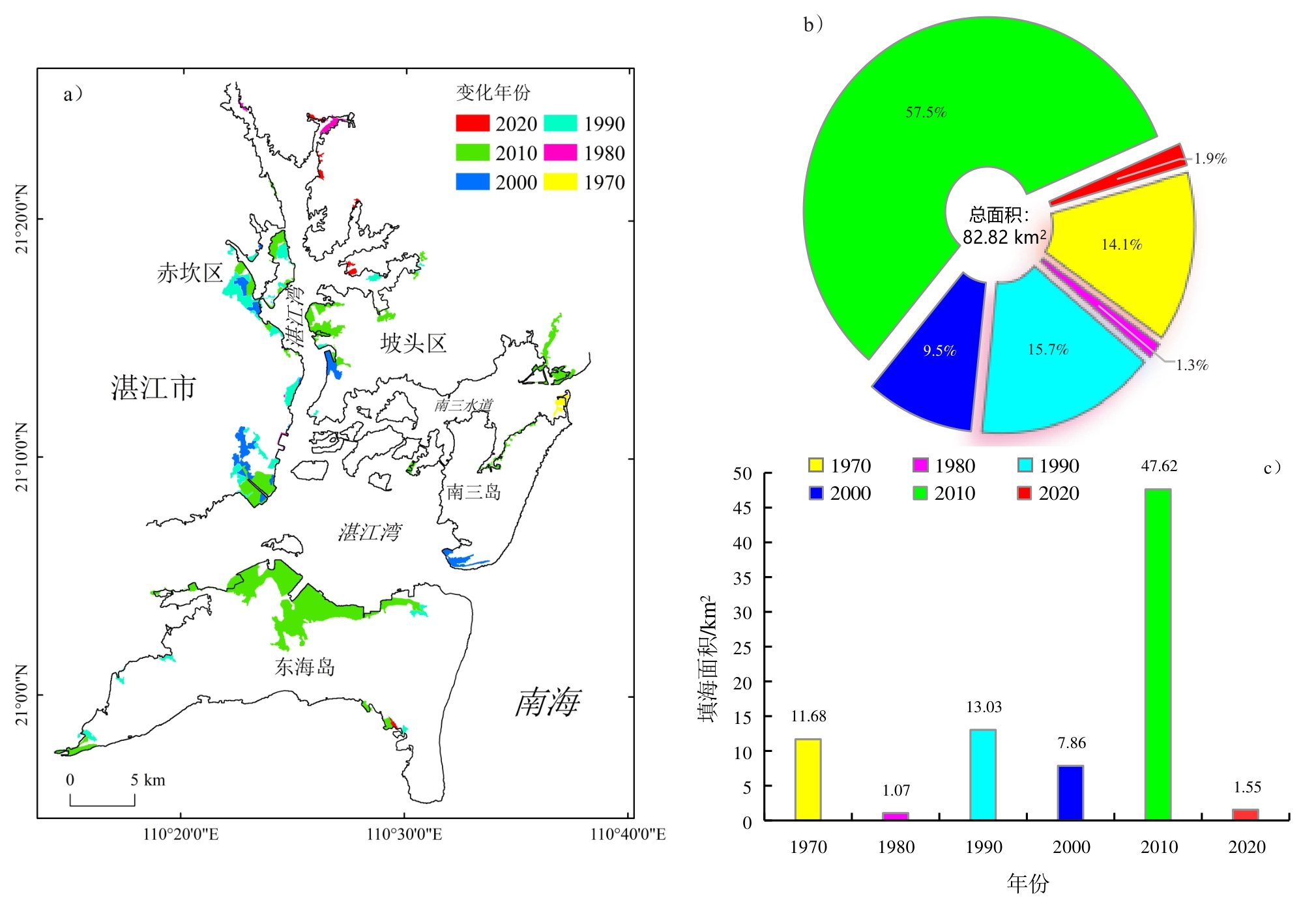
The coastline of Zhanjiang Bay has undergone profound changes under the combined action of natural and human factors, making the rational protection and utilization of coastal resources a research hotspot. As a typical tropical bay in China, analyzing the coastline changes in Zhanjiang Bay can provide basic data to support the development and utilization of coastal zones. In this study, 42 optical satellite images from 1973 to 2023 were used in conjunction with the random forest method to extract the shoreline, analyze the spatiotemporal evolution of the Zhanjiang Bay coastline, and investigate its driving factors. Additionally, shoreline complexity changes were explored, and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) was introduced for the correlation analysis of shoreline indicators. The results showed that the total length of the Zhanjiang Bay coastline increased by 103.13 km over the past 50 years. Coastline changes are influenced by both natural and anthropogenic factors, with anthropogenic factors having the most significant impact. Natural factors include erosion caused by storm surges, sea level rise, and dynamic coastal conditions. Anthropogenic factors include construction of coastal aquaculture farms, land reclamation, coastal engineering projects, coastal infrastructure development, and industrial land development. The main areas of change were concentrated along the main channel and the Nansan Waterway. The proportions of shoreline segments expanding seaward on the east and west coasts were 51.4% and 71.6%, respectively, whereas the landward erosion shoreline segment on Donghai Island was 58.0%. Specifically, the southeastern section of the east coast experienced massive shoreline expansion. Coastal engineering along the west coast, southeastern village, and town construction projects on the east coast resulted in shoreline advancement of more than 2 km seaward. Erosion was observed at the western end of the coastline, across several estuaries from the west coast, and along the shoreline of the Nansan Channel on the south side of the east coast, with the most severe shoreline erosion occurring at the end of the west coast shoreline, where the average setback was 1 km, with a maximum setback of nearly 1.8 km. Except for the 2010s, the change in the intensity of the coastline of Zhanjiang Bay was positive. The fractal dimension of the coastline increased from 1.086 to 1.124, consistent with the trend in its length. The primary driver of coastline expansion was large-scale land reclamation on the western bank of Zhanjiang Bay, southwestern bank of the eastern bank, and northern part of Donghai Island, with a total reclaimed area of 82.82 km2. The proportion of the reclaimed area after 2010 reached 57.5%, the area of coastal aquaculture farms increased by 26.98 km2 over the past 30 years. Large-scale erosion occurred on the eastern and southern sides of Donghai Island. In addition, the fractal dimension and length of the Zhanjiang Bay coastline were strongly negatively correlated with the inverse of the GDP of Zhanjiang, with correlation coefficients of -0.96 and -0.99, respectively. These findings suggests that the economic benefits of shoreline shifting can be quantified using shoreline indicators, whereas differences in shoreline indices between different harbors affect the relevance of the economic benefits. Owing to the narrow and long topographic structure of Zhanjiang Bay, there is a delay in tidal signal propagation from the bay mouth to the interior. Therefore, when exploring the water margins obtained from optical remote sensing images, the water level information of the corresponding region must be utilized to correct the tidal variations in Zhanjiang Bay. Based on this, numerical models will be used in the future to obtain tidal data for each region and the corresponding water margins.
Zhuoqiang Guan , Junyi Li , Lingling Xie , Quan'an Zheng , Xiaomin Ye . Analysis of Coastline Changes in Zhanjiang Bay from 1973 to 2023[J]. Tropical Geography, 2024 , 44(11) : 2025 -2038 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20230865
表1 卫星参数信息Table 1 Parameters of satellite images |
| 序号 | 卫星 | 轨道号 Path/Row | 成像时间 | 空间分辨率/m | 序号 | 卫星 | 轨道号 Path/Row | 成像时间 | 空间分辨率/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Landsat1 | 133/45 | 1973-12-27 | 60 | 22 | Landsat7 | 124/45 | 2003-10-23 | 30 |
| 2 | Landsat2 | 133/45 | 1976-12-02 | 60 | 23 | Landsat7 | 124/45 | 2004-10-25 | 30 |
| 3 | Landsat2 | 133/45 | 1977-02-12 | 60 | 24 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 2005-11-21 | 30 |
| 4 | Landsat4 | 124/45 | 1983-11-01 | 60 | 25 | Landsat7 | 124/45 | 2006-10-31 | 30 |
| 5 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1986-07-28 | 30 | 26 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 2007-04-01 | 30 |
| 6 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1987-12-22 | 30 | 27 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 2008-11-13 | 30 |
| 7 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1988-10-21 | 30 | 28 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 2009-01-16 | 30 |
| 8 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1989-02-26 | 30 | 29 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 2010-11-19 | 30 |
| 9 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1990-12-14 | 30 | 30 | Landsat7 | 124/45 | 2011-11-14 | 30 |
| 10 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1991-10-30 | 30 | 31 | Landsat7 | 124/45 | 2012-09-29 | 30 |
| 11 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1992-10-16 | 30 | 32 | Landsat8 | 124/45 | 2013-10-26 | 30 |
| 12 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1993-12-06 | 30 | 33 | Landsat8 | 124/45 | 2014-11-14 | 30 |
| 13 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1994-01-23 | 30 | 34 | Landsat8 | 124/45 | 2015-01-01 | 30 |
| 14 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1995-09-23 | 30 | 35 | Landsat7 | 124/45 | 2016-11-27 | 30 |
| 15 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1996-10-11 | 30 | 36 | Landsat7 | 124/45 | 2017-10-13 | 30 |
| 16 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1997-06-08 | 30 | 37 | Landsat7 | 124/45 | 2018-11-01 | 30 |
| 17 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1998-10-17 | 30 | 38 | Sentinel2A | 0212/075 | 2019-05-18 | 10 |
| 18 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 1999-12-23 | 30 | 39 | Landsat8 | 124/45 | 2020-04-28 | 30 |
| 19 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 2000-03-28 | 30 | 40 | Landsat8 | 124/45 | 2021-12-03 | 30 |
| 20 | Landsat5 | 124/45 | 2001-11-26 | 30 | 41 | Landsat8 | 124/45 | 2022-10-11 | 30 |
| 21 | Landsat7 | 124/45 | 2002-11-05 | 30 | 42 | Sentinel2A | 0509/075 | 2023-03-23 | 10 |
表2 地面控制点及纠正误差 (m)Table 2 Ground control points and positioning accuracy |
| 验证点 | 实测X | 实测Y | 矢量化X | 矢量化Y | 距离差 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 443 041 | 2 355 957 | 443 041 | 2 355 984 | 39 |
| P2 | 434 306 | 2 349 838 | 434 291 | 2 349 871 | 35 |
| P3 | 448 594 | 2 342 859 | 448 581 | 2 342 846 | 18 |
| P4 | 424 450 | 2 338 706 | 424 427 | 2 338 710 | 23 |
| P5 | 425 489 | 2 338 018 | 425 493 | 2 338 032 | 14 |
| P6 | 430 080 | 2 330 524 | 430 085 | 2 330 540 | 16 |

1 https://www.zhanjiang.gov.cn/zjsfw/bmdh/tjxxw/zwgk/tjsjzl/tjnj
关焯强:论文的撰写与修改;
李君益:论文指导,论文审阅;
谢玲玲:论文指导,基金支持;
郑全安、叶小敏:提供论文修改思路与建议。
|
毕修颖. 2010. 湛江港特殊日期潮汐推算图的制作和使用方法. 航海技术,(6):11-13. [Bi Xiuying. 2010. Special Date Tidal Calculation Chart Making and its Usage. Marine Technology, (6): 11-13. ]
|
|
程阳艳,付东洋,祁雅莉,李志强,刘贝,余果,何露雪. 2022. 基于Landsat 影像的近30年湛江东北海岸线变迁分析. 海洋科学进展,40(2):261-273.
Cheng Yangyan, Fu Dongyang, Qi Yali, Li Zhiqiang, Liu Bei, Yu Guo, and He Luxue. 2022. Analysis on Coastline Change of Northeast Zhanjiang in the Last 30 Years Based on Landsat Image. Advances in Marine Science, 40(2): 261-273.
|
|
崔红星,汪驰升,杨红,胡忠文,王春峰. 2020. 近40年苏北海岸线时空动态变迁分析. 海洋环境科学,39(5):694-702.
Cui Hongxing, Wang Chisheng, Yang Hong, Hu Zhongwen, and Wang Chunfeng. 2020. Analysis of Spatiotemporal Dynamic Changes of the North Jiangsu Coastline in the Past 40 Years. Marine Environmental Science, 39(5): 694-702.
|
|
Frankhauser P. 2017. Between Self-Organization and Planning: Cities and the Fractal Ordering Principle. In: Claudia Yamu, Alenka Poplin, Oswald Devisch, and Gert de Roo. The Virtual and the Real in Planning and Urban Design. London: Taylor & Francis (Routledge), 112-135.
|
|
高法成. 2024. 南海渔民生计脆弱性的内生问题——基于广东硇洲岛的田野调查. 热带地理,44(2):248-257.
Gao Facheng. 2024. Endogenous Problem of Fishermen's Livelihood in South China Sea: Based on Field Work of Naozhou Island in Guangdong. Tropical Geography, 44(2): 248-257.
|
|
侯西勇,毋亭,王远东,徐新良,陈晴,于良巨. 2014. 20世纪40年代以来多时相中国大陆岸线提取方法及精度评估. 海洋科学,38(11):66-73.
Hou Xiyong, Wu Ting, Wang Yuadong, Xu Xinliang, Chen Qing, and Yu Liangju. 2014. Extraction and Accuracy Evaluation of Multi-Temporal Coastlines of Mainland China since 1940s. Marine Sciences, 38 (11): 66-73.
|
|
胡歆怡,王云鹏,荆文龙 . 2021. 全球多尺度海岸线数据在珠江口岸线的精度评价及适用性分析 . 热带地理,41(3):609-621.
Hu Xinyi, Wang Yunpeng, and Jing Wenlong. 2021. Assessment of Precision and Usability of a Global Multi-Scale Coastline Dataset Using the Pearl River Estuary as a Test Model. Tropical Geography, 41(3): 609-621.
|
|
黄森文,韦春竹. 2021. 广东省沿海城市人工水产养殖基地变化——基于2015—2019年Sentinel-1数据的实证研究. 热带地理,41(3):622-634.
Huang Senwen and Wei Chunzhu. 2021. Spatial-Temporal Changes in Aquaculture Ponds in Coastal Cities of Guangdong Province: An Empirical Study Based on Sentinel-1 Data during 2015-2019. Tropical Geography, 41 (3): 622-634.
|
|
Hu X Y and Wang Y P. 2020. Coastline Fractal Dimension of Mainland, Island, and Estuaries Using Multi-Temporal Landsat Remote Sensing Data from 1978 to 2018: A Case Study of the Pearl River Estuary Area. Remote Sensing, 12(15): 2482.
|
|
李垒,任越美. 2016. 基于随机森林的高光谱遥感图像分类. 计算机工程与应用,52(24):189-193.
Li Lei and Ren Yuemei. 2016. Classification of Hyperspectral Data Based on Random Forest. Computer Engineering and Applications, 52(24): 189-193.
|
|
李梦,曹庆先,胡宝清,姜宁. 2022. 近60年广西钦州湾岸线变迁与开发利用空间格局评价. 海洋技术学报,41(6):76-86.
Li Meng, Cao Qingxian, Hu Baoqing, and Jiang Ning. 2022. Spatial Pattern Change of The Coastline Development and Utilization of Qinzhou Bay in Recent 60 Years. Journal of Ocean Technology, 41(6): 76-86.
|
|
李团结,刘春杉,李涛,陈亮,刘激,周英,卢映玲. 2011. 雷州半岛海岸侵蚀及其原因研究. 热带地理,31(3):243-250.
Li Tuanjie, Liu Chunshan, Li Tao, Chen Liang, Liu Ji, Zhou Ying, and Lu Yinling. 2011. Coastal Erosion and Its Occurring Mechanism in Lei Zhou Peninsula. Tropical Geography, 31(3): 243-250.
|
|
Lu J F, Zhang Y B, Shi H H, and Lv X Q. 2023. Spatio-Temporal Changes and Driving Forces of Reclamation Based on Remote Sensing: A Case Study of the Guangxi Beibu Gulf. Frontiers in Marine Science, 10: 1112487.
|
|
李苑君,吴旗韬,陈聪,张玉玲,张争胜,张虹鸥. 2020. 珠江三角洲海岸线旅游价值评估.热带地理,40(1):164-174.
Li Yuanjun, Wu Qitao, Chen Cong, Zhang Yuling, Zhang Zhengsheng, and Zhang Hong'ou. 2020. Coastline Tourism Value Evaluation in the Pearl River Delta. Tropical Geography, 40 (1): 164-174.
|
|
彭文琦. 2023. 环境可视性对广东省湛江市南三岛旅游社区形象感知的影响研究. 西部旅游,(21):63-65.
Peng Wenqi. 2023. A Study on the Impact of Environmental Visibility on the Perceived Image of Tourist Communities in the South Three Islands of Zhanjiang City, Guangdong Province. Western Travel, (21): 63-65.
|
|
任宗海,余建奎,王庆,战超,耿文倩,曹印,李瑞,钱张帆. 2023. 1958年以来莱州湾南部海岸线及水下地形演变. 海洋地质前沿,39(11):1-12.
Ren Zonghai, Yu Jiankui, Wang Qing, Zhan Chao, Gen Wenqian, Cao Ying, Li Rui, and Qian Zhangfan. 2023. On the Change of Coastline and Underwater Terrain of the Southern Laizhou Bay since 1958. Marine Geology Frontiers, 39(11): 1-12.
|
|
Smith T L, Himmelstoss E A, and Thieler E R. 2013. Massachusetts Coastline Change Project—A GIS Compilation of Vector Coastlines and Associated Coastline Change Data. [2013-06-24]. http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2012/1183/.
|
|
Stockdon H F, Sallenger A H, List J H, and Holman R A. 2002. Estimation of Coastline Position and Change from Airborne Topographic Lidar Data. Journal of Coastal Research, 18: 502-513.
|
|
Thomas I, Frankhauser P, and Biernacki C. 2008. The Morphology of Built-Up Landscapes in Wallonia (Belgium): A Classification Using Fractal Indices. Landscape and Urban Planning, 84: 99-115.
|
|
石泳昊,贾良文,张恒. 2020. 湛江湾水体滞留时间及影响因子分析. 环境科学与技术,43(11):17-24.
Shi Yonghao, Jia Liangwen, and Zhang Heng. 2020. Analysis of the Water Residence Time and Influencing Factors in Zhanjiang Bay. Environmental Science &Technology, 43(11): 17-24.
|
|
孙杰,詹文欢,姚衍桃,刘守金,冯英辞. 2015. 广东省海岸侵蚀现状及影响因素分析. 海洋学报,37(7):142-152.
Sun Jie, Zhan Wenhuan, Yao Yantao, Liu Shoujin, and Feng Yingci. 2015. Current Situation and Influence Factors of Coastal Erosion in Guangdong. Haiyang Xuebao, 37(7): 142-152.
|
|
王江波,陈书润,苟爱萍. 2023. 1988年以来深圳市大陆海岸线时空演化特征. 海洋地质前沿,39(11):26-35.
Wang Jiangbo, Chen Shurun, and Gou Aiping. 2023. Temporal and Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Coastline in Shenzhen Since 1988. Marine Geology Frontiers, 39(11): 26-35.
|
|
王德江. 2022. 基于潮汐模型与余水位监控法的水位改正法在湛江港航道验收工程中的应用. 工程技术研究,7(21):10-12.
Wang Dejiang. 2022. The Application of Water Level Correction Method Based on Tidal Model and Residual Water Level Monitoring Method in Zhanjiang Port Waterway Acceptance Project. Engineering and Technological Research, 7 (21): 10-12.
|
|
王猛,张新长,王家耀,孙颖,箭鸽,潘翠红. 2020. 结合随机森林面向对象的森林资源分类. 测绘学报,49(2):235-244.
Wang Meng, Zhang Xinchang, Wang Jiayao, Sun Ying, Jian Ge, and Pan Cuihong. 2020. Forest Resource Classification Based on Random Forest and Object Oriented Method. Ata Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 49(2): 235-244.
|
|
王瑶斌,魏永亮,付东洋,刘大召. 2022. 30 a以来雷州半岛大陆岸线时空演变的遥感估算. 海洋技术学报,41(5):9-18.
Wang Yaobin, Wei Yongliang, Fu Dongyang, and Liu Dazhao. 2022. Remote Sensing Estimation of the Temporal and Spatial Evolution of the Continental Coastline in Leizhou Peninsula since 30 Years. Journal of Ocean Technology, 41(5): 9-18.
|
|
谢玲玲,曹瑞雪,尚庆通. 2012. 粤西近岸环流研究进展. 广东海洋大学学报,32(4):94-98.
Xie Lingling, Cao Ruixue, and Shang Qingtong. 2012. Progress of Study on Coastal Circulation near the Shore of Western Guangdong. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 32(4): 94-98.
|
|
Xu J Y, Zhang Z X, Zhao X L, Wen Q K, Zuo L J, Wang X, and Yi L. 2014. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Coastlines in Northern China (2000‒2012). Journal of Geographical Sciences, 24(1): 18-32.
|
|
杨庆乐. 2015. 东海岛海岸侵蚀研究. 青岛:国家海洋局第一海洋研究所.
Yang Qinyue. 2015. Erosion Research in Donghai Island. QingDao: First Institute of Oceanography, MNR.
|
|
叶小敏,丁静,徐莹,刘宇昕. 2016. 渤海湾近30年海岸线变迁与分析. 海洋开发与管理,33(2):56-62.
Ye Xiaomin, Ding Jing, Xu Ying, and Liu Yuxin. 2016. On the Changes of the Coastline in Bohai Bay during the Last 30 Years. Ocean Development and Management, 33(2): 56-62.
|
|
应秩甫,王鸿寿. 1996. 湛江湾的围海造地与潮汐通道系统. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),(6):102-106.
Ying Zhifu and Wang Hongshou. 1996. The Relationship Between Fill-Block Engineering and Tidal Inlet System Response in Zhanjiang Bay. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, (6): 102-106.
|
|
于杰,陈国宝,黄梓荣,陈作志. 2014. 近10年间广东省3个典型海湾海岸线变迁的遥感分析. 海洋湖沼通报,(3):91-96.
Yu Jie, Chen Guobao, Huang Zirong, and Chen Zuozhi. 2014. Change in Coastline of Three Typical Bays in Guangdong During Recent 10 Years Revealed by Satellite Image. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (3): 91-96.
|
|
张丽,廖静娟,袁鑫,穆晓东,宋茜茜,毕京鹏 . 2020. 1987—2017年海南岛海岸线变化特征遥感分析. 热带地理,40(4):659-674.
Zhang Li, Liao Jingjuan, Yuan Xin, Mu Xiaodong, Song Xixi, and Bi Jingpeng. 2020. Remote Sensing Analysis of Coastline Changes in Hainan Island during 1987‒2017. Tropical Geography, 40 (4): 659-674.
|
|
张彤辉,李辉权,罗伟成,周治刚. 2021. 海岸线修测中围海养殖区岸线界定问题分析. 海洋开发与管理,38(1):24-27.
Zhang Tonghui, Li Huiquan, Luo Weicheng, and Zhou Zhigang. 2021. Analysis on Definition of Coastline of Sea Reclamation Aquaculture in the Coastline Survey. Ocean Development and Management, 38 (1): 24-27.
|
|
张晓羽,李凤日,甄贞,赵颖惠. 2016. 基于随机森林模型的陆地卫星-8遥感影像森林植被分类. 东北林业大学学报,44(6):53-57,74.
Zhang Xiaoyu, Li Fengri, Zhen Zhen, and Zhao Yinghui. 2016. Forest Vegetation Classification of Landsat8 Remote Sensing Image Based on Random Forests Model. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 44(6): 53-57, 74.
|
|
章志,陈鹏,冒士凤,常曼. 2022. 20年间盐城海岸线变迁及影响因素分析. 海洋湖沼通报,44(2):136-142.
Zhang Zhi, Chen Peng, Mao Shifeng, and Chang Man. 2022. Analysis of Coastline Changes and the Influencing Factors in Yancheng in the Last 20 Years. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 44(2): 136-142.
|
|
章志,刘宪光,周凯,林伟波,冒士凤,李兰满. 2023. 海岸侵蚀脆弱性及驱动因子分析——以江苏中部海岸为例. 海洋学研究,41(4):70-83.
Zhang Zhi, Liu Xianguang, Zhou Kai, Lin Weibo, Mao Shifeng, and Li Lanman. 2023. Vulnerability and Driving Factors of Coastal Erosion: A Case Study of the Central Coast of Jiangsu. Joummal of Marine Sciences, 41(4): 70-83.
|
|
赵冲久. 1999. 湛江湾水文泥沙特性分析. 水道港口,(4):16-21.
Zhao Chongjiu. 1999. Hydrographic and Sediment Analysisi of Zhanjiang Bay. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, (4): 16-21.
|
|
赵连杰,吴孟泉,郑龙啸,栾绍鹏,赵贤峰,薛明月,刘佳燕,刘晨曦. 2022. 胶东半岛北部海岸线时空变迁及驱动分析. 自然资源遥感,34(4):87-96.
Zhao Lianjie, Wu Mengquan, Zheng Longxiao, Luan Shaopeng, Zhao Xianfeng, Xue Mingyue, Liu Jiayan, and Liu Chenxi. 2022. Temporal-Spatial Changes and Driving Analysis of the Northern Shorelines of Jiaodong Peninsula. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 34(4): 87-96.
|
|
钟蕊,刘春杉,陈鑫祥. 2021. 广东省大陆海岸线分形特征及空间分异. 广东海洋大学学报,41(4):70-76.
Zhong Rui, Liu Chunshan, and Chen Xinxiang. 2021. Fractal Characteristics and Spatial Heterogenicity of Continental Coastline in Guangdong Province. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 41(4): 70-76.
|
|
周晨,李君益,郑全安,谢玲玲. 2023. 南海北部冬季陆架波特征. 广东海洋大学学报,43(3):89-97.
Zhou Chen, Li Junyi, Zheng Quan'an, and Xie Lingling. 2023. Characteristics of Winter Continental Shelf Waves in the Northern South China Sea. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 43(3): 89-97.
|
|
Zhu Y D, Li Z J, Zhao Z, Lu L J, Yang S C, and Wang Z Y. 2023. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Coastline in Jiaozhou Bay from 1987 to 2022 Based on Optical and SAR Data. Frontiers in Marine Science, 10: 1233410.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |