

Spatial Patterns and Perception Differences in Slow-Tourism Behavior: Insights from Popular Citywalk Routes in Chengdu, Wuhan, and Shanghai, China
Received date: 2025-03-19
Revised date: 2025-05-12
Online published: 2025-07-21
As the pace of life accelerates and the demand for tourism quality increases, slow tourism, which emphasizes experiences, relaxation, and sustainability, has emerged. However, slow-tourism behaviors and perceptions differ widely across different urban contexts. We applied the basic framework of landscape perception theory to popular Citywalk routes in Chengdu, Wuhan, and Shanghai, which were obtained from the Xiaohongshu platform. By integrating spatial, multimodal data, and content analyses, as well as other methods, we explored the spatial behavioral patterns, perceptual differences, and the associated mechanisms of tourists during Citywalk activities in different urban contexts. The findings indicate that Citywalk activities mainly occurred within the second rings of cities, representing small-scale urban exploration that emphasizes experiential feelings over conventional mobile tourism. Tourists preferred culturally and artistically vibrant urban destinations. Citywalks are generally free, thereby embodying a subcultural phenomenon that contrasts with the stressful rhythm of life emitomized by "involution" and "996" work culture. Notable differences in cognitive imagery, emotional imagery, and cultural perception were present among the tourists in different cities, which shaped unique urban Citywalk tourism experiences. Based on different models and perceptual differences, Chengdu's Citywalk was defined as "a slow city tour centered around creative cultural districts that blends creative spaces and gourmet exploration," whereas those in Wuhan and Shanghai were defined as "a slow city tour centered around historical architecture, that blends cultural spaces and natural scenery" and "a slow city tour centered around urban landscapes that blends humanities, arts, and modern fashion," respectively. Differing geographical locations, planning concepts, development orientations, and historical backgrounds affected the Citywalk tourism experiences by influencing aspects such as the natural environment, spatial layout, developmental direction, and cultural characteristics of each city, which created different place perceptions. Geographical location affects the natural environment, tourism facilities, and cultural atmosphere of a city, whereas planning concepts influence urban spatial layouts, functional zoning, and the mode of tourism resource development, which affect the form and experiences in slow tourism. Development orientation determines the development direction of a city, thereby crafting unique attractions. Differing historical backgrounds create distinct urban cultural features, lifestyles, and tourism resources, which affect the direction of slow-tourism development. The findings of this study present the differences in Citywalk behaviors and perceptions in various urban contexts, filling a gap in comparative studies of cities within slow-tourism scenes. The findings also provide a new theoretical perspective for understanding the interactions between tourism behavior and urban spaces and offers reference experiences for other cities to develop slow tourism, enhance urban cultural tourism competitiveness, and promote sustainable urban tourism development.
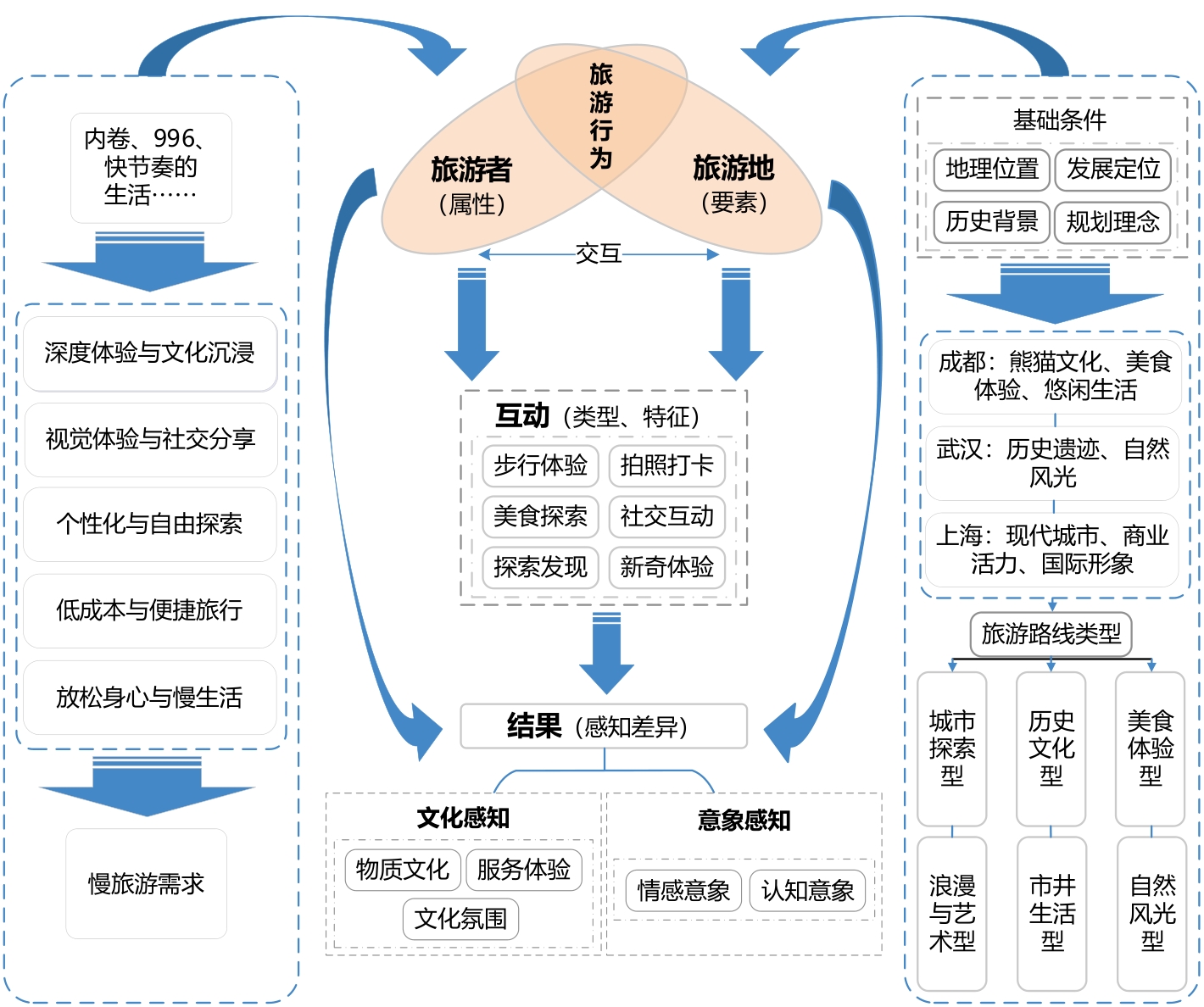
Chenglong Han , Lingling Li , Gang Li , Li Lan , Ying He , Jianying Guo . Spatial Patterns and Perception Differences in Slow-Tourism Behavior: Insights from Popular Citywalk Routes in Chengdu, Wuhan, and Shanghai, China[J]. Tropical Geography, 2025 , 45(7) : 1136 -1149 . DOI: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.20250165
图3 不同城市Citywalk热门旅游路线属性特征Fig.3 Characteristics of popular Citywalk troutes in different cities |
表1 不同城市Citywalk目的地类型差异Table 1 Differences in Citywalk destination types across various cities |
| 旅游目的地 类型 | 成都 | 武汉 | 上海 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 频次/次 | 占比/% | 频次/次 | 占比/% | 频次/次 | 占比/% | |||
| 艺术街区类 | 857 | 62.83 | 377 | 38.55 | 667 | 52.85 | ||
| 历史文化类 | 265 | 19.43 | 289 | 29.55 | 281 | 22.27 | ||
| 都市风光类 | 168 | 12.32 | 188 | 19.22 | 252 | 19.97 | ||
| 自然景观类 | 74 | 5.43 | 124 | 12.68 | 62 | 4.91 | ||
图4 不同城市Citywalk热门旅游路线空间分布 Fig.4 Spatial distribution of popular Citywalk routes in different cities |
表2 不同城市Citywalk旅游热点片区Table 2 Popular Citywalk tourism hotspots in different cities |
| 城市(片区/个) | 热点片区名称 |
|---|---|
| 成都(4) | 春熙路片区(春熙路、华兴街等);玉林路片区(玉林路、芳草街等);青羊宫片区(青羊宫、杜甫草堂等); 宽窄巷子片区(宽窄巷子、人民公园等) |
| 武汉(5) | 龟山公园片区(龟山公园、晴川阁等);咸安坊片区(咸安坊、江汉路步行街等);宝岛公园片区(宝岛公园、万象城等); 黄鹤楼片区(黄鹤楼、昙华林等);郝梦龄片区(汉口江滩、郝梦龄路) |
| 上海(6) | 淮海中路片区(淮海路、淮海坊等);武康路片区(武康大楼、常熟路等);南京路片区(南京路步行街、外滩等); 徐家汇片区(徐家汇书院、徐家汇藏书楼等);江苏路片区(江苏路、宣化路等);陆家嘴片区(东方明珠、陆家嘴等) |
表3 LDA模型与大语言模型分析结果对比Table3 Comparison of analysis results between LDA and Large Language Model |
| 笔记 | LDA主题模型输出结果 | 大语言模型输出结果 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 时尚 | 时尚与现代 |
| 2 | 步行街 | 城市探索 |
| 3 | 老街区、街道、建筑、历史 | 历史与现代的交融、文化艺术体验 |
| 4 | 咖啡馆、茶馆、建筑 | 文化探索、美食之旅 |
| 5 | 老街、汉派、风情 | 历史与现代的融合、艺术与文化的交融 |
| 6 | 美食、面包店 | 美食探索、城市漫步 |
| 7 | 房子、大楼、步行街 | 历史文化之旅、现代都市探索 |
| 8 | 夜行、鸡尾酒、魅力 | 夜生活体验、文化探索型 |
| 9 | 文艺、建筑、小店 | 文化体验、历史建筑 |
| 10 | 社会、烟火、方式 | 城市烟火气、寻找惊喜 |
表4 不同城市Citywalk旅游者文化感知差异Table 4 Differences in cultural perceptions among Citywalk tourists in different cities |
| 感知 维度 | 二级分类 维度 | 高频词 |
|---|---|---|
| 物质 文化 | 文化与历史地标 | 成都:宽窄巷子、祠堂街、书店、小店、熊猫、 人民公园 武汉:黄鹤楼、古德寺、巴公房子、江汉关 上海:豫园、东方明珠、静安寺 |
| 商业区 | 成都:春熙路、太古里、望平街 武汉:江汉路 上海:淮海中路、南京路步行街 | |
| 美食体验 | 成都:美食、火锅 武汉:美食 | |
| 特色街道 | 成都:玉林路、街道 武汉:黎黄陂路、昙华林、咸安坊 上海:武康路、安福路、愚园路、北外滩 | |
| 城市地标 | 武汉:景点、汉口、长江大桥、东湖 上海:外滩、武康大楼、陆家嘴 | |
| 服务 体验 | 旅游活动 | 成都:打卡、拍照 武汉:打卡、拍照 上海:拍照、打卡 |
| 审美与体验 | 成都:好吃、好看、可爱、体验、适合 武汉:适合、好看、好吃、方便、漂亮 上海:好看、适合、方便、漂亮、可爱、好吃 | |
| 文化 氛围 | 文化与情感体验 | 成都:历史、感受、文艺、浪漫、氛围 武汉:感受、氛围、文艺、浪漫、好玩 |
| 城市特色 | 成都:烟火、宝藏 武汉:风格、特色 上海:魔都 |
表5 不同城市Citywalk旅游者认知形象差异Table 5 Differences in cognitive perceptions of Citywalk tourists across various cities |
| 认知形象一级指标 | 认知形象 二级指标 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| 自然景观场景A | 自然风光A1 | 自然景观、河流、湖泊、植物等 |
| 人物 场景B | 自拍照B1 | 游客自拍照 |
| 人群B2 | 当地人是照片主题 | |
| 旅游配套设施场景C | 美食C1 | 食物特写,餐馆照片等 |
| 交通设施C2 | 车站、道路、交通工具、等设施, 包括道路指示牌 | |
| 人文景观场景D | 特色景观 小品D1 | 用于装饰作用的建筑、壁画 或其他呈现形式的设施 |
| 文创产品D2 | 具有创意的特色产品,包括文创店铺 | |
| 城市建筑D3 | 展示城市风光的建筑 | |
| 特色街巷D4 | 具有人文、艺术、历史特色的街区 | |
| 文化展示D5 | 博物馆、书法字画等 | |
| 景观建筑D6 | 具有文化特色的亭台楼阁,历史建筑 |
图7 不同城市Citywalk旅游者行为认知形象统计 Fig.7 Statistical analysis of behavioral and cognitive perceptions of Citywalk tourists in different cities |
表6 不同城市Citywalk旅游者情感感知差异Table 6 Differences in emotional erceptions among Citywalk tourists in different cities |
| 城市 | 情感倾向/% | 主要正面特征词 | 主要负面特征词 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正面 | 负面 | |||
| 成都 | 75.4 | 4.9 | 熊猫;文创;成都美食;巴适 | 累;隐形消费 |
| 武汉 | 68.8 | 3.3 | 好吃;氛围感;出片;性价比 | 出租车;人多;嘈杂 |
| 上海 | 72.2 | 3.8 | 繁华;好吃;惬意;复古;震撼;迷人 | 热;消费高;累 |
|
Beerli A and Martin J D. 2004. Tourists Characteristics and the Perceived Image of Tourist Destinations: A Quantitative Analysis: A Case Study of Lanzarote, Spain. Tourism Management, 25(5): 623-636.
|
|
曹宁,明庆忠. 2015. “慢旅游”开发的基本理念与开发路径探讨. 旅游论坛,8(1):81-86.
Cao Ning and Ming Qingzhong. 2015. Exploration on Basic Concept and Development Path about Slow Travel. Tourism Forum, 8(1): 81-86.
|
|
曹瑞芳. 2017. 基于文化感知的历史文化名村景观保护与改造设计——以卫坡历史文化名村为例. 西安:西安建筑科技大学.
Cao Ruifang. 2017. Cultural Perception-Based Landscape Conservation and Renovation Design of Historic Cultural Villages: A Case Study of Weipo Historic Cultural Village. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology.
|
|
Chao R F. 2015. Development of Slow Tourism Challenge and Operation Architecture: A Case Study on Green Island, Taiwan. Acta Oeconomica, 65(2): 351-367.
|
|
陈钢华,师慧敏. 2024. 川藏南线自驾游客情感体验的特征与影响机制. 旅游学刊,39(9):117-134.
Chen Ganghua and Shi Huimin. 2024. Examining Self-Drive Tourists' Emotional Experience along the South Section of Sichuan-Xizang Highway: Characteristics and Influencing Mechanism. Tourism Tribune, 39(9): 117-134.
|
|
陈玉雪,李娜,陈鹏. 2016. 南京高淳桠溪慢旅游地形象认知——基于游记文本分析法. 旅游纵览(下半月),(8):185-188.
Chen Yuxue, Li Na, and Chen Peng. 2016. Nanjing Gaochun Yaxi Slow Tourism Destination Image Cognition—Analysis Based on Travelogue Texts. Panorama of Tourism(Second Half), (8): 185-188.
|
|
Conway D and Timms B F. 2010. Re-Branding Alternative Tourism in the Caribbean: The Case for 'Slow Tourism'. Tourism and Hospitality Research, 10(4): 329-344.
|
|
戴光全,陈欣. 2009. 旅游者摄影心理初探——基于旅游照片的内容分析. 旅游学刊,24(7):71-77.
Dai Guangquan and Chen Xin. 2009. An Initial Discussion about Tourists' Photographic Psychology—Based on the Content Analysis of Tourist Photos. Tourism Tribune, 24(7): 71-77.
|
|
代浩宇,马国强,汪胜兰,黄银洲. 2024. 基于ChatGPT和ROST方法的敦煌旅游地形象感知分析与对比. 干旱区资源与环境,38(12):151-159.
Dai Haoyu, Ma Guoqiang, Wang Shenglan, and Huang Yinzhou. 2024. Analysis of the Image Perception of Dunhuang as Tourist Destination: A Comparison between ChatGPT and ROST Method. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 38(12): 151-159.
|
|
Dickinson J E, Robbins D, and Lumsdon L. 2010. Holiday Travel Discourses and Climate Change. Journal of Transport Geography, 18(3): 482-489.
|
|
高伟洁,朱蓉菲. 2023. 基于慢城理念的历史文化名镇目的地形象优化研究——以朱仙镇为例. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版),51(5):89-96.
Gao Weijie and Zhu Rongfei. 2023. Research on Destination Image Optimization of Famous Historical and Cultural Town Based on Cittaslow Concept: A Case Study of Zhuxian Town. Journal of Henan Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 51(5): 89-96.
|
|
Gartner W C. 1994. Image Formation Process. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 2(2/3): 191-216.
|
|
管婧婧,毕家萍,董雪旺. 2021. 家与途:情境迁移下的旅游地感知重构. 旅游学刊,36(1):112-122.
Guan Jingjing, Bi Jiaping, and Dong Xuewang. 2021. Home and Away: Reconstructing Tourist' Perception of Destination in the Context of Situation Transfer. Tourism Tribune, 36(1): 112-122.
|
|
韩雪,刘爱利. 2019. 旅游感知的研究内容及测评方法. 旅游学刊,34(4):106-118.
Han Xue and Liu Aili. 2019. Measurements of Tourist Perception: A Review. Tourism Tribune, 34(4): 106-118.
|
|
何蔓莉,卢长宝. 2024. 超越异化的心灵之旅:慢旅游的观念、本质及发展. 福建师范大学学报(哲学社会科学版),(5):148-157.
He Manli and Lu Changbao. 2024. A Spiritual Journey beyond Alienation: Concepts, Essence and Development of Slow Tourism. Journal of Fujian Normal University(Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), (5): 148-157.
|
|
侯楚,李志文,孙丽,李向洁,李世乾,陈晓倩. 2023. 居民地方感知、地方依恋与农业保护态度的关系——以佛山市典型基塘农业村落为例. 地域研究与开发,42(4):162-167.
Hou Chu, Li Zhiwen, Sun Li, Li Xiangjie, Li Shiqian, and Chen Xiaoqian. 2023. Relationships between Residents' Place Perception, Place Attachment and Attitudes toward Agricultural Conservation—A Case Study of a Typical Kitang Agricultural Village in Foshan City. Geographic Research and Development, 42(4): 162-167.
|
|
蒋长春. 2013. 国内游客对红色文化感知的差异性研究——以延安红色旅游为例. 河北大学学报(哲学社会科学版),38(4):75-80.
Jiang Changchun. 2013. The Study on the Differences of the Red Culture Perceptions of Domestic Tourists—Taking Yanan Red Tourism as an Example. Journal of Hebei University(Philosophy and Social Science Edition), 38(4): 75-80.
|
|
Li D Y, Xu D, Zhou Y B, Lv L, and Chen X Y. 2024. Sustainable Rural Development through Slow Tourism Images: A Case Study of Gaochun International Cittàslow in China. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 32: 100903.
|
|
李东晔,黄震方,叶滨鸿,徐冬,汤傅佳. 2020. 游客慢文化感知维度分异与影响因素研究——以高淳国际慢城为例. 人文地理,35(1):150-160.
Li Dongye, Huang Zhenfang, Ye Binhong, Xu Dong, and Tang Fujia. 2020. Research on Dimensions Differentiation Influencing Factors of Tourists' Slow—Culture Perception: A Case Gaochun. Human Geography, 35(1): 150-160.
|
|
刘彬,甘巧林. 2015. Web2.0时代下的旅游摄影与婺源旅游地形象研究——基于旅游摄影照片的内容分析. 旅游论坛,8(2):54-60.
Liu Bin and Gan Qiaolin. 2015. Research on the Tourist Photography and the Image of Wuyuan under the Web2. 0 Era—Based on the Content Analysis of Travel Photographs. Tourism Forum, 8(2): 54-60.
|
|
刘建国,黄杏灵,晋孟雨. 2017. 游客感知:国内外文献的回顾及展望. 经济地理,37(5):216-224.
Liu Jianguo, Huang Xingling, and Jin Mengyu. 2017. Research Progress and Enlightenment of Tourist Perception. Economic Geography, 37(5): 216-224.
|
|
Lopes H D, Remoaldo P C, Ribeiro V, and Martín-Vide J. 2021. Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Tourist Risk Perceptions—The Case Study of Porto. Sustainability, 13(11): 6399.
|
|
Manthiou A, Klaus P, and Luong V H. 2022. Slow Tourism: Conceptualization and Interpretation—A Travel Vloggers' Perspective. Tourism Management, 93: 104570.
|
|
MI-Soon L and WII-Joo Y. 2009. A Study on the Development of Slow Tourism in Busan. Journal of North East Asian Cultures, 1(20): 283-297.
|
|
潘盛之. 1997. 旅游民族学. 贵州:贵州民族出版社,88-89.
Pan Shengzhi. 1997. Ethnology of Tourism. Guizhou: Guizhou Nationalities Publishing House, 88-89.
|
|
庞朴. 1986. 文化结构与近代中国. 北京:中国社会科学,82-99.
Pang Pu. 1986. Cultural Structure and Modern China. Beijing: China Social Sciences Press, 82-99.
|
|
Shen J B, Hao X P, Liang Z Y, Liu Y, Wang W G, and Shao L. 2016. Real-Timesuperpixel Segmentation by DBSCAN Clustering Algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 25(12): 5933-5942.
|
|
史鹏飞,明庆忠,韩剑磊,刘安乐,韩璐. 2020. 慢山:山地旅游发展的适宜模式研究. 山地学报,38(4):608-618.
Shi Pengfei, Ming Qingzhong, Han Jianlei, Liu Anle, and Han Lu. 2020. Slow Mountain: A Suitable Model for the Development of Mountain Tourism. Journal of Mountain Science, 38(4): 608-618.
|
|
Son A. 2005. The Measurement of Tourist Destination Image: Applying a Sketch Map Technique. International Journal of Tourism Research, 7(4/5): 279-294.
|
|
王慧娴,刘筱喆. 2024. Citywalk何以“出圈”?——青年城市漫步中“三感”的评价、检验及提升. 中国青年社会科学,43(5):43-58.
Wang Huixian and Liu Xiaozhe. 2024. Why Does Citywalk Become Widely Known?—Evaluating, Testing and Improving the "Three Senses" in Youth Citywalks. Chinese Youth Social Science, 43(5): 43-58.
|
|
魏宇. 2011. 慢旅游与云旅游的对接——新型自由行与半自由行旅游模式的构建. 中国外资,(16):117.
Wei Yu. 2011. The Alignment of Slow Tourism with Cloud Tourism—Construction of New Independent Travel and Semi-Independent Travel Models. Foreign Capital in China, (16): 117.
|
|
许春晓,朱湘平. 2016. 旅游地文化氛围的内涵及其测定方案. 湖南财政经济学院学报,32(1):133-140.
Xu Chunxiao and Zhu Xiangping. 2016. Connotation of Tourist Destination Cultural Atmosphere and its Measurement Scheme. Journal of Hunan Finance and Economics College, 32(1): 133-140.
|
|
喻丰,彭凯平. 2018. 文化从何而来? 科学通报,63(1):32-37.
Yu Feng and Peng Kaiping. 2018. Where are the Roots of Human Culture? Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(1): 32-37.
|
|
诸慧. 2016. 基于视觉表征的上海旅游感知形象对比硏究——以中西方游客摄影照片为例. 上海:上海师范大学.
Zhu Hui. 2016. Comparative Study on Visual Representation of Shanghai's Tourism Perception—Using Photographs Taken by Chinese and Western Tourists as Examples. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University.
|
|
朱啸宇. 2019. 高淳国际慢城游客慢旅游体验感知影响因素研究. 南京:东南大学.
Zhu Xiaoyu. 2019. The Research on the Influencing Factors of Tourist Perception of Slow Tourism Experience in Gaochun International Slow City. Nanjing: Southeast University.
|
|
Zube E H, Sell J L, and Taylor J G. 1982. Landscape Perception: Research, Application and Theory. Landscape Planning, 9(1): 1-33.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |