

Quartz Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Dating of River Terraces in the Zhenjiang River of the Upper Beijiang River
Received date: 2024-08-10
Revised date: 2024-12-24
Online published: 2025-03-14
River terraces are important geomorphic indicators that reveal the evolution of rivers, and their climatic and tectonic responses. Dating is key to studying terrace evolution. In the past decade, electron spin resonance (ESR) dating has been widely applied in Quaternary geology and environmental research, and has solved a series of Quaternary chronology problems. This study selected well-exposed river terrace sections of the Zhenjiang River in the upper reaches of the Beijiang River as the research object and used ESR dating to analyze the ages and formation mechanisms of the terraces of the Zhenjiang River system. The experimental data show that the Ti-Li core dose-response curve of quartz in the sediment samples of the Zhenjiang River terraces fits well with the ESR signal strength, indicating that the terrace samples are stable and meet the requirements of ESR dating. Two age data were obtained from the bottom and the top of the ZJ-P1 profile, with ages of 654 ± 79 ka and 231 ± 29 ka respectively; three age data (576 ± 38 ka, 523 ± 55 ka and 256 ± 26 ka) were obtained from the bottom to the top of the ZJ-P2 profile, and three age data (392 ± 56 ka, 132 ± 15 ka and 41 ± 6 ka) were obtained from the bottom to the top of the ZJ-P3 profile, being respectively. These results reflect the continuous sedimentation of the strata. Through the comparative analysis with the existing thermoluminescence age data of the Zhenjiang River and adjacent basins, it is determined that there are two distinct river terraces on the left bank of the Zhenjiang River in the upper reaches of the Beijiang River, and the final formation times of T2 and T1 are approximately 231 ± 29 and 41 ± 6 ka, respectively. Similarly, the ages of the river terraces in the main basins of northern Guangdong obtained by different dating methods were similar, indicating that the rivers in northern Guangdong were generally incised during the Middle and Late Middle Pleistocene and that the main rivers in northern Guangdong have synchronous evolution characteristics. On the basis of sedimentary characteristics of the river terraces in the Zhenjiang section of the upper reaches of the Beijiang River, terrace dating data, and previous research, it is shown that the formation of the second terrace in the Zhenjiang section was mainly influenced by tectonic uplift movements; the final formation time was in the Middle and Late Pleistocene, and the first terrace was formed under the combined action of climate change and tectonic activity during the late Pleistocene. Based on the ages of the samples at the top of the T2 and T1 gravel layers and the incision heights, the corresponding incision rates were calculated to be 0.056 and 0.524 mm/a, respectively. Finally, a comparison with the downcutting rates of other river terraces in neighboring areas showed that the Jinjiang and Zhenjiang Rivers exhibited higher downcutting rates since the Middle to Late Pleistocene, indicating the presence of tectonic uplift in northern Guangdong during this period. This study determined the ages and formation mechanisms of low-level river terraces in the Zhenjiang River section using ESR dating and provides an important reference for the study of climatic and tectonic responses in northern Guangdong.
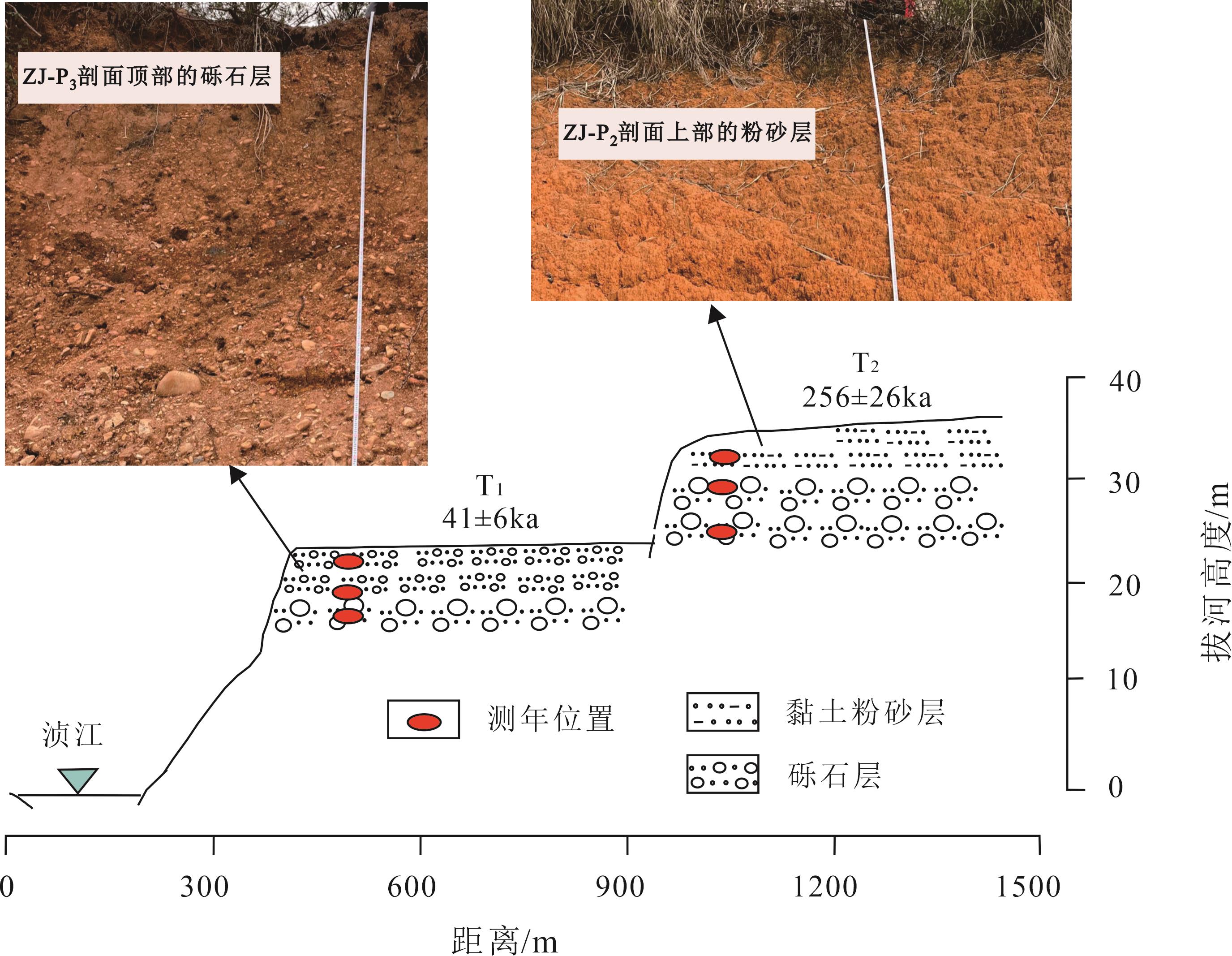
Ziye Cheng , Anying Li , Wanrou Zheng , Xinyu Zhang , Zhanpeng Liu , Hao Ji , Xiaochun Tang . Quartz Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Dating of River Terraces in the Zhenjiang River of the Upper Beijiang River[J]. Tropical Geography, 2025 , 45(3) : 504 -513 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20240527
表1 北江上游浈江段河流阶地剖面描述Table 1 Description of river terraces of the Zhenjiang River in the upper Beijiang River |
| 剖面 | 深度/cm | 沉积特征 |
|---|---|---|
| ZJ-P1 | 0~260 | 漫滩相黏土质粉砂,粉砂以石英为主 |
| >260~580 | 砾石层,粒径较小,颗粒大小为2~3 mm级别,砾石的分选性较好,有一定磨圆,其中间杂1 cm大小的砾石。 砾石成分为硅质岩、砂岩及石英岩等 | |
| ZJ-P2 | 0~470 | 粉砂黏土层,其中粉砂以石英为主 |
| >470~560 | 砾石层,粒径较小,分选较好,为2~4 mm粒径,该层砾石夹杂少量细砂,砾石成分主要为硅质岩及石英岩 | |
| >560~700 | 砾石层,粒径较大,最大粒径可达10 cm以上,分选差,大中小混杂,未见明显定向排列 | |
| ZJ-P3 | 0~30 | 砾石层,可看见一层明显砾石层,磨圆较差,分选较好,粒径为3 cm上下 |
| >30~270 | 砾石层,砾石颗粒明显变小,有一定分选,粒径主要为1 cm左右,砾石层中砂质成分复杂,岩屑及石英可见 | |
| >270~470 | 砾石层,砾石块夹杂小砾石与松散细砂,粒径较大,砾石成分包含花岗岩、砂岩、硅质岩等 |
表2 北江上游浈江段河流阶地沉积物ESR测年结果Table 2 ESR dating results of river terrace sediments in the Zhenjiang River |
| 剖面编号 | 采样深度/cm | U/(ug·g-1) | Th/(ug·g-1) | K/% | 含水量/% | 等效剂量/Gy | 剂量率/(Gy·ka-1) | 年龄/ka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZJ-P1 | 180 | 2.59±0.10 | 12.9±0.26 | 0.65±0.03 | 15±5 | 418±53 | 1.81±0.09 | 231±29 |
| ZJ-P1 | 550 | 2.77±0.11 | 14.4±0.29 | 0.77±0.03 | 10±5 | 1424±172 | 2.18±0.11 | 654±79 |
| ZJ-P2 | 90 | 4.49±0.18 | 29.1±0.58 | 1.18±0.05 | 24±5 | 808±82 | 3.16±0.16 | 256±26 |
| ZJ-P2 | 470 | 3.27±0.13 | 22.8±0.46 | 0.95±0.04 | 25±5 | 1263±133 | 2.41±0.12 | 523±55 |
| ZJ-P2 | 600 | 2.84±0.11 | 22.4±0.45 | 2.16±0.09 | 20±5 | 1954±128 | 3.39±0.17 | 576±38 |
| ZJ-P3 | 120 | 5.70±0.23 | 41.2±0.82 | 1.27±0.05 | 9±5 | 206±28 | 5.02±0.25 | 41±6 |
| ZJ-P3 | 270 | 13.20±0.53 | 53.9±1.08 | 0.80±0.03 | 15±5 | 864±97 | 6.53±0.33 | 132±15 |
| ZJ-P3 | 420 | 3.44±0.14 | 23.0±0.46 | 1.28±0.05 | 13±5 | 1248±179 | 3.18±0.16 | 392±56 |
程子烨:论文撰写与修改,基金支持;
李岸莹:论文修改与绘图;
郑婉柔:数据整理及论文校对;
张欣宇:论文绘图;
刘展鹏:论文修改;
姬 昊:处理和分析数据;
唐晓春:论文指导与审阅。
|
Aitken M J. 1998. Introduction to Optical Dating: The Dating of Quaternary Sediments by the Use of Photon-stimulated Luminescence. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
|
|
Bridgland D R and Westaway R. 2014. Quaternary Fluvial Archives and Landscape Evolution:A Global Synthesis. Proceedings of the Geologists' Association, 125(5/6): 600-629.
|
|
常宏,安芷生,强小科,宋友桂,符超峰. 2005. 河流阶地的形成及其对构造与气候的意义. 海洋地质动态,21(2):8-11,37-38.
Chang Hong, An Zhisheng, Qiang Xiaoke, Song Yougui, and Fu Chaofeng. 2005. The Formation of River Terraces and Their Significance for Tectonics and Climate. Marine Geological Dynamics, 21(2): 8-11, 37-38.
|
|
Cordier S, Harmand D, Frechen M, and Beiner M. 2006. Fluvial System Response to Middle and Upper Pleistocene Climate Change in the Meurthe and Moselle Valleys (Eastern Paris Basin and Rhenish Massif). Quaternary Science Reviews, 25(13/14): 1460-1474.
|
|
戴盼. 2019. 太原西山汾河峡谷出口处二龙山古汾河河流砂电子自旋共振(ESR)测年. 太原:太原理工大学.
Dai Pan. 2019. ESR Dating of Channel Sand Deposited on the Er Long Hill by Ancient Fen River, Taiyuan, China. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology.
|
|
Demuro M, Arnold L J, Duval M, Clemente A C, Santonja M, and Pérez-González A. 2024. Extended-Range Luminescence and ESR Dating of Iberian Fluvial Terraces (Duero and Guadiana Basins) Associated with the Lower Palaeolithic Sites of La Maya I, II, III, Burganes and Albalá (West-Central Spain). Quaternary Geochronology, 83: 101567.
|
|
Ding R, Zhang K, Min K, and Zou H. 2024. Reconstruction of the Topographic Evolution of the Nanling Range in South China and Its Implications for the East Asian Monsoon Evolution. Palaeogeography. Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 634: 111947.
|
|
Duval M, Arnold L J, and Rixhon G. 2020. Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Dating in Quaternary Studies: Evolution, Recent Advances and Applications. Quaternary International, 556: 1-10.
|
|
Erkens G, Hoffmann T, Gerlach R, and Klostermann J. 2011. Complex Fluvialresponse to Lateglacial and Holocene Allogenic Forcingin the Lower Rhine Valley (Germany). Quaternary Science Reviews, 30(5/6): 611-627.
|
|
樊云龙,刘建建,朱克卫,李洪波,邹细霞. 2021. 喀斯特峡谷河流下切速率研究——以北盘江尼珠河大峡谷为例.第四纪研究,41(6):1558-1564.
Fan Yunlong, Liu Jianjian, Zhu Kewei, Li Hongbo, and Zou Xixia. 2021. Study on the Downcutting Rate of Karst Canyon Rivers: Taking the Nizhu River Grand Canyon of Beipan River as an Example. Quaternary Research, 41(6): 1558-1564.
|
|
樊云龙,王懿萱,罗光杰,任大银,李宗盟,刘芬良,罗绪强,唐亮,白庆玲,黎成都. 2022. 晚更新世以来贵州清水江阶地发育及地貌意义. 地理科学,42(9):1676-1684.
Fan Yunlong, Wang Yixuan, Luo Guangjie, Ren Dayin, Li Zongmeng, Liu Liangfen, Luo Xuqiang, Tang Liang, Bai Qinglin, and Li Chengdu. 2022. The Development of Terraces and the Implications for the Geomorphologic Evolution of the Qingshuijiang River in Guizhou Plateau since the Late Pleistocene. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 42(9): 1676-1684.
|
|
高斌,沈冠军,邱立诚. 2007. 马坝人地点南支洞铀系定年初步结果. 暨南大学学报:自然科学版,28(3):308-311.
Gao Bing, Shen Guanjun, and Qiu Licheng. 2007. Preliminary U-Series Dating of Southern Branch Cave of Maba Hominid Site. Quaternary Research, 28(3): 308-311.
|
|
黄进,刘尚仁,黄瑞红. 1994. 丹霞盆地河流阶地的研究.经济地理,14(S):22-26.
Huang Jin, Liu Shangren, and Huang Ruihong. 1994. A Study on River Terraces in the Danxia Basin. Journal of Jinan University(Natural Science), 14 (S): 22-26.
|
|
Lavé J and Avouac J P. 2001. Fluvial Incision and Tectonic Uplift across the Himalayas of Central Nepal. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 106: 26561-26591.
|
|
李宏卫,何树荣,蒋成豹,李阳桂. 2023. 南岭6亿年演变和李四光粤北山字形构造. 森林与人类,(7):40-47.
Li Hongwei, He Shurong, Jiang Chengbao, and Li Yanggui. 2023. Nanling 600 Million Years Evolution and Li Siguang North Guangdong Mountain Structure. Forest and Man, (7): 40-47.
|
|
Lisiecki L E and Raymo M E. 2005. A Pliocene- Pleistocene Stack of 57 Globally Distributed Benthic δ 18O Records. Paleoceanography, 20(1): PA1003.
|
|
刘尚仁. 1987. 北江水系的形成和发育. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),(2):8-14.
Liu Shangren. 1987. The Formation and Development of the Beijiang Water System. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, (2): 8-14.
|
|
刘尚仁,黄瑞红,张治邦. 1996. 广东阶地的特征. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),(S1):33-41.
Liu Shangren, Huang Ruihong, and Zhang Zhibang. 1996. Characteristics of Guangdong Terraces. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, (S1): 33-41.
|
|
刘尚仁. 2006. 广东省英德宝晶宫的科学价值与美景. 热带地理,26(2):173-176.
Liu Shangren. 2006. Scientific Value and Beautiful Landscape of the Baojing Palace in Yingde,Guangdong. Tropical Geography, 26(2): 173-176.
|
|
刘尚仁,黄进. 2011. 粤北地区的河流阶地——广东河流阶地研究之三. 热带地理,31(1):3-7.[Liu Shangren and Huang Jin. 2011. The River Terraces in North Guangdong. Tropical Geography, 31(1): 3-7.]
|
|
刘尚仁. 2012. 粤东地区的河流阶地. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),51(2):131-136.
Liu Shangren. 2012. River Terrace in East Guangdong. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 51(2): 131-136.
|
|
Murray A, Arnold L J, Buylaert J P, Guérin G, Qin J T, Singhvi A K, Smedley R, and Thomsen K J. 2021. Optically Stimulated Luminescence Dating Using Quartz. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 1(1): 1-38. DOI:10.1038/s43586-021-00068-5.
|
|
Nie J S, Ruetenik G, Gallagher K, Hoke G, Garzione C N, Wang W T, Stockli D, Hu X F, Wang Z, Wang Y, Stevens T, Danišík M, and Liu S P. 2018. Rapid Incision of the Mekong River in the Middle Miocene Linked to Monsoonal Precipitation. Nature Geoscience, 11: 944-948.
|
|
Pan B T, Hu Z B, Wang J P, Vandenberghe J, Hu X F, Wen Y H, Li Q, and Cao B. 2012. The Approximate Age of the Planation Surface and the Incision of the Yellow River. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 356/357: 54-61.
|
|
潘保田,邬光剑,王义祥,刘志刚,管清玉. 2000. 祁连山东段沙沟河阶地的年代与成因. 科学通报,45(24):2669-2675.
Pan Baotian, Wu Guangjian, Wang Yixiang, Liu Zhigang, and Guan Qingyu. 2000. The Age and Genesis of the Shahe River Terrace in the Eastern Section of the Qilian Mountains. Chinese Science Bulletin, 45(24): 2669-2675.
|
|
Prescott J R and Hutton J T. 1988. Cosmic Ray and Gamma Ray Dosimetry for TL and ESR. International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Part D. Nuclear Tracks and Radiation Measurements, 14(1/2): 223-227.
|
|
Prescott J R and Hutton J T. 1994. Cosmic Ray Contributions to Dose Rates for Luminescence and ESR Dating: Large Depths and Long-Term Time Variations. Radiation measurements, 23(2/3): 497-500.
|
|
王营. 2019. 渭河三阳川盆地阶地序列的ESR和宇生核素26Al/10Be埋藏年代学研究. 兰州:兰州大学.
Wang Ying. 2019. ESR and Cosmogenic Nuclides 26Al/10Be Burial Dating of Terrace Sequence in the Sanyangchuan Basin of the Weihe River. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University.
|
|
魏传义. 2020. 石英ESR法在长江流域沉积物源示踪中的探讨及应用. 武汉:中国地质大学.
Wei Chuanyi. 2020. Multiple ESR Center Signals and Crystallinity Index of Quartz: Shed New Light on Yangtze River Sediments Provenance Tracing. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences.
|
|
魏传义,尹功明,刘春茹,李亚伟,姬昊. 2022. 长江现代河流沉积物石英ESR信号强度空间分布特征及其物源示踪意义. 第四纪研究,42(4):1168-1180.
Wei Chuanyi, Yi Gongming, Liu Chunru, Li Yawei, and Ji Hao. 2022. Spatial Diversity of Quartz ESR Signal Intensity of the Modern Yangtze River Fluvial Sediments and Its Implications for Sediment Provenance. Quaternary Sciences, 42(4): 1168-1180.
|
|
吴甲添,刘建雄,廖示庭. 2002. 奥北周田—大桥一带浈江流域河流阶地划分. 广东地质,17(1):61-66.
Wu Jiatian, Liu Jianxiong, and Liao Shiting. 2002. The River Terraces in the Zhenjiang River Basin in the Area of Zhoutian-Bridge in Aobei are Divided. Guangdong Geology, 17(1): 61-66.
|
|
谢卫军. 2011. 浈江流域河流泥沙特性分析. 水利科技与经济,17(1):70-71.
Xie Weijun. 2011. Analysis of Sediment Characteristics in Zhenjiang River Basin. Water Conservancy Science and Technology and Economy, 17(1): 70-71.
|
|
许刘兵,周尚哲. 2007. 河流阶地形成过程及其驱动机制再研究. 地理科学,27(5):672-677.
Xu Liubing and Zhou ShangZhe. 2007. Formation Process and Driving Mechanisms of Fluvial Terrace. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 27(5): 672-677.
|
|
Yang R, Willett S D, and Goren L. 2015. In Situ Low-Relief Landscape Formation as a Result of River Network Disruption. Nature, 520: 526-529.
|
|
Yu Y, Wang X Y, Yi S W, Miao X D, Vandenberghe J, Li Y Q, and Lu H Y. 2021. Late Quaternary Aggradation and Incision in the Headwaters of the Yangtze River, Eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. GSA Bulletin, 134(1/2): 371-388.
|
|
张金玉,刘静,王伟,唐茂云,李占飞. 2018. 活动造山带地区河流阶地与下切速率及其时空分布样式. 第四纪研究,38(1):204-219.
Zhang Jinyu, Liu Jing, Wang Wei, Tang Maoyun, and Li Zhanfei. 2018. River Terrace and Downcutting Rates and Their Spatial and Temporal Distribution Patterns in Active Orogenic Zones. Quaternary Sciences, 38(1): 204-219.
|
|
赵秋月,魏明建,周锐,宋波,潘宝林,陈淑贞,赵晓红. 2014. 释光技术在水成沉积物测年中的应用进展. 地质论评,60(1):31-38.
Zhao Qiuyue,Wei Mingjian, Zhou Rui, Song Bo, Pan Baolin, Chen Shuzhen, and Zhao Xiaohong. 2014. The Application Progress of Water-Laid Deposits Luminescence Dating. Geological Review, 60(1): 31-38.
|
|
朱燕燕,周亚利,羊俊敏,贾彬彬,庞奖励. 2022. 汉江上游二级阶地光释光测年研究. 第四纪研究,42(5):1260-1276.
Zhu Yanyan, Zhou Yali, Yang Junmin, Jia Bingbing, and Pang Jiangli. 2022. Optical Luminescence Dating Research of the Second Terrace in the Upper Hanjiang River. Quaternary Sciences, 42(5): 1260-1276.
|
|
邹小娟,周尚哲,谢金明,孙勇,黄耀婷. 2019. 粤北锦江扶溪段河流阶地的光释光测年. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版),51(2):76-85.
Zou Xiaojuan, Zhou Shangzhe, Xie Jinming, Sun Yong, and Huang Yaoting. 2019. Photoluminescence Dating of River Terraces in the Fuxi Section of Jinjiang River, Northern Guangdong Province. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 51(2): 76-85.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |