

Resilience of Fishery Economy in Fujian Coastal Areas from the Perspective of Institutional Evolution
Received date: 2024-01-26
Revised date: 2024-07-09
Online published: 2025-01-02
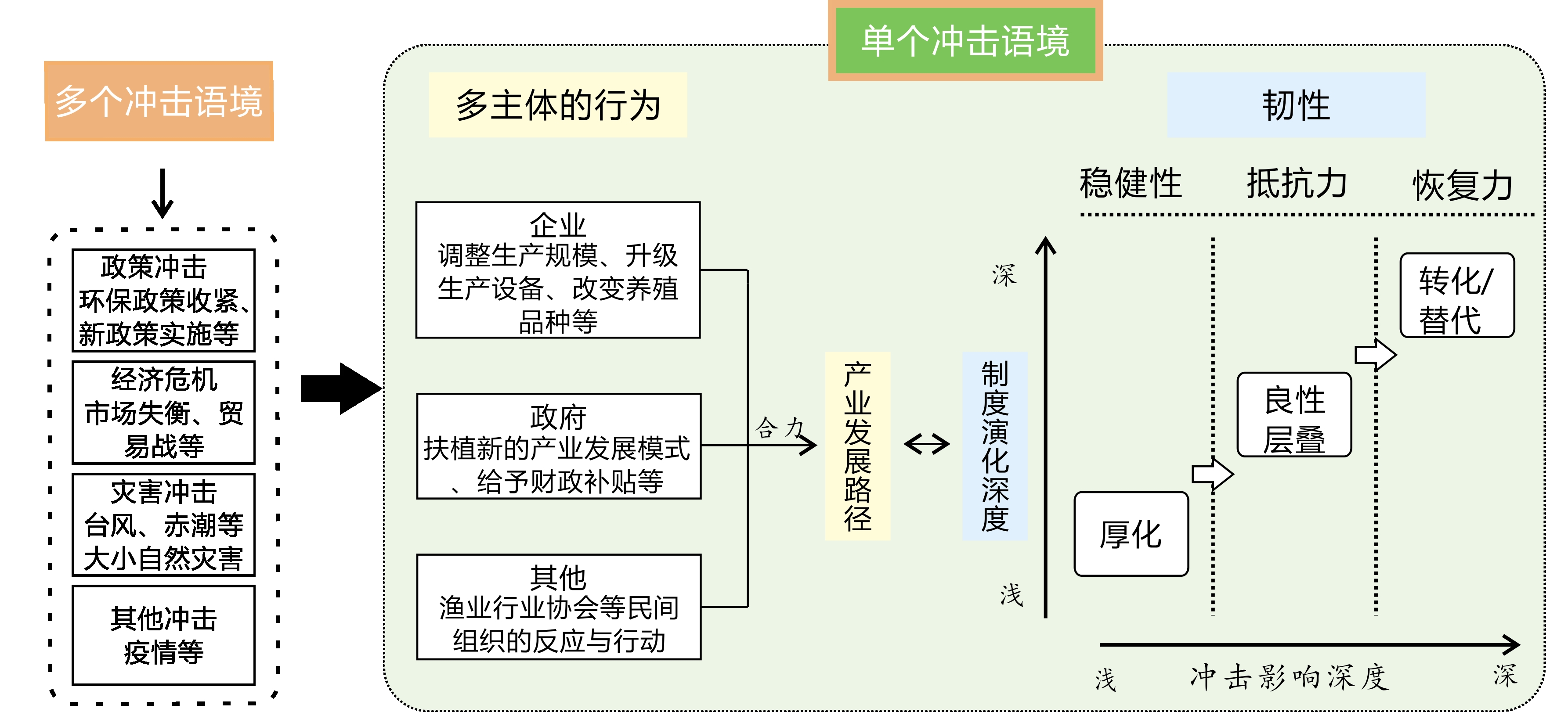
This study considers the fishery industry in the coastal area of Fujian Province as an example, measures the resilience resistance of the fishery industry using output value and output, and constructs an analytical framework by combining the "Robustness-Resistance-Recovery" resilience assessment framework and the theory of institutional change to give explanations for the formation of the differences in fishery resilience. The four types of gradually deepening institutional changes are layering (thickening and positive layering), conversion, and displacement. The robustness dimension of resilience corresponds to thickening, the resistance dimension corresponds to positive layering, and recovery corresponds to conversion or displacement. Three main conclusions are drawn: 1) Under the influence of different types of shocks (the super-typhoon in 2006, the financial crisis in 2008, and the upgrading of the fishing industry in 2017), the output value fluctuates significantly owing to the dual effects of production and supply, and the output is more strongly affected by production and more drastically reflective of natural disasters. 2) A spatial regularity exists in the impact of regional crises (typhoons) on industrial resilience resistance; the closer to the disaster center, the poorer the performance of industrial resilience resistance. The economic and industrial transformation crises have a homogeneous effect on the fishery economy, and the spatial differences in the resilience of the fishery economy are more influenced by historical foundations and institutional evolution. 3) The 25 research units in coastal areas were divided into five categories. The spatial distribution of fishery resilience is affected by coastline length. High-resilience areas were mainly concentrated in the middle of the coastal region in the study units with longer coastlines. The resilience of the north and south ends improved from year to year, and the length of the coastline in the areas with lower resilience was shorter. Differences were noted in the performance of each region in terms of resilience to shocks, including robustness, resistance, and resilience, as well as differences in the depth of institutional change types. Regions that choose the right development path and the right mode of institutional change in a crisis are more resilient and help the region reduce resource constraints on fisheries development, even if it is a thickening of the original system that can defuse the crisis, whereas a few regions are less resilient in choosing a direction of institutional change that is separatedfrom the region's industrial base, where new development paths have yet to take root. This study highlights the importance of regional institutional change in the formation of fishery resilience, provides a new perspective on how institutional change affects economic activity, and uses quantitative methods to investigate the relationship between institutional change and industrial resilience. In addition, this study has important implications for disaster response and risk management, helping firms and governments better prepare for and respond to potential economic shocks.
Yun Leng , Suqiong Wei , Xiaojun You , Zhihuang Ren . Resilience of Fishery Economy in Fujian Coastal Areas from the Perspective of Institutional Evolution[J]. Tropical Geography, 2025 , 45(1) : 37 -51 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20240053
表1 福建省沿海地区渔业发展历程、制度演化与韧性评价Table 1 The fisheries development history, institutional evolution, and resilience assessment in the coastal areas of Fujian Province |
| 类型及其包含的研究单元 | 渔业发展历程 | 制度演化模式 | 韧性3Rs评价 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 稳健性 | 抵抗力 | 恢复力 | ||||
| 低韧性区域 (福州市区、仙游县、 泉州市区、漳州市区) | 以传统渔业捕捞为主,经营以家庭为单位,规模较小,一直无法进行产业升级。 | 厚化(边缘化下渔业缺少政府调控的无序自主发展) | 资源禀赋与产业基础较差,韧性稳健性较差 | 低中-低-低 | 落后产业发展路径的不断厚化 | |
| 韧性断崖式下滑区域 (厦门市区) | 2006年前期,有实现渔业多样化经营孵化的契机,渔业发展较好。2006年后,其他产业对渔业作业空间的争夺,政府机构逐步将渔业边缘化,产业发展不断后退。 | 替代(渔业边缘化下渔业核心功能的替代) | 资源禀赋与产业基础较好,有一定的稳健性,后期逐渐变差。 | 中-低-低 | 制度引导下的产业退出 | |
| 韧性逐年变差区域 (闽侯县、惠安县) | 2017年以前以传统渔业捕捞为主,经营以中小型企业为主,渔业规模中等,且逐渐难以适应产业外部环境的变化。2017年冲击后,政府带头开展金鱼产业,但目前由于内在动能不足,尚未实现自主化发展。 | 厚化(依附于政府引导,追求产业的持续) | 资源禀赋与产业基础较好,有一定稳健性 | 中-中低-低 | 短暂且不可持续的转型 | |
| 高韧性区域 (福清市、连江县、 莆田市区、东山县) | 2008年前,以传统渔业起步,得益于良好的资源禀赋,逐步找到利基市场,发展远洋渔业,渔业产业基础深厚。2008年后积极主动地发展现代海洋产业体系,实现渔业多样化生产。 | 良性层叠与转化(以企业为主体、政府积极配合的 面向路径创新) | 资源禀赋与产业基础好,韧性稳健性强 | 高-高-高 | 创造可持续、有活力的新路径 | |
| 韧性 逐年 变好 区域 | I型 (宁德市区、福鼎市、 龙海市、漳浦县) | 2008年前,以传统渔业起步,渔业发展缺少特色,产业发展以低效率扩张为主,有一定产业基础。2008年后,在高韧性区域发展多样化渔业的成功经验下,各个区域先后进行自身的渔业产业升级改造。 | 从厚化转到良性层叠与转化(地方政府引导以及先进渔业知识溢出下的路径复制) | 资源禀赋与产业基础较好,有一定稳健性 | 中低-中高- 中高 | 能成功复制,因地制宜地 发展新路径 |
| Ⅱ型 (长乐市、平潭县、罗源县、霞浦县、诏安县) | 中低-中-中高 | |||||
| Ⅲ型 (晋江市、石狮市、南安市、云霄县、福安市) | 低中-低-中 | |||||
|
1 福建省海洋与渔业局. 2001—2020年。
冷 韵:提出研究思路、负责数据分析与论文撰写修改;
韦素琼:修订研究方案,论文撰写与修改;
游小珺:修订研究方案,论文修改;
任之煌:图表制作、数据收集。
|
Biggs R, Schlüter M, Biggs D, Bohensky E L, BurnSilver S, Cundill G, Dakos V, Daw T M, Evans L S, Kotschy K, Leitch A M, Meek C, Quinlan A, Raudsepp-Hearne C, Robards M D, Schoon M L, Schultz L, and West P C. 2012. Toward Principles for Enhancing the Resilience of Ecosystem Services. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 37(1): 421-448.
|
|
Bristow G and Healy A. 2014. Regional Resilience: An Agency Perspective. Regional Studies, 48(5): 923-935.
|
|
Bristow G, Healy A, Martin R, and Sunley Peter. 2020. Handbook on Regional Economic Resilience. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar Publishing.
|
|
Christopherson S, Michie J, and Tyler P. 2010. Regional Resilience: Theoretical and Empirical Perspectives. Cambridge Journal of Regions Economy and Society, 3(1): 3-10.
|
|
Coulthard S. 2012. Can We be both Resilient and Well, and What Choices do People have? Incorporating Agency into the Resilience Debate from a Fisheries Perspective. Ecology and Society, 17(1): 4.
|
|
Dodgson D G. 2006. What are Institutions? Journal of Economic Issues, 40(1): 1-25.
|
|
Dempwolf C S and Lylse L W. 2012. The Uses of Social Network Analysis in Planning: A Review of the Literature. Journal of Planning Literature Incorporating the Cpl Bibliographies, 27(1): 3-21.
|
|
Di Caro P. 2015. Recessions, Recoveries and Regional Resilience: Evidence on Italy. Cambridge Journal of Regions Economy and Society, 8(2): 273-291.
|
|
Duer-balkind M, Jacobs K R, Güneralp B, and Basurto X. 2013. Resilience, Social-Ecological Rules, and Environmental Variability in a Two-Species Artisanal Fishery. Ecology and Society, 18(4): 34.
|
|
杜志威,文志敏,金利霞. 2022. “结构-能动性”框架下短期经济韧性的动态演化与影响机制——基于新冠肺炎疫情冲击下对东莞企业的访谈. 热带地理,42(8):1217-1227.
Du Zhiwei, Wen Zhimin, and Jin Lixia. 2022. Dynamic Evolution and Mechanism of Short-Term Economic Resilience from a Structure-Agency Framework: Based on In-Depth Interviews with Dongguan's Manufacturing Enterprises during COVID-19. Tropical Geography, 42(8): 1217-1227.
|
|
Evenhuis E. 2017. New Directions in Researching Regional Economic Resilience and Adaptation. Geography Compass, 11: 15.
|
|
干春晖,郑若谷,余典范. 2011. 中国产业结构变迁对经济增长和波动的影响. 经济研究,46(5):4-16,31.
Gan Chunhui, Zheng Ruogu, and Yu Dianfan. 2011. An Empirical Study on the Effects of Industrial Structure on Economic Growth and Fluctuations in China. Economic Research Journal, 46(5): 4-16, 31.
|
|
高法成. 2024. 南海渔民生计脆弱性的内生问题—基于广东硇洲岛的田野调查. 热带地理,44(2):248-257.
Gao Facheng. 2024. Endogenous Problem of Fishermen's Livelihood in South China Sea: Based on Field Work of Naozhou Island in Guangdong. Tropical Geography, 44(2): 248-257.
|
|
Garud R, Kumaraswamy A, and Karnoee P. 2010. Path Dependence or Path Creation? Journal of Management Studies, 47(4): 760-774.
|
|
Gherhes C, Vorley T, and Williams N. 2018. Entrepreneurship and Local Economic Resilience: The Impact of Institutional Hysteresis in Peripheral Places. Small Business Economics, 51: 577-590.
|
|
Grafton R Q, Doyen L, BéNé C, Borgomeo E, Brooks K, Chu L, Cumming G S, Dixon J, Dovers S, Garrick D, Helfgott A, Jiang Q, Katic P, Kompas T, Little L R, Matthews N, Ringler C, Squires D, Steinshamn S I, Villasante S, Wheeler S, Williams J, and Wyrwoll P R. 2019. Realizing Resilience for Decision-Making. Nature Sustainability, 2(10): 907-913.
|
|
Grafton R Q, Kompas T, and Pham V. 2009. Cod Today and None Tomorrow: The Economic Value of a Marine Reserve. Land Economics, 85(3): 454-469.
|
|
Grillitsch M and Sotarauta M. 2020. Trinity of Change Agency, Regional Development Paths and Opportunity Spaces. Progress in Human Geography, 44(4): 704-723.
|
|
关皓明,杨青山,浩飞龙,冯章献. 2021. 基于“产业-企业-空间”的沈阳市经济韧性特征. 地理学报,76(2):415-427.
Guan Haoming, Yang Qingshan, Hao Feilong, and Feng Zhangxian. 2021. Economic Resilience Characteristics of Shenyang City Based on a Perspective of Industry-Enterprise-Space. Acta Geographica Sinica, 76(2): 415-427.
|
|
关美,陈晓宇,李春林. 2024. 中国海洋渔业经济韧性评价及时空演变特征研究. 海洋开发与管理,41(8):90-100.
Guang Mei, Chen Xiaoyu, and Li Chunlin. 2024. A Study on the Resilience Evaluation and Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of China's Marine Fisheries Economy. Ocean Development and Management, 41(8): 90-100.
|
|
韩增林,朱文超,李博. 2022. 中国海洋渔业经济韧性与效率协同演化研究. 地理研究,41(2):14.
Han Zenglin, Zhu Wenchao, and Li Bo. 2022. Synergistic Analysis of Economic Resilience and Efficiency of Marine Fishery in China. Geographical Research, 41(2): 14.
|
|
Hassink R. 2010. Regional Resilience: A Promising Concept to Explain Differences in Regional Economic Adaptability?. Cambridge Journal of Regions Economy and Society, 3(1): 45-58.
|
|
Hou N, Zhu Q Y, Yang J L, Zhang D H, Liu W W, and Chang H. 2021. The Impact of Environmental Governance on the Development of Fishery Economy-The Intermediary Role of Technological Innovation. Sustainability, 13(20): 15.
|
|
Hu Xiaohui and Hassink R. 2017. Exploring Adaptation and Adaptability in Uneven Economic Resilience:a Tale of Two Chinese Mining Regions. Cambridge Journal of Regions Economy and Society, 10(3): 527-541.
|
|
Hu Xiaohui and Yang Chun. 2019. Institutional Change and Divergent Economic Resilience: Path Development of two Resource-Depleted Cities in China. Urban Studies, 56(16): 3466-3485.
|
|
Huizar L H, Lansey K E, and Arnold R G. 2018. Sustainability, Robustness, and Resilience Metrics for Water and other Infrastructure Systems. Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure, 3: 16-35.
|
|
胡晓辉,董柯,杨宇. 2021. 战略耦合演化视角下的区域经济韧性分析框架. 地理研究,40(12):3272-3286.
Hu Xiaohui, Dong Ke, and Yang Yu. 2021. An Analytical Framework on Regional Economic Resilience from the Perspective of Evolutionary Strategic Coupling. Geographical Research, 40(12): 3272-3286.
|
|
胡晓辉,张文忠. 2018. 制度演化与区域经济弹性——两个资源枯竭型城市的比较. 地理研究,37(7):1308-1319.
Hu Xiaohui and Zhang Wenzhong. 2018. Institutional Evolution and Regional Economic Resilience: A Comparison of Two Resource-Exhausted Cities in China. Geographical Research, 37(7): 1308-1319.
|
|
Isaksen A. 2015. Industrial Development in Thin Regions:Trapped in Path Extension? Journal of Economic Geography, 15(3): 585-600.
|
|
姜雨青,张俊波,国志兴,万荣. 2023. 我国沿海渔业养殖设施空间分布与台风影响关联性研究. 海洋湖沼通报,45(1):183-192.
Jiang Yuqing, Zhang Junbo, Guo Zhixing, and Wan Rong. 2023. Studies on the Correlation between the Spatial Distribution of Aquaculture Facilities and the Influence of Typhoon in Southeast China. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 45(1): 183-192.
|
|
蒋正云,刘庆芳,宋金平. 2023. 中国区域经济韧性的格局特征及演化机制. 经济地理,43(6):1-12.
Jiang Zhengyun, Liu Qingfang, and Song Jinping. 2023. Pattern Characteristics and Evolution Mechanism of China's Regional Economic Resilience. Economic Geography, 43(6): 1-12.
|
|
Kleisner K M, Ojea E, Battista W, Cunningham E, Fujita R, Karr K, Amoros S, Mason J, Rader D, Rovegno N, and Thomas-Smyth A. 2022. Identifying Policy Approaches to Build Social-Ecological Resilience in Marine Fisheries with Differing Capacities and Contexts. Ices Journal of Marine Science, 79(2): 552-572.
|
|
Lemke L K G, Sakdapolrak P, and Trippl M. 2023. Unresolved Issues in Regional Economic Resilience: Conceptual Ways forward. Progress in Human Geography, 47(5): 699-717.
|
|
梁贝贝,毛伟. 2023. 渔业经济韧性时空演变及其关联性分析——以长江经济带为例. 中国渔业经济,41(4):43-52.
Liang Beibei and Mao Wei. 2023. Analysis on the Spatiotemporal Evolution and Correlation of Fishery Economic Resilience: Take the Yangtze River Economic Belt as an Example.Chinese Fisheries Economics, 41(4): 43-52.
|
|
李连刚,张平宇,谭俊涛,关皓明. 2019. 韧性概念演变与区域经济韧性研究进展. 人文地理,34(2):1-7,151.
Li Liangang, Zhang Pingyu, Tan Juntao, and Guan Haoming. 2019. Review on the Evolution of Resilience Concept and Research Progress on Regional Economic Resilience. Human Geography, 34(2): 1-7, 151.
|
|
刘逸,纪捷韩,张一帆,杨宇. 2020. 粤港澳大湾区经济韧性的特征与空间差异研究. 地理研究,39(9):2029-2043.
Liu Yi, Ji Jiehan, Zhang Yifan, and Yang Yu. 2020. Economic Resilience and Spatial Divergence in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in China. Geographical Research, 39(9): 2029-2043.
|
|
Ma J T, Wu Z J, Guo M Q, and Hu Q G. 2024. Dynamic Relationship between Marine Fisheries Economic Development, Environmental Protection and Fisheries Technological Progress—A Case of Coastal Provinces in China. Ocean & Coastal Management, 247: 13.
|
|
Mackinnon D, Dawley S, Steen M, Menzel M P, Karlsen A, Sommer P, Hansen G H, and Normann H E. 2019. Path Creation, Global Production Networks and Regional Development:A Comparative International Analysis of the Offshore Wind Sector. Progress in Planning, 130: 1-32.
|
|
Martin R. 2012. Regional Economic Resilience, Hysteresis and Recessionary Shocks. Journal of Economic Geography, 12: 1-32.
|
|
Martin R and Gardiner B. 2019. The Resilience of Cities to Economic Shocks: A Tale of Four Recessions (and the Challenge of Brexit). Papers in Regional Science, 98(4): 1801-1833.
|
|
Martin R and Sunley P. 2015. On the Notion of Regional Economic Resilience: Conceptualization and Explanation. Journal of Economic Geography, 15(1): 1-42.
|
|
Martin R, Sunley P, Gardiner B, and Tyler P. 2016. How Regions React to Recessions: Resilience and the Role of Economic Structure. Regional Studies, 50: 561-585.
|
|
Quimby B, Roque A D, Nébié E K I, Levine A, Amaama S A, Wutich A, Brewis A, and Samuelu L E. 2023. Blue Food Sovereignty Benefits Social-Ecological Resilience: A Case Study of Small-Scale Fisheries Co-Management and Mariculture in Samoa. Human Ecology, 51(2): 279-289.
|
|
Scott J and Latham. 2009. Contrasting Strategic Response to Economic Recession in Start-Up versus Established Software Firms. Journal of Small Business Management, 47(2): 180-201.
|
|
Simmie J and Martin R. 2010. The Economic Resilience of Regions: Towards an Evolutionary Approach. Cambridge Journal of Regions Economy and Society, 3(1): 27-43.
|
|
Smallbone D, Deakins D, Battisti M, and Kitching J. 2012. Small Business Responses to a Major Economic Downturn: Empirical Perspectives from New Zealand and the United Kingdom. International Small Business Journal, 30(7): 754-777.
|
|
Stanford R J, Wiryawan B, Bengen D G, Febriamansyah R, and Haluan J. 2017. The Fisheries Livelihoods Resilience Check (FLIRES Check): A Tool for Evaluating Resilience in Fisher Communities. Fish and Fisheries, 18(6): 1011-1025.
|
|
孙久文,孙翔宇. 2017. 区域经济韧性研究进展和在中国应用的探索. 经济地理,37(10):1-9.
Sun Jiuwen and Sun Xiangyu. 2017. Research Progress of Regional Economic Resilience and Exploration of Its Application in China. Economic Geography, 37(10): 1-9.
|
|
Tan J T, Hu Xiaohui, Hassink R, and Ni J W. 2020. Industrial Structure or Agency: What Affects Regional Economic Resilience? Evidence from Resource-Based Cities in China. Cities, 106: 11.
|
|
Thelen K. 2003. How Institutions Evolve. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
|
|
Van der Heijden J. 2010. A Short History of Studying Incremental Institutional Change: Does Explaining Institutional Change Provide any New Explanations? Regulation & Governance, 4(2): 230-243.
|
|
Streeck W and Thelen K. 2005. Beyond Continuity: Institutional Change in Advanced Political Economies. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
|
|
王琛,郭一琼. 2018. 地方产业抵御经济危机的弹性影响因素——以电子信息产业为例. 地理研究,37(7):11.
Wang Chen and Guo Yiqiong. 2018. Resilience and Resistance of Local Industry to Economic Crisis: Case Study of China's IT Industry. Geographical Research, 37(7): 11.
|
|
Wintergalen E W, Oyanedel R, Villaseñor-derbez J C, Fulton S, and Molina R. 2022. Opportunities and Challenges for Livelihood Resilience in Urban and Rural Mexican Small-Scale Fisheries. Ecology and Society, 27(3): 19.
|
|
吴祖立,崔雪森,张胜茂,周为峰. 2018. 南海台风活动特征及其对渔业活动的影响. 海洋渔业,40(5):548-559.
Wu Zuli, Cui Xuesen, Zhang Shengmao, and Zhou Weifeng. 2018. An Analysis of Characteristics of Typhoons and their Impacts on Fishery Activities in the South China Sea. Marine Fisheries, 40(5): 548-559.
|
|
夏国庆,郑凌燕. 2023. 产业结构门槛下双重环境规制对海洋渔业经济的影响研究. 科技与经济,36(3):66-70.
Xia Guoqing and Zheng Lingyan. 2023. Research on the Influence of Dual Environmental Regulation on Marine Fishery Economy under the Threshold of Industrial Structure. Science & Technology and Economy, 36(3): 66-70.
|
|
熊彬,胡振绅. 2019. 空间视角下资源型城市转型效率差异演化及影响因素分析——以东北地区资源型城市为例. 华东经济管理,33(7):78-86.
Xiong Bin and Hu Zhenshen. 2019. Analysis on the Evolution and Influence Factors of the Transformation Efficiency of Resource-Based Cities from the Perspective of Spatial Perspective—A Case Study of the Empirical Study of Resource-Based Cities in Northeast China. East China Economic Management, 33(7): 78-86.
|
|
杨林,王邵瑜. 2009. 国际金融危机对水产品加工业的影响及其应对策略. 工业技术经济,28(9):23-25.
Yang Lin and Wang Shaoyu. 2009. The Impact of the International Financial Crisis on the Aquatic Product Processing Industry and Its Response Strategies. Journal of Industrial Technology and Economy, 28(9): 23-25.
|
|
杨润言. 2024. 沿海省份渔业经济韧性测度及其时空演变规律研究. 中国渔业经济,42(1):52-62.
Yang Runyan. 2024. Research on Measurement of Fishery Economic Resilience and Its Spatiotemporal Evolution in Coastal Provinces. Chinese Fisheries Economics, 42(1): 52-62.
|
|
杨子江. 2009. 金融危机下中国渔业的“危”与“机”. 中国水产,(2):12-15.
Yang Zijiang. 2009. The "Danger" and "Opportunity" of China's Fisheries under the Financial Crisis. China Fisheries, (2): 12-15.
|
|
叶海军,唐丹玲,潘刚. 2014. 强台风鲶鱼对中国南海浮游植物及渔业资源的影响. 生态科学,33(4):657-663.
Ye Haijun, Tang Danling, and Pan Gang. 2014. The Contribution of Typhoon Megi on Phytoplankton and Fishery Productivity in the South China Sea. Ecological Science, 33(4): 657-663.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |