

Evaluating the Maturity and Obstacle Factors Affecting the Sichuan-Tibet Tourism Corridor, China
Received date: 2024-06-18
Revised date: 2024-11-06
Online published: 2025-07-16
Tourism corridors are a new type of activity carrier with the advent of self-driving tours and transportation integration in tourism. Tourism corridors can help to reconstruct spatial tourism patterns and optimize regional tourism industry structures. Performing tourism corridor maturity assessments can be used to guide corridor construction. However, few studies have included both linear corridor maturity assessments and obstacle factors. Using the entropy weight method and obstacle degree model, we constructed an evaluation index system for the Sichuan-Tibet tourism corridor maturity based on four aspects: resource endowment, reception level, infrastructure, and security guarantee. The obstacle factors of the corridor were combined with the results obtained from the evaluation system and discussed. The Sichuan-Tibet tourism corridor is currently at a relatively low maturity level and sections with low maturity levels and below account for 89.04% of the total mileage. Owing to the fact that the economic development level of Tibet lags behind that of Sichuan, as well as the geographical complexity, the low maturity sections were mostly concentrated in Tibet. The maturity of the tourism corridor exhibited a "high-low-high" spatial distribution, in which the high-maturity regions were located in Chengdu and Lhasa at both ends of the corridor. In contrast, the low-maturity regions were mainly concentrated in the Bomi-Mangkang and Litang-Yajiang sections in the central part of the corridor. The main obstacles to the maturity of the Sichuan-Tibet tourism corridor had effects that decreased in the order of reception level > infrastructure > security guarantee > resource endowment. Based on the specified indicators, service facilities, tourist catering, medical level, entertainment facilities, and communication conditions were the main obstacles. The main obstacle factors in each section of the tourism corridor differed and were divided into resource obstacle, reception facility obstacle, and security obstacle sections. Among these, security obstacle factors were present in most sections. Sections with differing obstacles should therefore take measures according to local conditions to reduce the impacts of their obstacles. This study addressed the spatial evaluation of linear corridor development and construction, which can be used to evaluate the maturities of other tourism corridors and provide support for the development and construction of the Sichuan-Tibet tourism corridor.
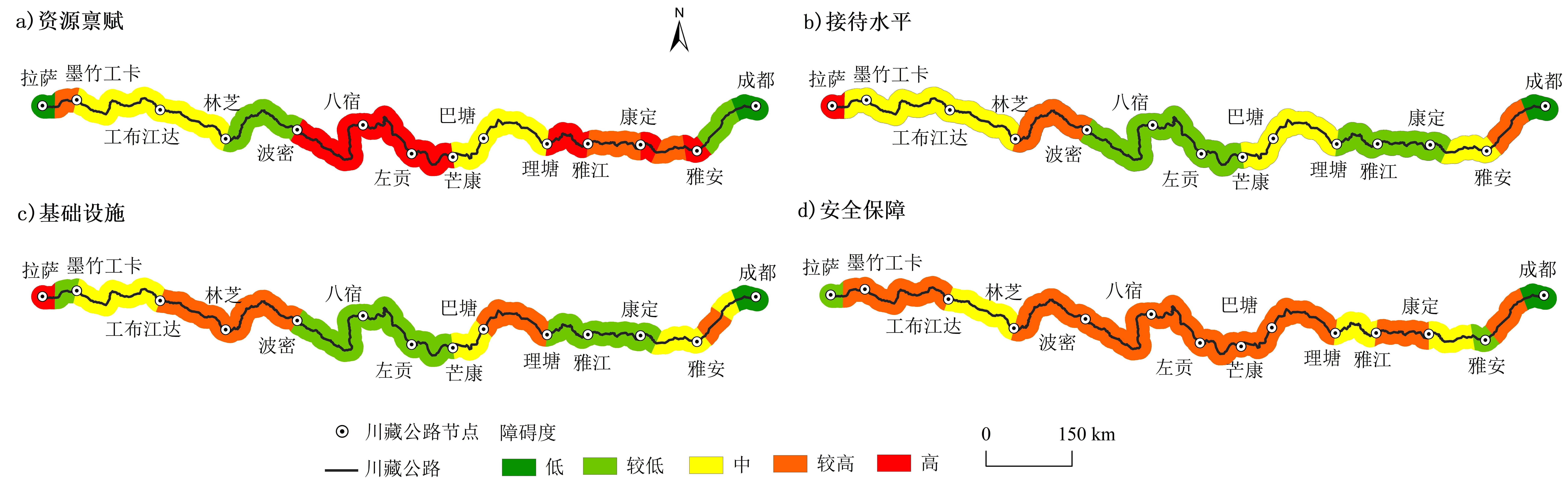
Mi Li , Jianchao Xi , Sui Ye , Ziqiang Li , Tai Huang . Evaluating the Maturity and Obstacle Factors Affecting the Sichuan-Tibet Tourism Corridor, China[J]. Tropical Geography, 2025 , 45(7) : 1164 -1173 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20240398
表1 川藏旅游廊道成熟度评价指标体系Table 1 Maturity evaluation index system of Sichuan-Tibet tourism corridor |
| 维度层 | 指标层 | 指标含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 资源 禀赋 | A级景区 | A级景区数量 |
| 大型景观 | 风景名胜区数量、自然保护区数量、 国家地质公园数量、国家森林公园数量 | |
| 其他资源 | 文化遗产数量、重点旅游村镇数量 | |
| 接待 水平 | 旅游餐饮 | 餐饮企业数量 |
| 旅游住宿 | 酒店民宿数量 | |
| 娱乐设施 | 农家乐数量、房车营地数量、自驾营地数量 | |
| 基础 设施 | 服务设施 | 旅游厕所数量、加油站数量、停车场数量 |
| 通讯条件 | 通信营业网点数 | |
| 交通条件 | 道路密度 | |
| 安全 保障 | 医疗水平 | 医疗场所数量 |
| 治安能力 | 派出所、警务室(站)、兵站数量 |
表2 川藏旅游廊道成熟度评价指标权重Table 2 Index weights of Sichuan-Tibet tourism corridor |
| 维度层 | 权重 | 指标层 | 权重 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 资源禀赋 | 0.16 | A级景区 | 0.03 |
| 大型景观 | 0.08 | ||
| 其他资源 | 0.08 | ||
| 接待水平 | 0.33 | 旅游餐饮 | 0.13 |
| 旅游住宿 | 0.07 | ||
| 娱乐设施 | 0.15 | ||
| 基础设施 | 0.33 | 服务设施 | 0.12 |
| 通讯条件 | 0.08 | ||
| 交通条件 | 0.13 | ||
| 安全保障 | 0.18 | 医疗水平 | 0.09 |
| 治安能力 | 0.04 |
表3 川藏旅游廊道成熟度综合评价Table 3 Comprehensive evaluation of Sichuan-Tibet tourism corridor maturity |
| 成熟度等级 | 区段 | 里程占比/% |
|---|---|---|
| 低 | 理塘—雅江;波密—芒康 | 31.93 |
| 较低 | 达孜—波密;芒康—理塘;雅江—天全 | 57.11 |
| 中 | 天全—邛崃 | 5.20 |
| 较高 | 邛崃—崇州;堆龙—达孜 | 3.34 |
| 高 | 崇州—成都 | 2.42 |
表4 旅游廊道成熟度指标障碍度及排名Table 4 Obstacle degree and ranking of tourism corridor maturity index |
| 维度层 | 分类指标 障碍度/% | 排名 | 指标层 | 单项指标 障碍度/% | 排名 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 资源禀赋 | 14.02 | 4 | A级景区 | 3.43 | 11 |
| 大型景观 | 4.85 | 10 | |||
| 其他资源 | 5.74 | 8 | |||
| 接待水平 | 34.30 | 1 | 旅游餐饮 | 12.63 | 2 |
| 旅游住宿 | 9.44 | 6 | |||
| 娱乐设施 | 12.22 | 4 | |||
| 基础设施 | 34.00 | 2 | 服务设施 | 14.26 | 1 |
| 通讯条件 | 11.49 | 5 | |||
| 交通条件 | 8.24 | 7 | |||
| 安全保障 | 17.68 | 3 | 医疗水平 | 12.42 | 3 |
| 治安能力 | 5.28 | 9 |
1 http://www.openstreetmap.org/
|
Blumentrath C and Tveit M S. 2014. Visual Characteristics of Roads: A Literature Review of People's Perception and Norwegian Design Practice. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 59(1): 58-71.
|
|
Chai J L, Wang Y, Liu X J, Wang W, and Tan C R. 2023. A Study on Modern Agricultural Park Landscape Road Design and Planning. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 60(2): 397-406.
|
|
柴畅. 2020. 为318国道川藏沿线旅游产业发展添把“火”,今天这场论坛干货满满. (2020-10-21)[2024-02-12]. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1681161818042657057&wfr=spider&for=pc.
Chai Chang. 2020. Today's Forum Was Brimming With Substantive Content, Aiming to Stoke the Flames of Tourism Industry Development along the Sichuan-Tibet Section of National Highway 318. (2020-10-21) [2024-02-12]. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1681161818042657057&wfr=spider&for=pc.
|
|
陈钢华,师慧敏. 2024. 川藏南线自驾游客情感体验的特征与影响机制. 旅游学刊,39(9):117-134.
Chen Ganghua and Shi Huimin. 2024. Examining Self-Drive Tourists' Emotional Experience along the South Section of Sichuan-Xizang Highway(G318): Characteristics and Influencing Mechanism. Tourism Tribune, 39(9): 117-134.
|
|
陈兴,王方,时攀琳,张雅彬. 2016. 移动互联背景下自驾旅游者行为特征及需求研究——以318国道川藏线为例. 西藏大学学报(社会科学版),31(1):150-156.
Chen Xing, Wang Fang, Shi Panlin, and Zhang Yabin. 2016. Mobile Internet, Travel Behavior and Tourist Demand of Self-Driving Tour—A Case Study of The Sichuan-Tibet Section of China National Highway 318. Journal of Tibet University, 31(1): 150-156.
|
|
崔丹,卜晓燕,徐祯,李国平,吴殿延. 2021. 中国资源型城市高质量发展综合评估及影响机理. 地理学报,76(10):2489-2503.
Cui Dan, Bu Xiaoyan, Xu Zhen, Li Guoping, and Wu Dianting. 2021. Comprehensive Evaluation and Impact Mechanism of High-Quality Development of China's Resource-Based Cities. Acta Geographica Sinica, 76(10): 2489-2503.
|
|
Dawson K J. 1995. A Comprehensive Conservation Strategy for Georgia's Greenways. Landscape and Urban Planning, 33(1): 27-43.
|
|
董仁才,孙晓泽,李春明,刘涛,苟亚青. 2011. 青藏铁路沿线生态环境敏感性评价GIS模型. 生态学杂志,30(9):2093-2098.
Dong Rencai, Sun Xiaoze, Li Chunming, Liu Tao, and Gou Yaqing. 2011. GIS Model for Eco-Environmental Sensitivity Assessment of the Areas along Qinghai-Tibetan Railway. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30(9): 2093-2098.
|
|
范春. 2009. 基于体验旅游的景区廊道空间设计. 人文地理,24(2):112-115.
Fan Chun. 2009. The Design for Corridor Space of Scenic Zone Based on Experience Tourism. Human Geography, 24(2): 112-115.
|
|
Eby D W and Molnar L J. 2002. Importance of Scenic Byways in Route Choice: A Survey of Driving Tourists in the United States. Transportation Research Part A-Policy and Practice, 36(2): 95-106.
|
|
Ginting N. 2016. How Self-Efficacy Enhance Heritage Tourism in Medan Historical Corridor, Indonesia. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 234(10): 193-220.
|
|
Holladay P, Skibins J C, Zach F J, and Arze M. 2017. Exploratory Social Network Analysis of Stakeholder Organizations Along the Illinois and Michigan Canal National Heritage Corridor. Journal of Park and Recreation Administration, 35: 37-48.
|
|
Kekki S. 2016. Route 66: A Road to America's Landscape, History, and Culture. American Studies in Scandinavia, 48(1): 87-88.
|
|
Kurdoglu B C and Kurt S S. 2017. Determination of Greenway Routes Using Network Analysis in Amasya, Turkey. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 143(1): 05016013.
|
|
李朝军. 2022. 基于空间错位测度模型的旅游资源与地区经济发展关系研究. 西南大学学报(自然科学版),44(10):81-90.
Li Chaojun. 2022. Study on the Relationship Between Tourism Resources and Regional Economic Development Based on Spatial Dislocation Measure Model. Journal of Southwest University(Natural Science Edition), 44(10): 81-90.
|
|
李龙,杨效忠. 2020. 旅游廊道:概念体系、发展历程与研究进展. 旅游学刊,35(8):132-143.
Li Long and Yang Xiaozhong. 2020. Tourism Corridor: Concept System, Development Process and Research Progress. Tourism Tribune, 35(8): 132-143.
|
|
李龙,杨效忠. 2021. 廊道型乡村旅游地农户生计资本评价与空间格局特征——以大别山国家风景道为例. 地理科学,41(2):340-349.
Li Long and Yang Xiaozhong. 2021. Evaluation and Spatial Pattern of Farmers' Livelihood Capital in Corridor-Type Rural Tourism Areas: A Case Study of the Dabie Mountain National Landscape. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 41(2): 340-349.
|
|
李伟,俞孔坚,李迪华. 2004. 遗产廊道与大运河整体保护的理论框架. 城市问题,23(1):28-31.
Li Wei, Yu Kongjian, and Li Dihua. 2004. Heritage Corridor and a Primary Theoretic Framework on Study of Integrated Conservation of the Great Canal. Urban Problems, 23(1): 28-31.
|
|
李许红,王永生,刘释疑. 2022. 豫陕鄂交界区县域综合发展水平测度及障碍因子分析. 地理科学,42(10):1757-1766.
Li Xuhong, Wang Yongsheng, and Liu Shiyi. 2022. Comprehensive Measurement and Obstacle Factor Analysis of County-Level Development of Junction Area in Henan-Shaanxi-Hubei. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 42(10): 1757-1766.
|
|
李自强,席建超,张瑞英. 2022. 滇藏公路沿线旅游安全风险评价. 山地学报,40(5):753-763.
Li Ziqiang, Xi Jianchao, and Zhang Ruiying. 2022. Assessment of Tourism Risk along the Yunnan-Tibet Highway. Mountain Research, 40(5): 753-763.
|
|
Liang J, Liu Y, Ying L X, Li P, Xu Y, and Shen Z H. 2014. Road Impacts on Spatial Patterns of Land Use and Landscape Fragmentation in Three Parallel Rivers Region, Yunnan Province, China. Chinese Geographical Science, 24: 15-27.
|
|
马慧强,燕明琪,李岚,王清. 2018. 我国旅游公共服务质量时空演化及形成机理分析. 经济地理,38(3):190-199.
Ma Huiqiang, Yan Mingqi, Li Lan, and Wang Qing. 2018. The Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Formation Mechanism of Tourism Public Service in China. Economic Geography, 38(3): 190-199.
|
|
邱海莲,由亚男. 2015. 旅游廊道概念界定. 旅游论坛,8(4):26-30. [Qiu Hailian and You Ya'nan. 2015. Conceptualization of Tourism Corridor. Tourism Forum, 8(4): 26-30. ]
|
|
石飞,刘峰贵,李春花,才让,陈蓉. 2014a. 川藏公路沿线旅游安全风险分析. 地域研究与开发,33(4):115-120.
Shi Fei, Liu Fenggui Li Chunhua, Cai Rang, and Chen Rong. 2014a. Risk Analysis of Tourism Security along the Sichuan-Tibet Highway. Areal Research and Development, 33(4): 115-120.
|
|
石飞. 2014b. 青藏、川藏公路沿线旅游安全风险对比分析. 西宁:青海师范大学.
Shi Fei. 2014b. The Comparative Risk Analysis of Tourism Security Along the Qinghai-Tibet Highway and the Sichuan-Tibet Highway. Xining: Qinghai Normal University.
|
|
石飞,刘峰贵,李春花,才让,陈蓉. 2014c. 基于旅游安全的川藏公路沿线自然灾害危险性分析. 干旱区资源与环境,28(7):121-126.
Shi Fei, Liu Fenggui, Li Chunhua, Cai Rang, and Chen Rong. 2014c. Analysis of the Natural Disaster Harm along the Sichuan-Tibet Highway Based on Travel Security. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 28(7): 121-126.
|
|
孙振杰,袁家冬,刘继斌. 2020. 中国典型旅游城市生活服务水平评价及障碍因素研究. 地理科学,40(2):289-297.
Sun Zhenjie, Yuan Jiadong, and Liu Jibin. 2020. Evaluation and Obstacle Factors of Life Services Level of Typical Tourism Cities in China. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 40(2): 289-297.
|
|
翁凌飞,白昊男,沈镭. 2021. 中老铁路建设对沿线景观格局影响的尺度效应. 资源科学,43(12):2451-2464.
Weng Lingfei, Bai Haonan, and Shen Lei. 2021. Scaling Impacts of China-Laos Railway Construction on Landscape Patterns. Resources Science, 43(12): 2451-2464.
|
|
王国洪,丁赛,马盛楠. 2024. 旅游资源禀赋、交通区位与旅游产业发展——基于民族地区85个县调查数据的分析. 海南大学学报(人文社会科学版),42(5):120-128.
Wang Guohong, Ding Sai, and Ma Shengnan. 2024. Tourism Resource Endowment, Transportation and Location, and Development in the Tourism Industry: An Analysis of the Survey Data from 85 Counties in Chinese Ethnic Areas. Journal of Hainan University(Humanities & Social Sciences), 42(5): 120-128.
|
|
王立国,陶犁,张丽娟,李杰. 2012. 文化廊道范围计算及旅游空间构建研究——以西南丝绸之路(云南段)为例. 人文地理,27(6):36-42.
Wang Liguo, Tao Li, Zhang Lijuan, and Li Jie. 2012. Study on Cultural Corridor Extent Calculation and the Construction of Its Tourism Spatial Structure: A Case Study of the Southwestern Silk Road. Human Geography, 27(6): 36-42.
|
|
王学基,解佳,孙九霞. 2019. 在路上:道路旅行者的流动实践及其意义解读. 旅游科学,33(5):1-13.
Wang Xueji, Xie Jia, and Sun Jiuxia. 2019. On Route: Road Travelers' Mobility Practice and an Interpretation of Its Significance. Tourism Science, 33(5): 1-13.
|
|
王学基,岳丁宜,孙九霞. 2023. 流动力与粘滞性:川藏公路道路旅行的空间实践. 地理研究,42(8):2211-2224.
Wang Xueji, Yue Dingyi, and Sun Jiuxia. 2023. Motility and Viscosity: Spatial Practices of Road Travel on Sichuan-Tibet Highway. Geographical Research, 42(8): 2211-2224.
|
|
王昱茜,朱俏俏. 2022. 西北五省(区)入境旅游合作路径研究——基于丝绸之路文化遗产廊道. 资源开发与市场,38(6):752-760.
Wang Yuqian and Zhu Qiaoqiao. 2022. Study on Inbound Tourism Cooperation Path of Five Provinces in Northwest China: Based on the Cultural Heritage Corridor of the Silk Road. Resource Development & Market, 38(6): 752-760.
|
|
吴必虎,李咪咪. 2001. 小兴安岭风景道旅游景观评价. 地理学报,56(2):214-222.
Wu Bihu and Li Mimi. 2001. A Linear Landscape Evaluation Technique: A Case Study on the Xiaoxinganling Scenery Drive. Acta Geographica Sinica, 56(2): 214-222.
|
|
徐影秋,刘志强,洪亘伟,王俊帝. 2021. 中国城市公园综合发展水平评价及障碍度分析. 生态经济,37(6):87-93,123.
Xu Yingqiu, Liu Zhiqiang, Hong Genwei, and Wang Jundi. 2021. Evaluation of Urban Parks on Comprehensive Development Level and Obstacle Degree in China. Ecological Economy, 37(6): 87-93, 123.
|
|
鄢方卫,杨效忠,吕陈玲. 2017. 全域旅游背景下旅游廊道的发展特征及影响研究. 旅游学刊,32(11):95-104.
Yan Fangwei, Yang Xiaozhong, and Lyu Chenling. 2017. The Development Features and Influence of Tourism Corridors under the Holistic Tourism Background. Tourism Tribune, 32(11): 95-104.
|
|
杨仁发,杨超. 2019. 长江经济带高质量发展测度及时空演变. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版),53(5):631-642.
Yang Renfa and Yang Chao. 2019. The High-Quality Development Measurement of the Yangtze River Economic Belt and the Evolution of Time and Space. Journal of Central China Normal University(Natural Sciences), 53(5): 631-642.
|
|
杨秀平,王睿,秦雨露,轩晚月. 2023. 中国省域旅游绿色发展水平演变及障碍因素分析. 地理与地理信息科学,39(1):120-128.
Yang Xiuping, Wang Rui, Qin Yulu, and Xuan Wanyue. 2023. Evolution and Obstacle Factors of Green Development Level of Provincial Tourism Destinations in China. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 39(1): 120-128.
|
|
张瑞英,席建超,姚予龙,葛全胜. 2014. 基于视觉廊道的青藏铁路沿线旅游动态景观评价. 生态学报,34(12):3320-3330.
Zhang Ruiying, Xi Jianchao, Yao Yulong, and Ge Quansheng. 2014. Evaluation of Tourism Dynamic Landscape along Qinghai-Tibet Railway Based on the Visual Corridor. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(12): 3320-3330.
|
|
张圆刚,陈希,余润哲,程静静,余向洋. 2020. 线型旅游体验空间: 风景道的体验性逻理嬗变. 自然资源学报,35(2):284-296.
Zhang Yuangang, Chen Xi, Yu Runzhe, Cheng Jingjing, and Yu Xiangyang. 2020. The Logic Transformation of the Scenic Byway System to the Linear Experience Space Transformation. Journal of Natural Resources, 35(2): 284-296.
|
|
赵书虹,白梦. 2020. 云南省品牌旅游资源竞争力与旅游流耦合协调特征及其影响因素分析. 地理科学,40(11):1878-1888.
Zhao Shuhong and Bai Meng. 2020. Coupling Coordination Characteristics and Its Influencing Factors of Brand Tourism Resources Competitiveness and Tourism Flow in Yunnan Province. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 40(11): 1878-1888.
|
|
郑鹏,刘壮,陈家怡,席建超,李金铠. 2023. 青藏高原县域旅游目的地竞争力评价及障碍分析. 干旱区资源与环境,37(2):177-185.
Zheng Peng, Liu Zhuang, Chen Jiayi, Xi Jianchao, and Li Jinkai. 2023. Evaluation of Tourist Destination Competitiveness on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: An County Perspective and Obstacle Analysis. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 37(2): 177-185.
|
|
钟栎娜,吴必虎,邵隽. 2011. 中国5A级旅游区门户网站的成熟度评估. 旅游学刊,26(12):30-36.
Zhong Lina, Wu Bifu, and Shao Jun. 2011. Evaluation of the Maturity of Portal Websites in China's 5A Rated Tourism Attractions. Tourism Tribune, 26(12): 30-36.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |