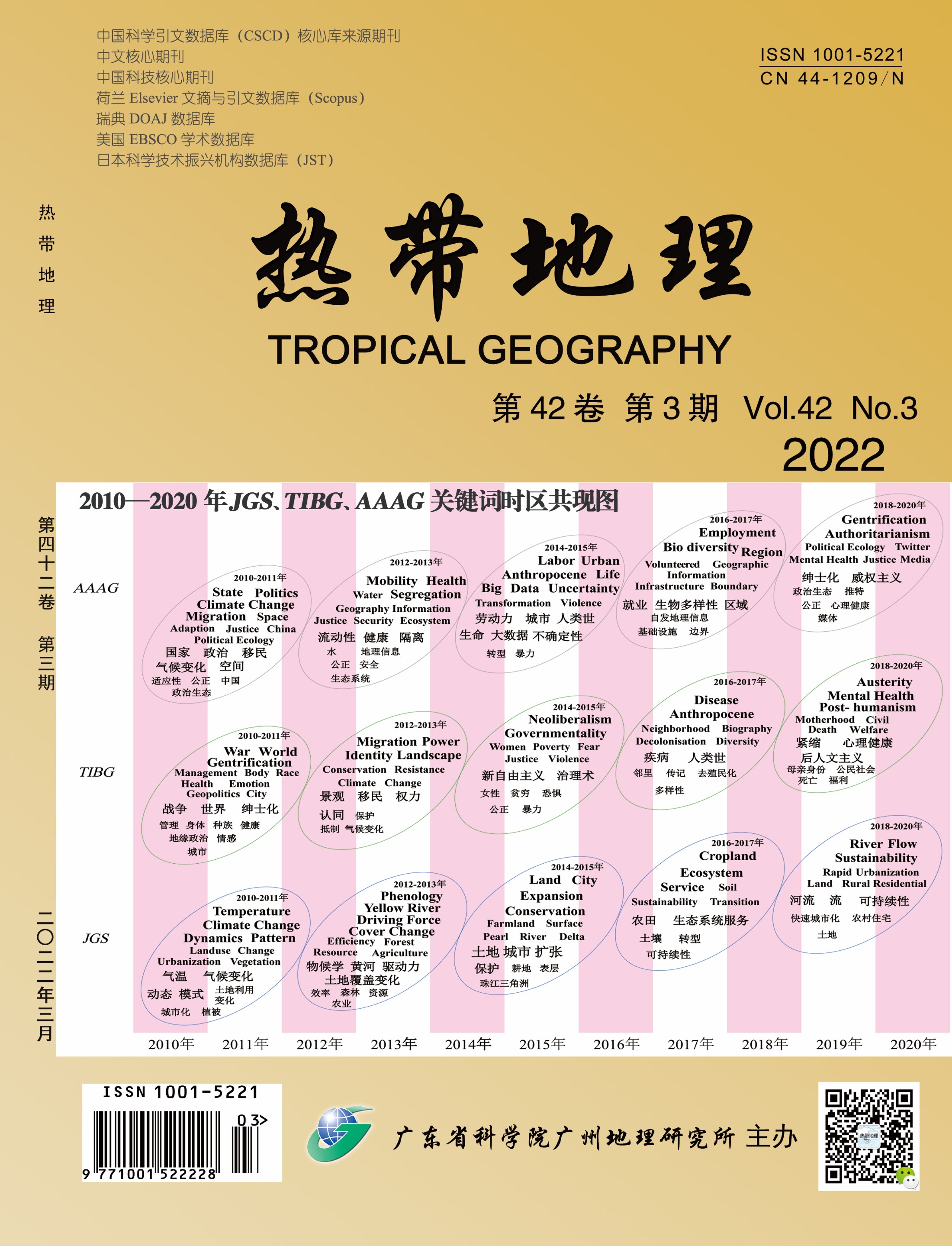
Internationalization and localization are important issues in the development of contemporary Chinese geography. China's local geographical knowledge research has become a force that cannot be ignored in the world's geographical knowledge system. This paper hopes to reveal the heterogeneity, complexity and diversity of the development of geography in the three countries by comparing the development characteristics of geography in China, Britain and the United States. By the knowledge mapping tool CiteSpace, this paper analyzes the literature of Journal of Geographical Sciences, Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers and Annals of the Association of American Geographers from 2010 to 2020, revealing the knowledge evolution, historical hot spots and thematic context of geography in the three countries in recent years. The findings are as follows: 1) American geography pays equal attention to both nature and humanity. In recent years, the comprehensive geographical research on the elements of "nature-environment-humanity-society" has been more active. It shows that American geography circle pays attention to the human-land contradiction and big politics of the world or other countries and regions on a large scale, as well as the human-land relationship and daily politics at the meso and micro scales. It pays attention to a wide range of topics, which are close to the hot spots and needs of American social development. 2) British geography is more "focused" on the study of human geography. In particular, the development of sociocultural geography is very characteristic, and the tradition of political geography is still distinct. There are common issues with the development of American geography, such as climate change, ethnic minorities and segregation. In addition, British geography has paid more and more attention to the research on the relationship between man and nature this year, and has gradually formed the voice of integrating natural and human geography research. 3) Chinese geography focuses on physical geography and regional research, which is different from the trend of American geography and British geography towards the research paradigm of "nature and human" integration. Human geography and geographic information science show rising trends, and the research area is mainly within China. Summarizing the development of geography research in the three countries is conducive to providing reference for the future research direction of Chinese geography and promoting the dialogue between China and world geography. Chinese geography needs to grasp the major demand traction of China's era change, deepen and strengthen the research of Chinese geography in theory and practice, and realize the diversified development of various branches and the transformation and integration of research paradigms.
As a newly developed branch, social and cultural geography has gradually become an important research field within human geography. With fast-changing research topics, methods, and theories, social and cultural geography has been attracting increasing attention in Chinese mainland over the past six years (2015-2020). New trends and criticisms deserve further analysis, such as the diversity of topics, the intersectionality of research methods, and the reflection and questioning of scientific research. Thus, from the perspective of disciplinary introspection, it is necessary to examine the trend of Chinese social and cultural geography from the perspective of comparing China and the West, so as to locate the characteristics of the discipline and to provide certain directions and enlightenment for domestic social and cultural geography research. Drawing on CiteSpace, this article collects, analyzes, and visualizes publications related to social and cultural geography in both English and Chinese (for English publication, we focus on Social & Cultural Geography (N=418), focusing on five selected leading Chinese journals: Acta Geographica Sinca, Scientia Geographica Sinica, Progress in Geography, Geographical Research, and Human Geography (N=400). Furthermore, the Delphi method was employed to see how Chinese social and cultural geographers (N=20) would comment on the recent development of social and cultural geography in Chinese mainland. With qualitative and quantitative analysis, the topics of Western social and cultural geography are reflected in: (1) migration studies and mobility research, (2) cultural landscape and more-than-human geography, and (3) research on disadvantaged groups and caring geography. In contrast to the West, Chinese social and cultural geography research themes include 1) subject theory introduction and reflection, 2) urbanization, mobility, diverse immigration, 3) tourism and place, and 4) rural transformation and homesickness. Given the comparison of research topics of social and cultural geography between China and the West, the findings of this article include 1) Western countries (the U.K. in particular) currently play key, if not dominant, roles in producing, shaping and consuming theories and knowledge of social and cultural geography; 2) "Politics" and "politics" are the main research focuses in the West, while "tourism" and "rurality" are the dominant topics among Chinese publications. It presents a critical difference between the two bodies of literature and reflects the trends of China's social development. 3) Social and cultural geography research in Chinese mainland is undergoing a significant process of internationalization. However, common knowledge (e.g., publications and theories being cited and discussed) shared by both sides remains insignificant. The boundary of knowledge becomes increasingly flexible but still relatively fixed. On the other hand, researchers' opinions also exposed the issue according to which social cultural geography researchers' sense of discipline belonging is yet to be strengthened, as well as the fact that systemization and consensus of research paradigm are insufficient. To further promote interdisciplinary dialogues and knowledge exchanges, explore the role of space in theorization, and show the contributions of Chinese stories, experience and theories to the current literature on research on social and cultural geography deserve further exploration.
By critically reviewing 159 academic publications in English and Chinese from a range of academic platforms that focus on the study of left-behind children, we advance new theoretical turns in children's geography in future research of left-behind children: to explicate children's use of space in everyday life, to explore their subjectivities and agency, and to unpack the diversity of childhoods across spatial and social scales. We first review literature on left-behind children in the context of transnational/international migration: Scholars have written about how left-behind children participate in reconfiguring transnational family strategies and social ties with their parents across spaces; how they act out their roles in different periods of the migration process and in response to different social and cultural environments; and how they interact with multiple and multilevel social actors, factors and processes to form heterogeneous life strategies and meaning-making. We then conduct a thematic analysis of existing scholarship on left-behind children in the context of internal migration in China, revealing a dominant 'problem' frame due to the prevalent positivism and adult-centrism in the research paradigm and an emerging resiliency perspective. We identify three gaps in this literature: 1) scholars tend to build upon an abstract space of 'the rural' at the institutional level, leaving children's everyday spaces and their social practices in these spaces unexplored, including home, school campus, community centers and so on; 2) children's agency and subjectivity remain obscure, with scant empirical and theoretical discussions; and 3) the literature lacks methodological and epistemological diversity and could not bring children's experiences, voices, emotions and beliefs to the forefront of research. We conclude by outlining a new research agenda on rural left-behind children in the Chinese context. In terms of research themes, we advocate for more attention to three potential areas: 1) explicating the spatiality of left-behind children's daily life practices, especially the spatiality related to the mobility patterns of rural-urban migrants in China; 2) divulging children's experiences and subjectivities vis-à-vis their everyday practices, and 3) unpacking the complexity and heterogeneity of left-behind children's childhood experiences in different contexts. In terms of methodology, we encourage the creative uses of diverse research methods such as in-depths interviews, ethnography and Geographic Information System (GIS) that render left-behind children's voices, thoughts, feelings, cognition and actions more visible. This new research agenda could yield a richer and more balanced literature on the everyday lives and subjectivities of left-behind children, providing fresh perspectives for policy making and public debates.
With the transformation of urban knowledge economy, cities pay more and more attention on efforts to attract knowledge talents, including young intellectuals. Taking college students in Guangzhou as an example, this research adopts a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods to explore the mobility of young intellectual migrants, and the characteristics and influencing factors of their employment city selection. The research has found the following. First, young intellectual migrants generally tend to choose cities where their undergraduate or postgraduate studies are located and cities with higher grades than their household registration and place of study (i.e., first-tier and new first-tier cities), which reflects their willingness and motivation for upward spatial and social mobility. Second, their employment mobility is a process of the interaction between urban and individual factors. Its influencing factors mainly include urban environment, economy, policy and culture, as well as the type of household registration and the city level of household registration, among others. Third, urban economy development (job opportunities) is the most important factor for attracting young intellectual migrants, along with employment opportunities, wage levels, and others. At the same time, amenities such as cultural facilities and educational institutions, as well as physical features such as climate and natural environment and other living comforts (living opportunities) play an increasingly important role in the employment mobility of young intellectual migrants. Therefore, urban environmental construction needs to pay attention to public cultural facilities, social comfort, transportation convenience, health service facilities, and urban natural and living environment. The urban policies of high-level cities are more attractive to young intellectual migrants, including talent introduction, housing subsidies and urban development policies. Fourth, in terms of personal factors, the type of household registration and the city level of the source of youth intellectual migration have significant impact on their employment mobility decisions. There are differences in the mobility costs between the different types and city level of household registration, which further affects their employment mobility behavior. A detailed exploration of the employment mobility law of young intellectual migrants and its influencing factors is necessary to understand and construct a knowledge-based talent mobility theory based on Chinese context in the new era. It is also the key to talent policy formulation and the realization of the value of knowledge talents.
Under the background of rural revitalization strategy, art intervention in rural areas, as a new way of rural construction in China, is attracting more and more attention since various art practices have appeared in Chinese villages during the last decade. Art intervention in rural areas has multi-dimensional benefits such as improving rural landscape, promoting villagers' income, enhancing community connections, and promoting cultural inheritance. On the basis of clarifying the connotation and typical modes of art intervention in rural areas in China, this paper constructs and analyzes the benefit hierarchy of art intervention in rural areas based on Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, and selects Xiaozhou and Fenghe villages in Guangzhou as typical cases to identify the benefit characteristics and problems of two modes of artist-led and capital-led art intervention through field investigation. Although previous studies have focused more on specific cases of art intervention in rural areas, which have revealed the work procedure and achievements in detail, the comparison of their differences and a systematic construction of the influence are still worth discussing. The research results show that: (1) Art intervention in rural areas is a typical mode of rural revitalization in which the government, capital, artists and cultural groups realize multi-level benefits such as rural landscape beautification, tourism economic benefits, community creation and governance, and local cultural inheritance through art practice in the context of rural revitalization. According to different driving subjects, the art intervention in rural areas can be divided into two types: artist-led and capital-led. (2) Art intervention in rural areas has four levels of benefits: material, economic, social and cultural, showing the characteristics of progression by level. (3) The artist-led type plays a significant role in realizing high-level benefits, while the low-level benefits are lacking; the capital-led type plays a significant role in realizing low-level benefits, while the high-level benefits are lacking. (4) Building a multi-party cooperation model with the collaboration of capital and artists, government support, and villagers' participation can combine the advantages of the benefits of the two modes and make the rural practice of art intervention more replicable. In summary, this study divides the practices of art intervention in rural China into two types: artist-led and capital-led, constructs the four-level benefits hierarchy based on Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory, compares the four-level benefits between Xiaozhou village and Fenghe village, and summarizes the benefit differences between the artist-led mode and the capital-led mode. For its contributions, it innovatively applies Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory into the study of art intervention from a theoretical perspective and enriches the case study of art intervention in rural China and explores the characteristics from a practical perspective.
The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) is built across three different governance contexts; these three cities have different socio-political structures, legal systems, and cultural identities. From the perspective of media geography, this article proposes a framework with four dimensions and three categories, to explore how cross-border media communication affects the formation and accumulation of social capital, and thus influences regional coordination under the political structure of "one country, two systems" in the region. To fully understand the different characteristics of each development stage, the research further divides the synergic development process into five phases: economic bonding, policy-economic bonding, policy-economic bridging, policy-social linking, and policy-economic-social bridging. The study found that even though media interactions between Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macao have intensified in frequency, social capital at the "socio-cultural" level is relatively weak. Owing to the lack of a widely accepted regional media platform that fits into the communication habits of people in all GBA cities, it is difficult to build an effective monitoring mechanism and feedback system that enables a detection and response to people's opinions on the ground. Consequently, disagreements and conflicts have led to high social costs for some cross-border infrastructure projects. By exploring the mechanisms of media interaction and social capital formation within the regional coordination process, this paper concludes with three strategies to achieve effective multilevel connection and coordination between GBA cities, especially in social and cultural aspects. 1) Governments in each city should work together to build up a regional platform and broaden media channels for the circulation of shared information, which fits various local situations and media usage habits. 2) There is a need for the GBA to establish an effective public opinion monitoring and feedback system on a regional scale, which penetrates people's daily lives, and is accessible to the wider public. Updating prompt information based on people's needs, views, and expectations helps strengthen the entire regional cooperation system and resilient governance structure. 3) Linking propagation is important for the stabilization of social development. Overall, there is a need for the GBA to build a more flexible multilevel dialogue mechanism that facilitates vertical communication to enhance non-institutional and effective bottom-level collaboration.
As China's reform enters deep water and the opening-up enters a new stage, the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region, an important spatial carrier of the national location policy, has become the focus of attention in terms of improving collaborative governance capabilities within the region and optimizing the spatial system structure of urban agglomerations. In this study, a "space of flows" network was developed based on the capital flow, constructed using the foreign investment behavior of A-share listed companies, traffic flow, constructed using population migration data, and information flow constructed using the search engine index. The social network analysis method was used to qualitatively describe and quantitatively analyze the spatial connection characteristics and evolution trend of the PRD cities. The study shows that the urban system of the PRD urban agglomeration has been developed into a "space of flows" network. Additionally, it shows that the spatial structure of the urban system of the PRD urban agglomeration is closely centered on the regional development corridor of Guangzhou, Florida, Dongguan, and Shenzhen, which is deep in the north-south direction. Capital, traffic, and information flows form a network structure with Guangzhou and Shenzhen as the regional extreme nuclei. The urban network shows a significant coresemi-edge-edge unbalanced structure, and the free flow of development factors among cities in the Bay Area is still hindered, with gradient development differences among cities. Overall, the factor flow network is mainly based on Guangzhou and Shenzhen as the dual cores, with spatial differentiation among capital, transportation, and information flows, forming a more apparent network power center on the east bank of the Pearl River. By measuring the degree of centrality of information, traffic, and capital flow of each city in the PRD, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen were found to significantly exceed other cities in terms of attraction and output of flow factors. In terms of investment flow, a narrow "N" structure is formed with Shenzhen as the core node which converges toward the Pearl River; in terms of traffic flow, a wide "N" structure is formed with Guangzhou, Shenzhen and Dongguan as the core, which undulates in the middle of the Bay Area; in terms of information flow, a narrow "N" structure is formed with Guangzhou, Shenzhen and Dongguan as the core. In terms of information flow, an inverse "y" structure is formed along the east bank of the Pearl River with Guangzhou and Shenzhen as the core. Based on the empirical study findings, the development planning of the PRD urban agglomeration is discussed in the light of its actual development. To promote the deep integration of urban agglomerations in the PRD region, it is necessary to avoid zero-sum competition caused by non-market factors through institutional innovation on the one hand, and through increasing the investment in infrastructure construction and accelerating the circulation of factors on the other. In addition, the rapid response of the Internet can help cities at the geographical periphery break free from the geographical constraints of physical distance to develop faster.
The identification of spatial development types of border areas is one of the research hotspots in human-economic geography. Current studies mostly focus on border areas affected by provincial boundaries, and limited studies have explored the spatial structure and development types of border towns affected by inter-city boundaries. Based on multiple types of data, such as China County Statistical Yearbook (villages and towns volume) and 1-kilometer grid GDP dataset of China, this study used quantitative methods of factor analysis, Moran's I, and GIS grouping analysis to explore the spatial development types of inter-city border towns in Guangdong Province. A total of 564 inter-city border towns were chosen for the study. The results show that: (1) the spatial structure of the inter-city border towns in Guangdong Province comprises five principal component factors: public service facilities and tourism resources, enterprises and population agglomeration, ecological background resources, people's living standards, and margin and poverty. Different principal component factors have different spatial correlation coefficients. The factors of ecological background resources and enterprises and population agglomeration have the strongest spatial autocorrelations, while the margin and poverty factor has the weakest spatial autocorrelation. (2) The spatial distribution pattern of the ecological background resources factor is consistent with the topographic distribution, indicating a trend of agglomeration in the plains of the Pearl River Delta, Chaozhou-Jieyang-Shantou area, and Zhanjiang-Maoming junction area. The spatial distribution pattern of the enterprises and population agglomeration factor shows a gradually decreasing distribution from the Pearl River Delta to eastern, western, and northern Guangdong. The spatial distribution pattern of the margin and poverty factor shows the characteristics of "small aggregation and large dispersion" outside the Pearl River Delta of Guangdong Province. (3) According to the strengths and weaknesses of the town and level of development, there are seven types of spatial development of inter-city border towns: strong development towns with a high standard of living, with industry and population agglomeration, with industry and public service support, with a lagging development in public service, and general towns with ecological development, ecological and tourism development, and remote and mountainous weak development towns. There is significant spatial heterogeneity between the different types of border towns. The inter-city border towns in Guangdong Province have outstanding characteristics of "core-periphery" from the perspective of the development level, and the barrier effect of the inter-city border is significant between the inside and outside of the Pearl River Delta. (4) The spatial heterogeneity of Guangdong's inter-city border towns can be attributed to five major factors: natural resource endowment and location, socio-economic development level and industrial structure, historical evolution, government policies and cultural differences. The research results can provide scientific support for countering the barrier effect of inter-city borders and formulating classification guidelines and policy measures for the development of border towns.
The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area (referred to as "GBA") is an important strategic deployment for China's current economic development. Clarifying the spatial structure characteristics of the GBA urban agglomeration is conducive to optimizing its spatial structure to develop into a multi-center network spatial structure and promoting coordinated regional development. This study uses the advantage of Luojia1-01 nighttime light data, which can distinguish the difference in urban night light intensity. Through multi-scale segmentation of nighttime light intensity, the potential center range is established. The point of interest (POI) data are used for spatial autocorrelation analysis and geographically weighted regression to identify the multi-center distribution of the GBA urban agglomeration, and to analyze its spatial structure characteristics from multiple perspectives such as functional structure identification, spatial correlation measurement, and main center service range. The following list illustrates what the results show. 1) The GBA has five main centers and 14 sub-centers, including the main centers of Guangfo, Shenguan, Hong Kong, Aozhu, and Zhongshan. The functional structures of the five main centers are mainly mixed functional areas, and 14 sub-centers (such as Huadu, Zengcheng, Conghua, Huicheng, Duanzhou, Xinhui, Shiqi) are distributed around the periphery of the main centers. 2) The correlation strength of the five main centers and nine cities plus two special administrative regions in the urban agglomeration, calculated based on the Luojia1-01 nighttime light data, shows characteristics of "strong in the east and weak in the west" and "strong inside and weak outside." 3) The study considered the distribution of the main centers of the urban agglomeration and their spatial correlation strength characteristics, as well as the three groups served by the main centers (Guangfozhao group, Gang-Shenguanhui group and Ao-Zhuzhongjiang group), combined with the planning requirements of the "Outline Development Plan for the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area" and "Guangdong Province Land and Space Planning (2020-2035)." The findings suggest that the GBA should build a regional spatial structure of "five centers, one area, three groups and four axes" to achieve pole-driven, axis-supported, and group cooperation and promote its coordinated development into a world-class urban agglomeration.
Exploring local employment is helpful in alleviating the dualistic imbalance of employment spaces for persons with disabilities in China. Based on previous studies, customer prejudice is an important obstacle for enterprises when considering hiring people with disabilities. To explore the possibility of employment of people with disabilities in tourist attractions, Behaviors from Intergroup Affect and Stereotypes Map was applied in this research, based on the investigation of 308 tourists from five scenic spots in three different provinces, and variance and linear regression were conducted to explore the feasibility of people with disabilities working in scenic spots. The study shows that, first, tourists generally have a mixed stereotype of "high enthusiasm and low ability" toward employees with disabilities in scenic spots, and they experience feelings of admiration and practice passive encouragement toward staff with disabilities, such as cooperating and talking with them closely. Moreover, intergroup contact between tourists and people with disabilities significantly affects tourists' attitudes toward disabled employees in scenic spots. Specifically, the experience of receiving services and providing nursing services for people with disabilities had an important positive impact on the tourists' stereotype of the capabilities of the employees, although the tourists felt jealous of them. Second, the frequency of contact with a person with disabilities had a significant positive effect on the arousal of the tourists' feelings of admiration and jealousy towards employees with disabilities. Finally, individuals who have no contact with people with disabilities in any form will experience more contempt and will reduce the occurrence of active facilitation behavior for workers with disabilities. Eventually, the gender, occupation, and personal income of tourists may interfere with the influence of intergroup contact on the attitude towards employees with disabilities in scenic spots. It should be noted that, excluding the effects of population characteristics of interference, visitors' positive emotions toward the employees, including envy and admiration, are significantly affected by service experience and contact frequency with the group with disabilities; in particular, this sentiment varies by profession and by gender of tourists: charity workers are significantly more jealous than pensioners, and women are significantly more admiring than men. Finally, several suggestions to hire people with disabilities in scenic spots in the central and western areas of China are outlined in the last part of this study. First, the leading role of the government in promoting employment needs to be strengthened, the judicial interpretation of the Labor Contract Law concerning the employment of people with disabilities should be supplemented, and insurance legislation should be promoted for their employment. In addition, vocational education and ability training for people with disabilities should be improved and scenic spots should be encouraged to allow bold employment of individuals with disabilities. Finally, more opportunities and platforms may be created to promote multimodal and frequent contact between the public and people with disabilities.
With the transformation and development of China's economy and society, the state attaches great importance to the equalization of public services to meet the growing demand for a better life. Museums are not only one of the most important needs of people's spiritual culture but are also an important part of the public cultural service system. Their reasonable layout has an important impact on the equalization of basic public services. Therefore, research on the temporal and spatial evolution of museums has become one of the hotspots of related disciplines, and is of great significance to deepen the basic public service theory. This study selects a list of museums from 1990 to 2018 and uses a nuclear density analysis, standard deviation ellipse, spatial autocorrelation, and geographic detector model, to analyze the evolution trend of museum quantity, evolution characteristics of spatial distribution mode, law of spatial differentiation, and influencing factors of the temporal and spatial distribution of the museums. The results show that: 1) in terms of quantity evolution trend, there are significant differences in the number of museums from 1990-2000, 2000-2010, and 2010-2018, with a gradual increase in the number. Overall, the number of museums showed an accelerated growth trend from 1990-2018. The differences between the East and West are obvious. The number of museums in the eastern region is dense and the development is rapid; contrastingly, the number of museums in the central and western regions is sparse and development is relatively slow. 2) In terms of the evolution of spatial distribution mode, over time, Chinese museums continue to gather spatially and gradually evolve from "single center" distribution mode to "multi center" distribution mode, and the degree of agglomeration continues to improve. 3) The standard deviation ellipse analysis shows that from 1990-2018, the center of gravity of the Chinese museums was always located in the East; the center of gravity shifted slightly over time, and the moving track was about "Z." 4) In terms of the spatial differentiation law, there has been a significant spatial agglomeration process of Chinese museums since 1990, forming a pattern of "hot in the East and cold in the west". The middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River are the hotspots of Chinese museums, and Xinjiang and Tibet are always in the cold spots. Additionally, the scope of hotspots continues to expand annually, extending to the northwest inland, which is consistent with China's strategy of "equalization of public cultural services" in recent years; it is also conducive to breaking the layout of public cultural facilities that are "strong in the East and weak in the West." 5) In terms of influencing factors, museum spatial differentiation is the result of the comprehensive action of multiple factors, which is mainly affected by the economy, society, policy, culture, and education. Among them, policy, cultural, and educational factors are the main influencing factors of museum spatial differentiation, followed by social factors, and economic factors are the general factors affecting its distribution.
Little attention has been paid to dry season streamflow and groundwater recharge dynamics compared to the systematic focus on measuring total annual streamflow changes associated with forest. However, in the tropics and subtropics, especially in regions with uneven seasonal distribution of precipitation, dry season streamflow and groundwater recharge are of great importance for the riverine ecosystem stability and downstream water supply safety. Recession analysis of -dQ/dt~Q is widely used for determining the catchment storage-discharge relationship and predicting dry season streamflow processes. When dQ/dt~Q plots of streamflow recession are constructed for individual events, the slopes of the curves are near constant in log space, but the intercepts vary with time. Previous studies used event-based analysis to hypothesize that the shifts in intercept in dQ/dt~Q curves were due to variations in concurrent evapotranspiration (ET), which is consistent with the dominant belief regarding controls on streamflow recession. On the contrary, increasing evidence suggests the possibility that other factors such as soil moisture, groundwater recharge, or active drainage network may play a role in dQ/dt variations. However, no consensus has been reached on the determinants of the shift. By using an event-based recession analysis, an experimental catchment with long-term hydrometeorological observations was selected to investigate the streamflow recession in the Nanling mountain forest. Our results showed that 1) faster recession rates were more likely to occur under dry conditions than those under wet conditions; 2) groundwater depth varied consistently with soil moisture in response to precipitation, indicating high soil infiltrability; 3) a significant correlation between the intercept a and concurrent groundwater depth demonstrated its potential role as explanatory variable of streamflow recession; 4) as a losing stream (groundwater depth always larger than 5.0 m near the catchment outlet), water loss to groundwater recharge appears to be the dominant factor affecting streamflow recession.
At present, rubber income is insufficient to encourage farmers to continue to plant rubber. Rubber farmers' forced cutting, abandonment, and malicious destruction of rubber trees have destroyed a large number of rubber forests, causing rubber production to drop sharply; natural rubber incentive policies such as seedling subsidies have not been effective in addressing this. If short-term policies remain weak, it is very likely that rubber production will reach a crisis in the next five to eight years. Policies are thus needed to ensure the safety of the national rubber strategy and to formulate the target subsidy price for natural rubber scientifically, as well as to slow down the rate of labor transfer from the rubber industry to other industries, while gaining trial time for the application and promotion of new technologies. Based on 947 pieces of cross-sectional data and regional statistical bulletins of 18 sample villages in Xishuangbanna in 2019, this study analyzes the validity boundary of the target price subsidy policy using an evolutionary game model and investigates the sensitivity of factors that affect the target price subsidy policy. 1) This study tests the effectiveness of the target price subsidy policy by establishing an evolutionary game model of "subsidy policy-farmer behavior." When the subsidy amount is less than 4.8, there is no evolutionary stable point in the game system, based on the 2019 data. Thus, the target price should be 12.8 yuan/kg when the rubber price is 8 yuan/kg, and farmers will then be expected to fully adopt the strategy of planting rubber. This target price can stabilize the expectations of farmers in rubber production areas and restrain farmers from reducing the scale of rubber planting. Based on this preliminary estimate, the unit cost of the target price subsidy policy is 5,400 yuan/(hm2·a-1), and Xishuangbanna thus needs about 1,485 million yuan/a to maintain the target of 275,000 hm2. 2) A single factor analysis method is adopted to calculate the sensitivity coefficient. Through the sensitivity analysis of the four factors of per capita disposable income of rural residents, rubber tree yield, planting cost, and dry rubber price in the game model, it is found that the corresponding financial subsidy cost will also decrease when the rubber price rises. Among the four factors that affect the target subsidy price, the sensitivity coefficient of the rubber tree yield is the largest, constituting a sensitive factor. When the planting cost and dry rubber price remain unchanged, as the yield of rubber trees increases from 2.5 kg to 2.75 kg, the target subsidy price amount drops from 5.7 yuan/kg to 4.4 yuan/kg, and the subsidy amount drops by 22.81%. The promotion of the target price subsidy policy may lead to greater financial pressure, thus, increasing the yield of rubber trees is a necessary coordinated measure.,and the natural rubber futures price insurance project will also help reduce fiscal costs while achieving policy goals. This study answers the question of how to determine the target subsidy price of natural rubber scientifically, and provides a basis for decision-making and significant guidelines for formulating scientific and effective rubber industry incentive policies.
In the 21st century, the refugees' situation is one of the key problematic issues in the international community, which not only affects the security and stability of border areas but also has a profound impact on neighboring countries and even the international community. In late August 2017, a new round of the Rohingya crisis broke out, and the "Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army" (ARSA) launched a series of attacks on Myanmar, resulting in a large-scale bloody conflict between the Rohingya and Rakhine. The outbreak of this incident led to hundreds of thousands of Rohingya people across the border between Myanmar and Bangladesh, fleeing to Cox's Bazar region of Bangladesh. The influx of refugees over a brief period of time brought excessive pressure to poor Bangladesh. The long-standing Rohingya refugee problem gradually evolved from Myanmar's domestic contradictions to the international community's intense issues. Based on the dynamic monitoring data of the UNHCR, this study analyzes the population scale and structure of Rohingya refugees on the Myanmar-Bangladesh border and its impact on regional geopolitical relations from January 2018 to September 2020 from the perspective of demographic geography and political geography. Given this background, this research shows : 1) Rohingya refugees in Palong Khali district on the Myanmar-Bangladesh borders are large and growing. There are more female refugees than men; the age structure of Rohingya refugees tends to be low, the main age is under 18 years old, and the proportion of young and middle-aged refugees in the total population is minor and grows rapidly; spatial structure shows a typical "law of distance decay from Myanmar-Bangladesh border,"that is, the refugee camps expand to the west, and the scale of refugees presents a spatial distribution law of decreasing from east to west. 2) The population scale and structure of Rohingya refugees have a significant impact on regional geopolitical relations. First, it has a profound affect on the democratization process of Myanmar; second, it poses a challenges to Myanmar-Bangladesh border security, which leads to tensions in Myanmar-Bangladesh relations; third, it arouses the intervention and attention of many geo-actors. This led to a geopolitical game surrounding the refugee issue, leading to divisions within ASEAN, as well as geopolitical spillover effects. 3) Compared with some western countries and international organizations, the "three-step" solution proposed by China is in line with the actual situation of Myanmar and Bangladesh. Under the mechanism of the China–Myanmar–Bangladesh Joint Working Group, the Rohingya refugee issue is moving toward cooperation and consultation. The study of the demographic characteristics of Rohingya refugees on the border between Myanmar and Bangladesh and their influence on regional geopolitical relations provides a reference for the solution of this complex issue.