

Understanding China's Metropolitan Area Development in the Context of Regional Governance Evolution
Received date: 2024-02-25
Revised date: 2024-06-27
Online published: 2024-12-24
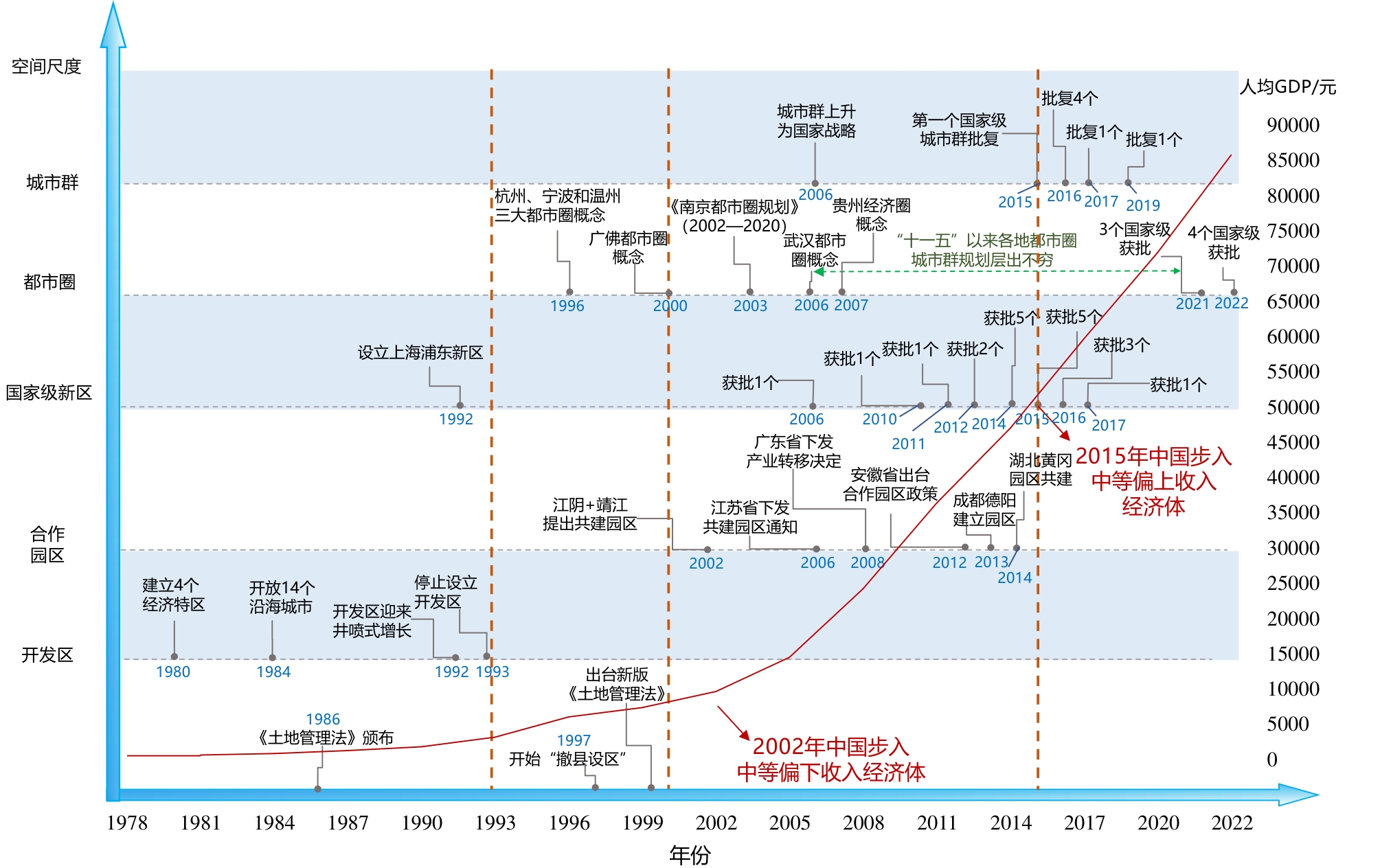
Based on a literature review and policy analysis, this study analyzes the evolution of the regional governance regime in China since its reform and opening-up, and examines how this process has influenced the development of contemporary metropolitan areas. Multiscale spatial development strategies and regional governance regimes have been formed because of different development goals and visions in regional development. As a crucial mediating scale in China's regional governance, the construction of metropolitan areas has exhibited notable variation in governance subjects, structures, and developmental effects during different development phases. From the perspective of spatial governance goals, factor allocation means, and their scalar characteristics, this study categorizes China's regional governance into four periods since the reform and opening-up in the late 1970s: i) regional economic growth driven by development zones (1978-1993), ii) regional resource reallocation through administrative adjustment (1994-2000), iii) regional coordinated development through the development of industrial parks and new national-level areas (2001-2015), and iv) multi-level governance of urban agglomerations and metropolitan areas (2016-present). Governance forms and functional characteristics varied across different periods, contributing to a shift in China's regional governance from a centralized planned economy to a multilevel regulatory governance model. As metropolitan areas have become a key strategy in the new type of urbanization process, their development at different stages has exhibited different governance structures and functional characteristics. This study systematically reviews the evolutionary characteristics and driving factors of the regional governance stages and compares the first three metropolitan areas approved by the central government: Nanjing, Chengdu, and Fuzhou. It was found that the differences in regional governance across these stages shaped the functional development and vision of metropolitan areas. The Nanjing metropolitan area is under a multilevel governance stage, representing developed regions, characterized by advanced cross-boundary cooperation and a well-established coordination system between the central city and surrounding cities and counties. In this model, multilevel governments and non-governmental organizations actively participate in cross-regional governance, with market integration playing a leading role in metropolitan development. This has resulted in multidimensional development, such as the cross-boundary development of infrastructure, industries, and ecological protection. The Chengdu metropolitan area remains in a hierarchical governance stage marked by uneven regional development between the central city and the surrounding cities and countries. Consequently, government-initiated projects, such as ecological protection and infrastructure development, have been implemented, but the lack of market actors has constrained the development of the industrial division of labor and cooperation. This region has yet to form a unified resource allocation platform, which limits the flow of resources and development factors across administrative boundaries. The Fuzhou metropolitan area is characterized by industrial collaboration initiatives through intercity cooperative zones, and its central city has a weak influence on the surrounding cities and counties. Support from the provincial government facilitated the establishment of cross-boundary cooperative parks; however, excessive reliance on administrative mechanisms hindered the emergence of market-driven mechanisms. The capacity for regional functional integration and cooperation was relatively weak compared to the Nanjing and Chengdu metropolitan areas. A comparative analysis of the three metropolitan areas reveals that more economically developed regions tend to focus on functional integration among different cities and counties. Meanwhile, regions with uneven economic development emphasize coordinated development and improve ad hoc cross-boundary development issues. The interaction of government and market actors leads to distinct forms of regional governance and impacts the realization of metropolitan area functions.
Haiyue Wang , Lei Wang , Jiangsheng Chen , Liuqing Yang , Yaoben Lin . Understanding China's Metropolitan Area Development in the Context of Regional Governance Evolution[J]. Tropical Geography, 2025 , 45(5) : 890 -902 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20240105
表1 2020年三大都市圈建设基本情况比较Table 1 The comparison of metropolitan area development in 2020 |
| 指标 | 福州都市圈 | 成都都市圈 | 南京都市圈 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 面积/km2 | 26 000 | 33 100 | 66 000 |
| 人均GDP/万元 | 11.8 | 8.9 | 13.2 |
| 人口密度/(人·km·2) | 573.3 | 808.8 | 535.7 |
| 中心城市GDP占比/% | 64.26 | 83.39 | 35.04 |
| 首位度 | 2.61 | 7.54 | 2.067 |
|
表2 都市圈建设优先内容比较Table 2 Comparison of the priorities of metropolitan area development |
| 都市圈建设内容 | 南京都市圈 | 成都都市圈 | 福州都市圈 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基础设施建设 | √ | √ | √ |
| 产业协作体系 | √ | √ | √ |
| 生态环境保护 | √ | √ | √ |
| 医疗卫生体系 | √ | × | × |
| 社会保障服务 | √ | × | × |
| 文旅资源共享 | √ | √ | √ |
| 人力资源共享 | √ | × | × |
| 政务互联互通 | √ | √ | √ |
| 金融平台建设 | √ | × | × |
|

王海月:数据及文献采集与处理、分析与图表制作、论文撰写;
王 磊:论文思路与研究设计、内容修改完善、经费支持;
陈江生:论文思路指导、内容审阅;
杨柳青:论文内容修改、完善;
林耀奔:论文内容完善、经费支持。
|
Brenner N. 2002. Decoding the Newest "Metropolitan Regionalism" in the USA: A Critical Overview. Cities, 19(1): 3-21.
|
|
Brenner N. 2004. Urban Governance and the Production of New State Spaces in Western Europe, 1960-2000. Review of International Political Economy, 11(3): 447-488.
|
|
晁恒,马学广,李贵才. 2015. 尺度重构视角下国家战略区域的空间生产策略——基于国家级新区的探讨. 经济地理,35(5):1-8.
Chao Heng, Ma Xue Guang, and Li Guicai. 2015. Production Strategy of Space under the National Strategy Region in the Perspective of Scale Rescaling: Based on the Analysis of the State-Level New Areas. Economic Geography, 35(5): 1-8.
|
|
晁恒,满燕云,王砾,李贵才. 2018. 国家级新区设立对城市经济增长的影响分析. 经济地理,38(6):19-27.
Chao Heng, Man Yanyun, Wang Shuo, and Li Guicai. 2018. Impact Analysis of Effect of National-Level New Area to the Urban Economic Growth in China. Economic Geography, 38(6): 19-27.
|
|
陈雯,王珏,孙伟. 2019. 基于成本-收益的长三角地方政府的区域合作行为机制案例分析. 地理学报,74(2):312-322.
Chen Wen, Wang Yu, and Sun Wei. 2019. Cost-Efficiency Mechanism and Game-Action of Inter-Local Governmental Cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Acta Geographcical Sinica, 74(2): 312-322.
|
|
方创琳,王振波,马海涛. 2018. 中国城市群形成发育规律的理论认知与地理学贡献. 地理学报,73(4):651-665.
Fang Chuang Lin, Wang Zhenbo, and Ma Haitao. 2018. The Theoretical Cognition of the Development Law of China's Urban Agglomeration and Academic Contribution. Acta Geographcical Sinica, 73(4): 651-665.
|
|
方创琳. 2021. 新发展格局下的中国城市群与都市圈建设. 经济地理,41(4):1-7.
Fang Chuanglin. 2021. China's Urban Agglomeration and Metropolitan Area Construction under the New Development Pattern. Economic Geography, 41(4): 1-7.
|
|
福建省发展和改革委员会. 2012. 关于深化山海协作的八条意见. (2012-10-30)[2024-10-25]. https://www.doc88.com/p-385772879216.html.
Fujian Provincial Development and Reform Commission. 2012. Eight Proposals on Deepening Cooperation between Mountains and Oceans. (2012-10-30) [2024-10-25]. https://www.doc88.com/p-385772879216.html.
|
|
福建省人民政府. 2021. 福州都市圈发展规划. (2021-06-27)[2023-06-19]. https://www.fujian.gov.cn/zwgk/zxwj/szfwj/202107/t20210709_5644123.htm.
Fujian Provincial People's Government. 2021. Development Planning of Fuzhou Metropolitan Area. (2021-06-27) [2023-06-19]. https://www.fujian.gov.cn/zwgk/zxwj/szfwj/202107/t20210709_5644123.htm.
|
|
福建省统计局,国家统计局福建调查总队. 2021. 福建省统计年鉴2021. 北京:中国统计出版社.
Statistics Bureau of Fujian Province and National Bureau of Statistics Survey Team in Fujian. 2021. Fujian Statistical Yearbook 2021. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
|
|
葛天任,李强. 2022. 从“增长联盟”到“公平治理”——城市空间治理转型的国家视角. 城市规划学刊,(1):81-88.
Ge Tian Ren and Li Qiang. 2022. From Growth Coalition to Equity Governance: A Political Logic of Spatial Governance in Urban China. Urban Planning Forum, (1): 81-88.
|
|
耿慧,焦华富,叶雷. 2022. 都市圈一体化研究进展与展望. 人文地理,37(4):1-9,86.
Geng Hui, Jiao Huafu, and Ye Lei. 2022. Research and Prospect of Metropolitan Area Integration. Human Geography, 37(4): 1-9, 86.
|
|
顾朝林. 2000. 论城市治理研究. 城市规划,(9):7-10. [Gu Chao lin. 2000. On Urban Governance. City Planning Review, (9): 7-10.]
|
|
顾朝林,王颖. 2013. 城市群规划中的治理研究——以绍兴城市群规划为例. 人文地理,28(2):61-66. [Gu Chaolin and Wang Ying. 2013. Governance of Urban Agglomerations: A Case of Shaoxing. Human Geography, 28(2): 61-66.]
|
|
胡剑双,孙经纬. 2020. 国家-区域尺度重组视角下的长三角区域治理新框架探析. 城市规划学刊,(5):55-61.
Hu Jianshuang and Sun Jingwei. 2020. A Research on the New Regional Governance Model of the Yangtze River Delta from the Perspective of State-Region Rescaling. Urban Planning Forum, (5): 55-61.
|
|
胡燕,孙羿,陈振光. 2013. 中国城市与区域治理研究十年回顾与前瞻. 人文地理,28(2):74-78.
Hu Yan, Sun Yi, and Chen Zhen'guang. 2013. A Review on the Research of Urban Regional Governance in China. Human Geography, 28(2): 74-78.
|
|
蒋费雯,罗小龙. 2016. 产业园区合作共建模式分析——以江苏省为例. 城市问题,(7):38-43.
Jiang Feiwen and Luo Xiaolong. 2016. Analysis on the Co-Construction Mode of Industrial Parks—Taking Jiangsu Province as an Example. Urban Problems, (7): 38-43.
|
|
江苏省人民政府. 2007. 省政府关于支持南北挂钩共建苏北开发区政策措施的通知. (2007-10-24)[2024-10-25]. https://www.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2007/10/24/art_47065_2685446.html.
Jiangsu Provincial People's Government. 2007. Notice of the Provincial Government on Supporting the Cooperation Between North and South to Build the Southeast China Development Zone. (2007-10-24) [2024-10-25]. https://www.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2007/10/24/art_47065_2685446.html.
|
|
江苏省人民政府. 2021. 南京都市圈发展规划. (2021-03-22)[2023-06-19]. http://www.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2021/4/16/art_46143_9750343.html.
Jiangsu Provincial People's Government. 2021. Development Planning of Nanjing Metropolitan Area. (2021-03-22) [2023-06-19]. http://www.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2021/4/16/art_46143_9750343.html.
|
|
江苏省统计局,国家统计局江苏调查总队. 2021. 江苏省统计年鉴2021. 北京:中国统计出版社.
Statistics Bureau of Jiangsu Province and National Bureau of Statistics Survey Team in Jiangsu. 2021. Jiangsu Statistical Yearbook 2021. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
|
|
巨量引擎城市研究院. 2022. 2022中国都市圈发展力白皮书——寻找中国最具竞争力的都市圈.(2022-12-21)[2024-06-03]. https://trendinsight.oceanengine.com/arithmetic-report/detail/856.
Giant Engine City Research Institute. 2022. China Metropolitan Area Development Strength White Paper in 2022—Find the Most Competitive Metropolitan Area. (2022-12-21) [2024-06-03]. https://trendinsight.oceanengine.com/arithmetic-report/detail/856.
|
|
孔冰清,王磊,段学军. 2023. 中国铁路建设与国土空间发展的关系演变——基于多层级治理视角. 热带地理,43(5):859-871.
Kong Bingqing, Wang Lei, and Duan Xuejun. 2023. Nexus between Railway Construction and National Territorial Development Strategies in China: A Multi-Level Governance Perspective. Tropical Geography, 43(5): 859-871.
|
|
Lefèvre C. 2002. Metropolitan Government and Governance in Western Countries: A Critical Review. International Journal of Urban and Regional Research, 22(1): 9-25.
|
|
李鲁奇,马学广,鹿宇. 2019. 飞地经济的空间生产与治理结构——基于国家空间重构视角. 地理科学进展,38(3):346-356.
Li Lu Qi, Ma Xueguang, and Lu Yu. 2019. The Production and Governance Structure of Enclave Economy: From the Perspective of State Spatial Restructuring. Progress in Geography, 38(3): 346-356.
|
|
李薇,郎嵬,张京祥. 2024. 典型都市圈空间结构与功能网络联系的演变研究. 现代城市研究,(3):96-102.
Li Wei, Lang Wei, and Zhang Jingxiang. 2024. Research on the Evolution of Spatial Structure and Functional Network of Typical Metropolitan Areas. Modern Urban Research, (3): 96-102.
|
|
刘玮辰,陆玉麒,徐旳. 2017. 南京都市圈空间相互作用时空演变分析. 人文地理,32(2):65-71.
Liu Weichen, Lu Yulin, and Xu Di. 2017. The Spatio-Temporal Evolvement Analysis of Spatial Interaction among Cities and Counties of Nanjing Metropolititan Area. Human Geography, 32(2): 65-71.
|
|
罗小龙,沈建法. 2008. 基于共同利益关系的长江三角洲城市合作——以长江三角洲城市经济协调会为例. 经济地理,28(4):543-547.
Luo Xiaolong and Shen Jianfa. 2008. Partnership-Oriented Inter-City Cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta Region—A Case Study on the Forum for the Coordination of Urban Economy of the Yangtze River Delta Region. Economic Geography, 28(4): 543-547.
|
|
罗小龙,殷洁,田冬. 2010. 不完全的再领域化与大都市区行政区划重组——以南京市江宁撤县设区为例. 地理研究,29(10):1746-1756.
Luo Xiaolong, Yin Jie, and Tian Dong. 2010. Administrative Boundary Re-Organization in Nanjing Metropolitan Region. Geographical Research, 29(10): 1746-1756.
|
|
罗震东,汪鑫,耿磊. 2015. 中国都市区行政区划调整——城镇化加速期以来的阶段与特征. 城市规划,39(2):44-49,64.
Luo Zhendong, Wang Xin, and Geng Lei. 2015. Administrative Division Adjustment in Metropolitan Areas of China: Stages and Characteristics in the Acceleration Period of Urbanization. City Planning Review, 39(2): 44-49, 64.
|
|
马学广,唐承辉. 2019. 新国家空间理论视角下城市群的国家空间选择性研究. 人文地理,34(2):105-115.
Ma Xueguang and Tang Chenghui. 2019. Study on State Spatial Selectivity of Urban Agglomeration from the Perspective of New State Space Theory. Human Geography, 34(2): 105-115.
|
|
Nicholls W J. 2005. Power and Governance Metropolitan Governance in France. Urban Studies, 42(4): 783-800.
|
|
申明锐,王紫晴,崔功豪. 2023. 都市圈在中国:理论源流与规划实践. 城市规划学刊,(2):57-66.
Shen Mingrui, Wang Ziqing, and Cui Gonghao. 2023. Planning Metropolitan Regions in China: Theoretical Origins and Planning Practices. Urban Planning Forum, (2): 57-66.
|
|
四川省人民政府. 2021. 成都都市圈发展规划. (2021-11-29)[2023-06-19]. https://www.sc.gov.cn/10462/10464/10797/2021/11/30/a01ce79949154818bf60517e0323cb26.shtml.
Sichuan Provincial People's Government. 2021. Development Planning of Chengdu Metropolitan Area. (2021-11-29) [2023-06-19]. https://www.sc.gov.cn/10462/10464/10797/2021/11/30/a01ce79949154818bf60517e0323cb26.shtml.
|
|
四川省统计局,国家统计局四川调查总队. 2021. 四川省统计年鉴2021. 北京:中国统计出版社.
Statistics Bureau of Sichuan Province and National Bureau of Statistics Survey Team in Sichuan. 2021. Sichuan Statistical Yearbook 2021. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
|
|
王磊,段学军,杨清可. 2017. 长江经济带区域合作的格局与演变. 地理科学,37(12):1841-1849.
Wang Lei, Duang Xuejun, and Yang Qingke. 2017. The Development Pattern and Its Evolution of Regional Cooperation in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 37(12): 1841-1849.
|
|
Wang L and Shen J F. 2016. Spatial Planning and Its Implementation in Provincial China: A Case Study of the Jiangsu Region along the Yangtze River Plan. Journal of Contemporary China, 25(101): 669-685.
|
|
王璇,郐艳丽. 2021. 国家级新区尺度政治建构的内在逻辑解析. 国际城市规划,36(2):32-39.
Wang Xuan and Gui Yanli. 2021. Analysis on the Political Construction of Scale of State-Level New Areas. Urban Planning International, 36(2): 32-39.
|
|
Williams G. 1999. Metropolitan Governance and Strategic Planning: A Review of Experience in Manchester, Melbourne and Toronto. Progress in Planning, 52(1): 1-100.
|
|
Wu F. 2017. China's Emergent City-Region Governance: A New Form of State Spatial Selectivity through State-Orchestrated Rescaling. International Journal of Urban and Regional Research, 40(6): 1134-1151.
|
|
吴耀华. 2020. 闽东北区域协同发展研究. 福州:福建农林大学.
Wu Yaohua. 2020. Research on the Coordinated Development of Northeast Fujian. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University.
|
|
Xu J. 2008. Governing City-Regions in China: Theoretical Issues and Perspectives for Regional Strategic Planning. The Town Planning Review, 79(2/3): 157-185.
|
|
杨凌凡,罗小龙,唐蜜,顾宗倪,刘晓曼. 2022a. 尺度重构视角下开发区整合转型机制研究——以江苏省为例. 经济地理,42(6):33-44.
Yang Lingfan, Luo Xiaolong, Tang Mi, Gu Zongni, and Liu Xiaoman. 2022a. The Integration and Transformation Mechanisms of Development Zones from the Perspective of Rescaling: A Case Study of Jiangsu Province. Economic Geography, 42(6): 33-44.
|
|
杨凌凡,罗小龙,唐蜜,丁子尧. 2022b. 城际合作园区转型的制度空间重构机制——以锡沂高新区为例. 地理科学,42(7):1196-1206.
Yang Lingfan, Luo Xiaolong, Tang Mi, and Ding Ziyao. 2022b. Changing Mechanisms of Institutional Space for Restructuring Inter-City Cooperative Zones: A Case of the Wuxi-Xinyi (Xiyi) High Tech Zone. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 42(7): 1196-1206.
|
|
杨柳青,季菲菲,陈雯. 2019. 区域合作视角下南京都市圈规划的实践成效及反思. 上海城市规划,(2):49-55.
Yang Liuqing, Ji Feifei, and Chen Wen. 2019. Practical Achievements and Reflections on the Planning of Nanjing Metropolitan Area under Regional Cooperation. Shanghai Urban Planning Review, (2): 49-55.
|
|
Ye L. 2014. State-Led Metropolitan Governance in China: Making Integrated City Regions. Cities, 41: 200-208.
|
|
殷洁,罗小龙,肖菲. 2018. 国家级新区的空间生产与治理尺度建构. 人文地理,33(3):89-96.
Yin Jie, Luo Xiaolong, and Xiao Fei. 2018. The Space Production and Governance Rescaling of State-Level New Areas. Human Geography, 33(3): 89-96.
|
|
尹稚,袁昕,卢庆强,林澎,王强. 2019. 中国都市圈发展报告2018. 北京:清华大学出版社.
Yin Zhi, Yuan Xin, Lu Qingqiang, Lin Peng, and Wang Qiang. 2019. The Development Report of China's Metrpolitan Area in 2018. Beijing: Tsinghua Unieversity Press.
|
|
尹稚,卢庆强,吕晓荷,王强. 2021. 中国都市圈发展报告2021. 北京:清华大学出版社.
Yin Zhi, Lu Qingqiang, Lu Xiaohe, and Wang Qiang. 2021. The Development Report of China's Metrpolitan Area in 2021. Beijing: Tsinghua Unieversity Press.
|
|
张践祚,李贵才,王超. 2016. 尺度重构视角下行政区划演变的动力机制——以广东省为例. 人文地理,31(2):74-82.
Zhang Jianzuo, Li Guicai, and Wang Chao. 2016. Dynamic Mechanism of Administrative Division Adjustment under the Context of Scale Rescaling: The Case of Guangdong Province. Human Geography, 31(2): 74-82.
|
|
张京祥,庄林德. 2000. 治理及城市与区域治理——一种新制度性规划理念. 城市规划,(6):36-39. [Zhang Jingxiang and Zhuang Linde. 2000. Governance and Governance for City and Region. City Planning Review, (6): 36-39.]
|
|
张京祥,罗小龙,殷洁. 2008. 长江三角洲多中心城市区域与多层次治理. 国际城市规划,(1):65-69.
Zhang Jingxiang, Luo Xiaolong, and Yin Jie. 2008. Polycentric Mega-City Regions and Multi-Level Governance of the Yangtze River Delta. Urban Planning International, (1): 65-69.
|
|
张京祥,耿磊,殷洁,罗小龙. 2011. 基于区域空间生产视角的区域合作治理——以江阴经济开发区靖江园区为例. 人文地理,26(1):5-9.
Zhang Jingxiang, Geng Lei, Yin Jie, and Luo Xiaolong. 2011. The Regional Cooperative Governance from the Perspective of Regional Spatial Production. Human Geography, 26(1): 5-9.
|
|
张京祥,陈浩,王宇彤. 2019. 新中国70年城乡规划思潮的总体演进. 国际城市规划,34(4):8-15.
Zhang Jingxiang, Chen Hao, and Wang Yutong. 2019. The Evolution of Thoughts on Urban and Rural Planning in China since the Founding of the People's Republic of China in 1949. Urban Planning International, 34(4): 8-15.
|
|
张京祥,胡航军. 2023. 新发展环境下的都市圈发展、规划与治理创新. 经济地理,43(1):17-25.
Zhang Jingxiang and Hu Hangjun. 2023. Innovation in the Development, Planning and Governance of Metropolitan Areas under the New Development Environment. Economic Geography, 43(1): 17-25.
|
|
张衔春,单卓然,许顺才,洪世键. 2016. 内涵·模式·价值:中西方城市治理研究回顾、对比与展望. 城市发展研究,23(2):84-90,104.
Zhang Xianchun, Shan Zhuoran, Xu Shuncai, and Hong Shijian. 2016. Connotation·Model·Value: The Review, Comparison and Expectation on Urban Governance: Research in Western Counties and China. Urban Development Studies, 23(2): 84-90, 104.
|
|
张衔春,胡国华,单卓然,李禕. 2021. 中国城市区域治理的尺度重构与尺度政治. 地理科学,41(1):100-108.
Zhang Xianchun, Hu Guohua, Shan Zhuoran, and Li Yi. 2021. Rescaling and Politics of Scale in China's City-Regional Governance. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 41(1): 100-108.
|
|
张衔春,陈宇超,杨宇,栾晓帆. 2023. 中国区域治理中公私合作伙伴关系研究. 地理研究,42(2):297-311.
Zhang Xianchun, Chen Yuchao, Yang Yu, and Luan Xiaofan. 2023. The Public-Private Partnerships in China's Regional Governance. Geographical Research, 42(2): 297-311.
|
|
张学良,林永然. 2019. 都市圈建设:新时代区域协调发展的战略选择. 改革,(2):46-55.
Zhang Xueliang and Lin Yongran. 2019. The Construction of Metropolitan Area: A Strategic Choice of Coordinated-Regional Development in the New Era. Reform, (2): 46-55.
|
|
赵民,王启轩. 2021. 我国“开发区”的缘起、演进及新时代的治理策略探讨. 城市规划学刊,(6):28-36.
Zhao Min and Wang Qixuan. 2021. On the Origin, Evolution and Transformation of the Development Zones in China: Perspectives and New Agendas. Urban Planning Forum, (6): 28-36.
|
|
甄峰,简博秀,沈青,郑俊. 2007. 城市治理、区划调整与空间整合——以常州市区为例. 地理研究,26(1):157-167,216.
Zhen Feng, Jian Boxiu, Shen Qing, and Zheng Jun. 2007. Urban Governance, the Adjustment of Administration and Spatial Integration: A Case Study of Changzhou. Geographical Research, 26(1): 157-167, 216.
|
|
周子航,张京祥,杨洁莹. 2023. 风险社会视角下国家级新区治理格局检视——以南京江北新区为例. 国际城市规划,38(1):91-99.
Zhou Zihang, Zhang Jingxiang, and Yang Jieying. 2023. Governance Modality of State-Level New Areas from the Perspective of Risk Society: A Case Study of Jiangbei New Area, Nanjing. Urban Planning International, 38(1): 91-99.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |